PET (polyethylene terephthalate) and HDPE (high-density polyethylene) are both widely used plastics with distinct properties and applications. PET is highly valued for its clarity, strength, and barrier properties, making it ideal for beverage bottles and food packaging, while HDPE offers superior chemical resistance, flexibility, and impact strength, commonly used in containers, pipes, and plastic lumber. Understanding the differences in recyclability and environmental impact between PET and HDPE helps optimize plastic waste management and promotes sustainable material selection.
Table of Comparison
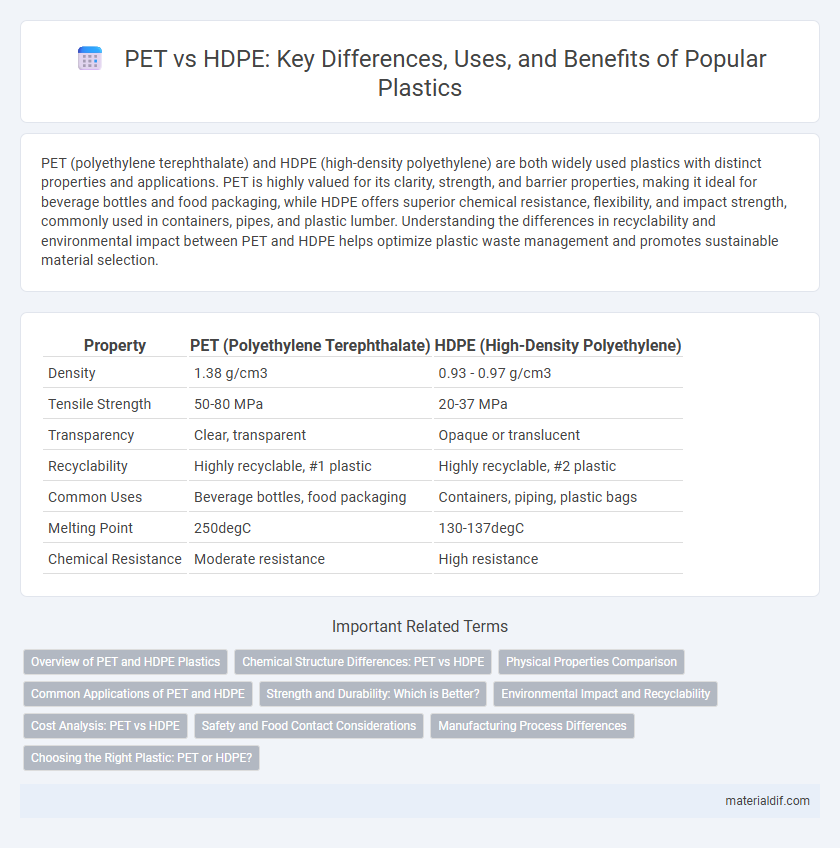
| Property | PET (Polyethylene Terephthalate) | HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene) |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 1.38 g/cm3 | 0.93 - 0.97 g/cm3 |
| Tensile Strength | 50-80 MPa | 20-37 MPa |
| Transparency | Clear, transparent | Opaque or translucent |
| Recyclability | Highly recyclable, #1 plastic | Highly recyclable, #2 plastic |
| Common Uses | Beverage bottles, food packaging | Containers, piping, plastic bags |
| Melting Point | 250degC | 130-137degC |
| Chemical Resistance | Moderate resistance | High resistance |
Overview of PET and HDPE Plastics
PET (polyethylene terephthalate) and HDPE (high-density polyethylene) are two widely used thermoplastics with distinct chemical structures and applications. PET is known for its clarity, strength, and excellent gas barrier properties, making it ideal for beverage bottles and food packaging. HDPE offers superior chemical resistance, higher impact strength, and durability, commonly used in containers, pipes, and household products.
Chemical Structure Differences: PET vs HDPE
PET (polyethylene terephthalate) consists of aromatic rings and ester functional groups in its polymer chain, giving it rigidity and excellent gas barrier properties. HDPE (high-density polyethylene) has a linear structure with only carbon and hydrogen atoms, resulting in high crystallinity and density but lower chemical resistance compared to PET. The chemical structure differences directly influence their mechanical strength, thermal stability, and application suitability in packaging industries.
