PETG offers higher durability and impact resistance compared to PLA, making it ideal for functional parts and prototypes that require strength. While PLA is biodegradable and easier to print with due to its lower melting point, PETG provides better chemical resistance and flexibility. Choosing between PETG and PLA depends on the application's strength requirements and environmental considerations.
Table of Comparison
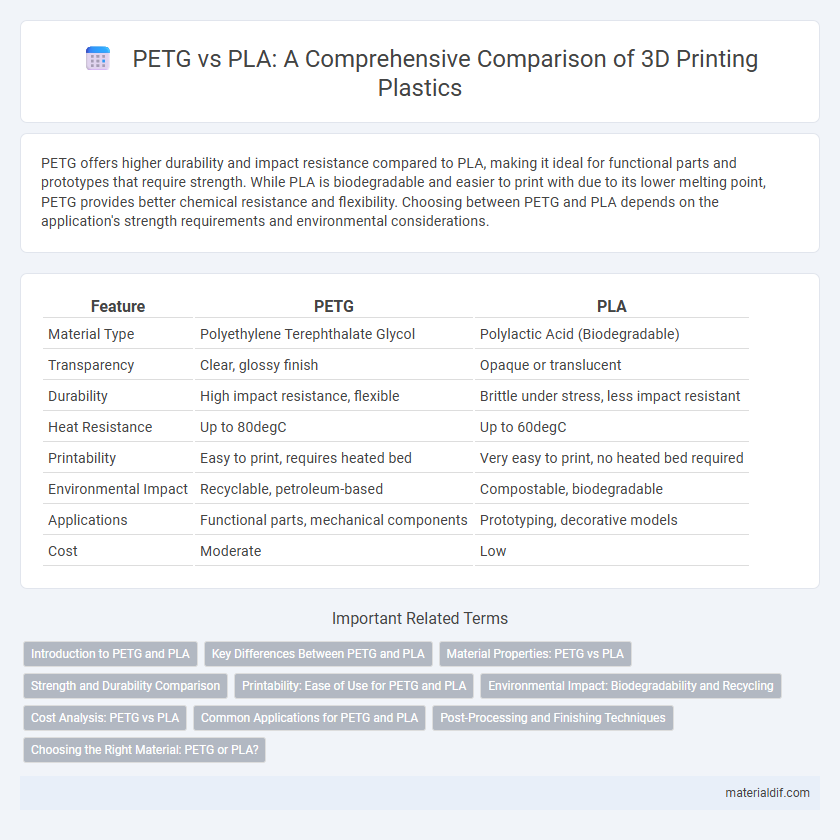
| Feature | PETG | PLA |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol | Polylactic Acid (Biodegradable) |
| Transparency | Clear, glossy finish | Opaque or translucent |
| Durability | High impact resistance, flexible | Brittle under stress, less impact resistant |
| Heat Resistance | Up to 80degC | Up to 60degC |
| Printability | Easy to print, requires heated bed | Very easy to print, no heated bed required |
| Environmental Impact | Recyclable, petroleum-based | Compostable, biodegradable |
| Applications | Functional parts, mechanical components | Prototyping, decorative models |
| Cost | Moderate | Low |
Introduction to PETG and PLA
PETG (Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol) is a durable, impact-resistant thermoplastic often used in 3D printing and packaging due to its clarity and chemical resistance. PLA (Polylactic Acid) is a biodegradable thermoplastic derived from renewable resources like corn starch, favored for its ease of printing and eco-friendly properties. Both materials serve distinct purposes: PETG offers greater flexibility and strength, while PLA excels in sustainability and printing precision.
Key Differences Between PETG and PLA
PETG offers superior impact resistance and flexibility compared to PLA, which is more brittle but biodegradable and easier to print with. PETG has a higher melting temperature around 230degC to 260degC, making it better for applications requiring durability and heat resistance, while PLA melts between 180degC and 220degC. PLA is derived from renewable resources such as cornstarch, contributing to its eco-friendliness, whereas PETG is a copolymer of PET and glycol, providing enhanced chemical resistance and durability.
Material Properties: PETG vs PLA
PETG offers superior impact resistance and flexibility compared to PLA, making it ideal for applications requiring durability and slight bending. PLA, derived from renewable resources, provides higher rigidity and ease of printing but is more brittle and less heat resistant than PETG. PETG's enhanced chemical resistance and lower moisture absorption extend the lifespan of printed parts in demanding environments.
Strength and Durability Comparison
PETG offers superior strength and durability compared to PLA, making it more resistant to impact and less prone to cracking under stress. Its enhanced chemical resistance and flexibility allow PETG to withstand harsher environments and repeated mechanical strain, unlike PLA which tends to be more brittle and susceptible to degradation over time. For applications requiring long-lasting performance and resilience, PETG is generally the preferred choice due to its balanced combination of toughness and durability.
Printability: Ease of Use for PETG and PLA
PETG offers higher printability with excellent layer adhesion and minimal warping, making it user-friendly for both beginners and experienced 3D printers. PLA is renowned for its ease of use due to low printing temperatures, minimal odor, and lower risk of clogging, suitable for detailed and intricate prints. Both materials demand proper temperature settings: PETG typically prints at 230-250degC while PLA prints optimally at 190-220degC, influencing overall print quality and reliability.
Environmental Impact: Biodegradability and Recycling
PETG offers superior recyclability due to its chemical stability, allowing repeated processing without significant degradation, whereas PLA is compostable under industrial conditions but degrades slowly in natural environments. PLA's biodegradability reduces landfill accumulation but requires specific temperature and humidity for effective breakdown, limiting its environmental advantage. PETG's recyclability supports circular economy initiatives, while PLA's eco-friendly end-of-life options depend on specialized facilities, influencing their overall ecological footprints.
Cost Analysis: PETG vs PLA
PETG generally costs more than PLA due to its enhanced durability and chemical resistance, making it ideal for functional parts despite the higher price. PLA remains a budget-friendly option favored for prototyping and non-load-bearing applications because of its affordability and ease of printing. When analyzing material costs, PETG's long-term durability can offset initial expenses, while PLA offers significant savings for short-term or decorative projects.
Common Applications for PETG and PLA
PETG is widely used for durable consumer goods, protective covers, and medical devices due to its chemical resistance and toughness. PLA is popular for biodegradable packaging, disposable cutlery, and 3D printing prototypes because of its eco-friendly and easy-to-print properties. Both materials serve distinct purposes in manufacturing and rapid prototyping based on their strength and environmental impact.
Post-Processing and Finishing Techniques
PETG exhibits superior chemical resistance, allowing for effective post-processing with solvents like isopropyl alcohol for surface smoothing, whereas PLA requires gentle sanding and polishing due to its lower heat resistance. PETG's flexibility reduces the risk of cracking during finishing, enabling techniques such as vapor smoothing and light sanding to achieve glossy surfaces, while PLA benefits from acetone vapor baths or epoxy coating for enhanced durability and shine. Both materials respond well to painting, but PETG's superior layer adhesion ensures smoother final finishes compared to the more brittle PLA.
Choosing the Right Material: PETG or PLA?
PETG offers superior impact resistance and flexibility compared to PLA, making it ideal for functional parts and outdoor applications requiring durability and weather resistance. PLA excels in ease of printing and biodegradability, preferred for prototyping, decorative items, and environmentally conscious projects. Selecting PETG or PLA depends on balancing mechanical strength, printability, and environmental impact based on the specific needs of the 3D printing project.
PETG vs PLA Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com