Polypropylene offers superior flexibility and chemical resistance compared to polystyrene, making it ideal for packaging and automotive components. Polystyrene excels in rigidity and clarity, often used for disposable cutlery and insulation materials. Both plastics serve distinct purposes due to differences in durability, weight, and cost-efficiency.
Table of Comparison
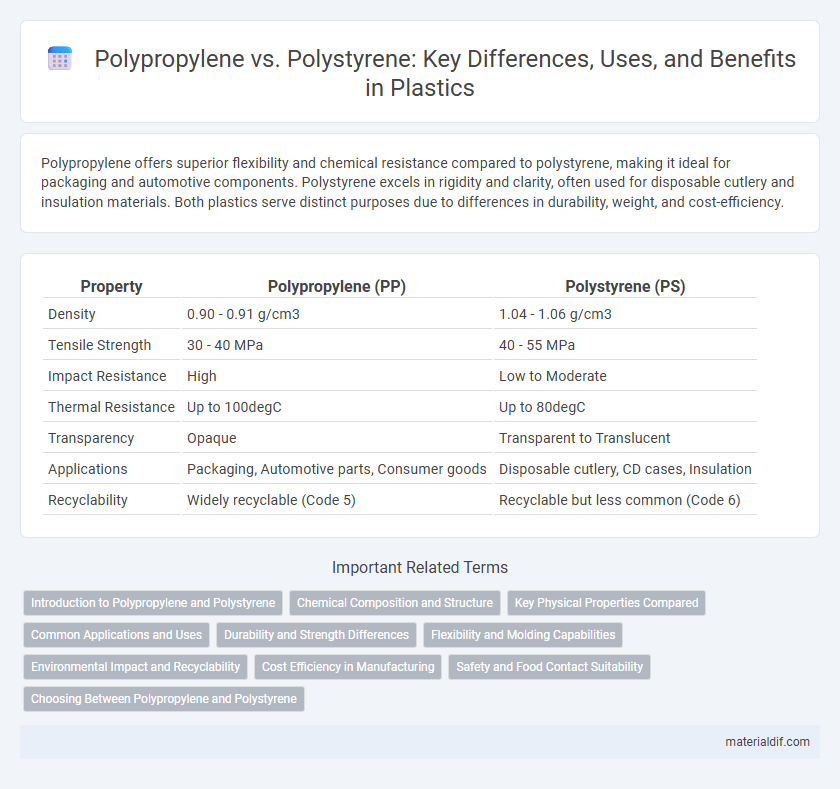
| Property | Polypropylene (PP) | Polystyrene (PS) |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 0.90 - 0.91 g/cm3 | 1.04 - 1.06 g/cm3 |
| Tensile Strength | 30 - 40 MPa | 40 - 55 MPa |
| Impact Resistance | High | Low to Moderate |
| Thermal Resistance | Up to 100degC | Up to 80degC |
| Transparency | Opaque | Transparent to Translucent |
| Applications | Packaging, Automotive parts, Consumer goods | Disposable cutlery, CD cases, Insulation |
| Recyclability | Widely recyclable (Code 5) | Recyclable but less common (Code 6) |
Introduction to Polypropylene and Polystyrene
Polypropylene is a thermoplastic polymer known for its durability, chemical resistance, and versatility in packaging, automotive parts, and textiles. Polystyrene, a synthetic aromatic hydrocarbon polymer, is widely used for insulation, disposable cutlery, and packaging foam due to its rigidity and lightweight properties. Both materials offer distinct physical characteristics that influence their application in various industries.
Chemical Composition and Structure
Polypropylene consists of repeating propylene monomers featuring a carbon-carbon backbone with pendant methyl groups, resulting in a semi-crystalline polymer with high chemical resistance and flexibility. Polystyrene is composed of styrene monomers containing aromatic benzene rings attached to the carbon backbone, which create a rigid, amorphous structure with lower chemical resistance compared to polypropylene. The presence of the bulky phenyl group in polystyrene hinders crystallinity, whereas polypropylene's smaller methyl groups promote crystallization and influence thermal and mechanical properties.
