Glass-filled plastic offers enhanced mechanical strength and rigidity due to glass fibers reinforcing the polymer matrix, making it ideal for high-performance applications. Mineral-filled plastic provides improved thermal stability and dimensional accuracy with fillers like calcium carbonate or mica, benefiting electrical insulation and cost reduction. The choice between them depends on whether the priority is structural reinforcement or thermal and dimensional properties.
Table of Comparison
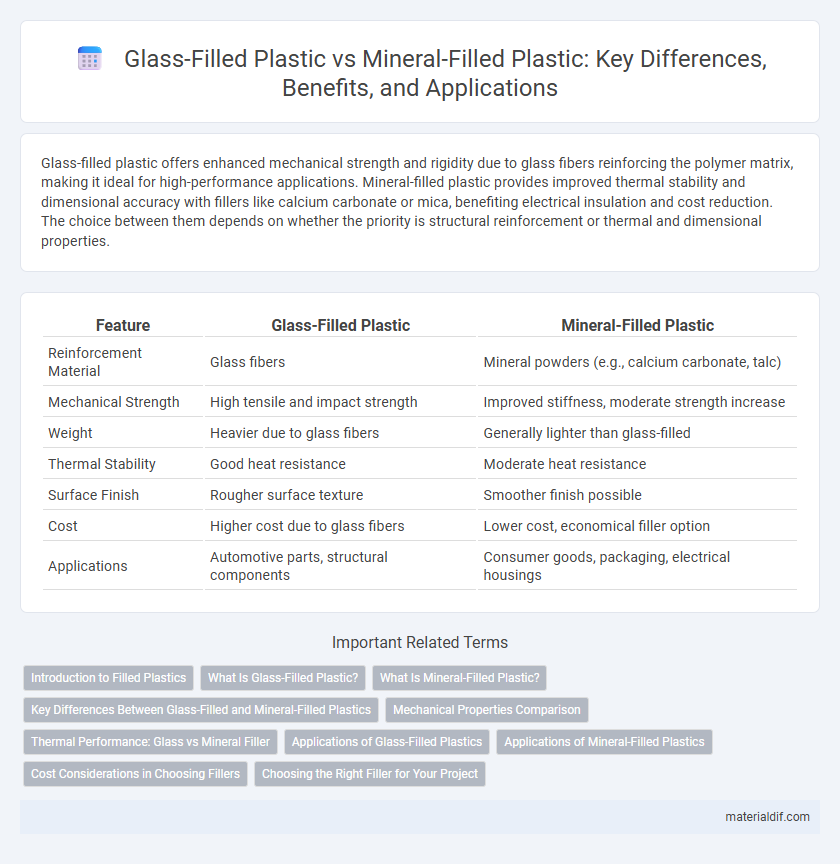
| Feature | Glass-Filled Plastic | Mineral-Filled Plastic |
|---|---|---|
| Reinforcement Material | Glass fibers | Mineral powders (e.g., calcium carbonate, talc) |
| Mechanical Strength | High tensile and impact strength | Improved stiffness, moderate strength increase |
| Weight | Heavier due to glass fibers | Generally lighter than glass-filled |
| Thermal Stability | Good heat resistance | Moderate heat resistance |
| Surface Finish | Rougher surface texture | Smoother finish possible |
| Cost | Higher cost due to glass fibers | Lower cost, economical filler option |
| Applications | Automotive parts, structural components | Consumer goods, packaging, electrical housings |
Introduction to Filled Plastics
Filled plastics enhance mechanical properties by incorporating additives such as glass or mineral fibers into the polymer matrix. Glass-filled plastics offer superior strength, stiffness, and thermal resistance, making them suitable for structural applications requiring high durability. Mineral-filled plastics improve dimensional stability, reduce shrinkage, and enhance surface finish, offering cost-effective solutions for moderate mechanical demands.
What Is Glass-Filled Plastic?