Physical Properties Comparison
PET (Polyethylene Terephthalate) exhibits higher tensile strength and better clarity compared to HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene), making it ideal for clear packaging applications. HDPE offers greater impact resistance and superior chemical resistance, along with a higher melting point around 130degC, whereas PET melts approximately at 260degC. The density of PET generally ranges from 1.38 to 1.41 g/cm3, while HDPE's density is lower, typically between 0.93 and 0.97 g/cm3, influencing their respective flexibility and rigidity.
Common Applications of PET and HDPE
PET (Polyethylene Terephthalate) is widely used in beverage bottles, food packaging, and synthetic fibers due to its clarity, strength, and barrier properties. HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene) is commonly employed in milk jugs, detergent containers, and piping because of its high tensile strength and chemical resistance. Both plastics serve essential roles in packaging industries, with PET preferred for transparent applications and HDPE chosen for durability and impact resistance.
Strength and Durability: Which is Better?
PET (Polyethylene Terephthalate) offers higher tensile strength and better impact resistance compared to HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene), making it ideal for applications requiring superior durability. HDPE features excellent chemical resistance and flexibility, which contributes to its toughness but generally falls short of PET in terms of rigidity and load-bearing capacity. For products demanding maximum strength and durability, PET is often the preferred choice due to its robust molecular structure and resistance to physical stress.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
PET (Polyethylene Terephthalate) and HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene) exhibit distinct environmental impacts and recyclability profiles; PET often has a higher carbon footprint due to its production process but offers excellent recyclability into fibers and new containers. HDPE is favored for its lower environmental impact, including reduced greenhouse gas emissions during production, and is widely recycled into durable products like piping and plastic lumber. Both plastics contribute significantly to reducing landfill waste when properly recycled, yet PET faces more challenges in contamination during recycling compared to the more resilient and chemically stable HDPE.
Cost Analysis: PET vs HDPE
PET (Polyethylene terephthalate) generally incurs higher production costs compared to HDPE (High-density polyethylene) due to its more complex polymerization process and energy-intensive crystallization. HDPE offers cost advantages in raw material prices and manufacturing efficiency, making it economically favorable for large-scale applications such as packaging and piping. Market fluctuations in crude oil prices also impact HDPE costs more significantly, while PET's recycling market supports its value retention despite higher initial expenses.
Safety and Food Contact Considerations
PET (Polyethylene Terephthalate) is widely recognized for its excellent safety profile and strong chemical resistance, making it a preferred choice for food and beverage packaging due to its inert nature and compliance with FDA food contact regulations. HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene) also meets stringent safety standards, offering superior resistance to impact and moisture, which reduces the risk of contamination in food storage. Both materials are BPA-free and approved for direct food contact, but PET's clarity and barrier properties often provide enhanced protection against oxygen and carbon dioxide, extending the shelf life of perishable products.
Manufacturing Process Differences
PET (Polyethylene Terephthalate) production involves the polymerization of terephthalic acid and ethylene glycol through a process called melt polycondensation, requiring precise temperature control to achieve a clear, strong polymer. HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene) is produced via polymerization of ethylene gas using catalysts such as Ziegler-Natta or metallocene, resulting in a linear polymer with minimal branching and high density. The manufacturing of PET demands higher processing temperatures and more complex reaction control compared to the relatively straightforward polymerization process of HDPE.
Choosing the Right Plastic: PET or HDPE?
PET (Polyethylene Terephthalate) and HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene) each offer distinct advantages for packaging applications; PET provides excellent clarity, strong barrier properties against moisture and gases, and is widely used for beverage bottles and food containers. HDPE is highly durable, resistant to chemicals, and ideal for heavier-duty containers such as detergent bottles and milk jugs. Choosing the right plastic depends on product requirements, with PET favored for transparency and shelf-life extension, while HDPE is preferred for strength and recyclability.
PET vs HDPE Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com