Key Physical Properties Compared
Polypropylene exhibits a higher melting point around 160degC compared to polystyrene's 100degC, enhancing its thermal resistance for hot applications. Its density ranges from 0.85 to 0.92 g/cm3, making it lighter than polystyrene, which typically has a density near 1.05 g/cm3, affecting weight-critical manufacturing. Additionally, polypropylene offers superior chemical resistance and flexibility, whereas polystyrene is more rigid but prone to brittleness under stress.
Common Applications and Uses
Polypropylene is widely used in packaging, automotive parts, and textiles due to its durability, chemical resistance, and flexibility, making it ideal for reusable containers, carpets, and automotive components. Polystyrene is commonly utilized in insulation, disposable cutlery, and packaging materials because of its rigidity, thermal insulation properties, and low cost, often found in foam packaging and single-use food containers. Both plastics serve distinct roles across industries, with polypropylene favored for applications requiring toughness and reusability, while polystyrene excels in lightweight, cost-effective, and insulating products.
Durability and Strength Differences
Polypropylene exhibits higher impact resistance and flexibility, making it more durable under stress and less prone to cracking compared to polystyrene. Polystyrene offers rigidity and hardness but tends to be brittle and can shatter under heavy impact or prolonged use. The inherent toughness of polypropylene makes it suitable for applications requiring repeated flexing and long-term durability, while polystyrene is better suited for rigid, lightweight uses where strength is less critical.
Flexibility and Molding Capabilities
Polypropylene offers superior flexibility compared to polystyrene, making it ideal for applications requiring repeated bending or resilience under stress. Polystyrene, while more rigid and brittle, excels in molding precision for detailed, high-resolution components. The choice between these plastics depends on whether flexibility or exact mold replication is prioritized in the manufacturing process.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Polypropylene offers superior recyclability with a recycling code of 5, enabling effective reuse and reducing landfill waste compared to polystyrene, which is often labeled with recycling code 6 but faces significant recycling challenges. Environmentally, polypropylene's lower greenhouse gas emissions during production and greater resistance to degradation mitigate pollution risks, while polystyrene's production emits more toxic chemicals and its non-biodegradability contributes heavily to microplastic pollution. The environmental footprint and recycling infrastructure favor polypropylene as a more sustainable plastic choice over polystyrene.
Cost Efficiency in Manufacturing
Polypropylene offers superior cost efficiency compared to polystyrene due to its lower raw material price and higher impact resistance, reducing waste and defect rates during manufacturing. Its ability to withstand higher processing temperatures enables faster cycle times and energy savings on injection molding lines. Polystyrene's lower melting point and brittleness may lead to increased material rejects and higher production costs, limiting its cost-effectiveness for large-scale manufacturing.
Safety and Food Contact Suitability
Polypropylene (PP) exhibits superior safety and food contact suitability compared to polystyrene (PS) due to its higher heat resistance and chemical stability, minimizing the risk of harmful chemical migration into food. Polypropylene's FDA approval for direct food contact in packaging and containers highlights its widespread use in microwave-safe and dishwasher-safe applications. Polystyrene, while commonly used for disposable food containers, poses concerns related to styrene leaching, especially when exposed to heat or fatty foods, limiting its safety for long-term or heated food storage.
Choosing Between Polypropylene and Polystyrene
Polypropylene offers higher chemical resistance, flexibility, and impact strength, making it ideal for automotive parts, packaging, and household goods. Polystyrene provides superior rigidity and clarity, commonly used in disposable cutlery, insulation, and packaging materials requiring transparency. Selecting between polypropylene and polystyrene depends on the application's need for durability, chemical exposure, and whether transparency is a priority.
Polypropylene vs Polystyrene Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com