Glass-filled plastic is a composite material reinforced with glass fibers to enhance strength, stiffness, and thermal stability, making it ideal for demanding industrial applications. The addition of glass fibers improves the mechanical properties of the plastic, such as tensile strength and impact resistance, without significantly increasing weight. This type of plastic is commonly used in automotive parts, electrical components, and structural applications requiring durability and dimensional stability.
What Is Mineral-Filled Plastic?
Mineral-filled plastic is a composite material where inorganic minerals such as calcium carbonate, talc, or mica are added to a polymer matrix to enhance properties like stiffness, heat resistance, and dimensional stability. Unlike glass-filled plastic, which uses glass fibers for reinforcement, mineral-filled plastics typically offer improved surface smoothness and lower density, making them suitable for applications requiring moderate mechanical strength and better machinability. These plastics are commonly used in automotive parts, consumer appliances, and electrical components where a balance of durability, cost-efficiency, and aesthetic finish is essential.
Key Differences Between Glass-Filled and Mineral-Filled Plastics
Glass-filled plastics incorporate fiberglass reinforcement to enhance tensile strength, impact resistance, and dimensional stability, making them ideal for load-bearing applications. Mineral-filled plastics use mineral additives like talc or calcium carbonate to improve stiffness, thermal stability, and reduce warping while maintaining lower cost and weight compared to glass-filled counterparts. The primary distinction lies in mechanical performance versus cost-efficiency, with glass-filled plastics offering superior strength and mineral-filled plastics providing enhanced rigidity and processability.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Glass-filled plastic exhibits higher tensile strength and improved rigidity compared to mineral-filled plastic, making it ideal for applications requiring enhanced mechanical performance. Mineral-filled plastic offers better impact resistance and dimensional stability under thermal stress, suitable for parts subjected to fluctuating temperatures. Both materials enhance the base polymer's mechanical properties, but glass-filled plastics excel in stiffness while mineral-filled variants provide improved toughness.
Thermal Performance: Glass vs Mineral Filler
Glass-filled plastics exhibit superior thermal conductivity and higher heat resistance compared to mineral-filled plastics, making them ideal for applications requiring enhanced thermal management. The glass fibers provide structural reinforcement while facilitating efficient heat dissipation, whereas mineral fillers often offer improved thermal stability but lower conductivity. Consequently, glass-filled plastics outperform mineral-filled counterparts in maintaining mechanical integrity under elevated temperatures.
Applications of Glass-Filled Plastics
Glass-filled plastics offer enhanced mechanical strength and thermal stability, making them ideal for automotive components, electrical housings, and industrial machinery parts. Their superior rigidity and resistance to wear and impact enable usage in structural applications requiring durability and precision. These materials also excel in aerospace and consumer electronics where lightweight and high-performance properties are critical.
Applications of Mineral-Filled Plastics
Mineral-filled plastics are extensively used in automotive components, electrical housings, and consumer appliances due to their enhanced dimensional stability and improved heat resistance compared to standard plastics. These materials offer superior stiffness and reduced shrinkage, making them ideal for precision parts and structural applications. Their ability to withstand thermal aging and provide better electrical insulation broadens their applicability in demanding industrial environments.
Cost Considerations in Choosing Fillers
Glass-filled plastic typically offers higher strength and rigidity but comes at a greater cost due to the expense of glass fibers and their processing requirements. Mineral-filled plastic often provides a more cost-effective solution with good dimensional stability and wear resistance, benefiting industries with tight budget constraints. Evaluating the balance between performance needs and budget limitations is crucial when selecting between glass-filled and mineral-filled plastic fillers.
Choosing the Right Filler for Your Project
Selecting the right filler between glass-filled plastic and mineral-filled plastic depends on the specific mechanical properties and application requirements. Glass-filled plastics offer superior tensile strength and dimensional stability, ideal for load-bearing components, while mineral-filled plastics provide enhanced stiffness and thermal resistance, suitable for automotive and electrical parts. Evaluating factors such as impact resistance, weight, and cost-effectiveness helps in optimizing material performance for your project's demands.
Glass-Filled Plastic vs Mineral-Filled Plastic Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com