Acrylic offers superior clarity and UV resistance, making it ideal for applications requiring transparency and outdoor durability, whereas polyvinyl chloride (PVC) is more versatile and resistant to chemicals, commonly used in construction and piping. Acrylic tends to be more brittle but lightweight, while PVC provides greater impact resistance and flexibility. Choosing between acrylic and PVC depends on the specific needs for strength, weather resistance, and chemical exposure in the intended use.
Table of Comparison
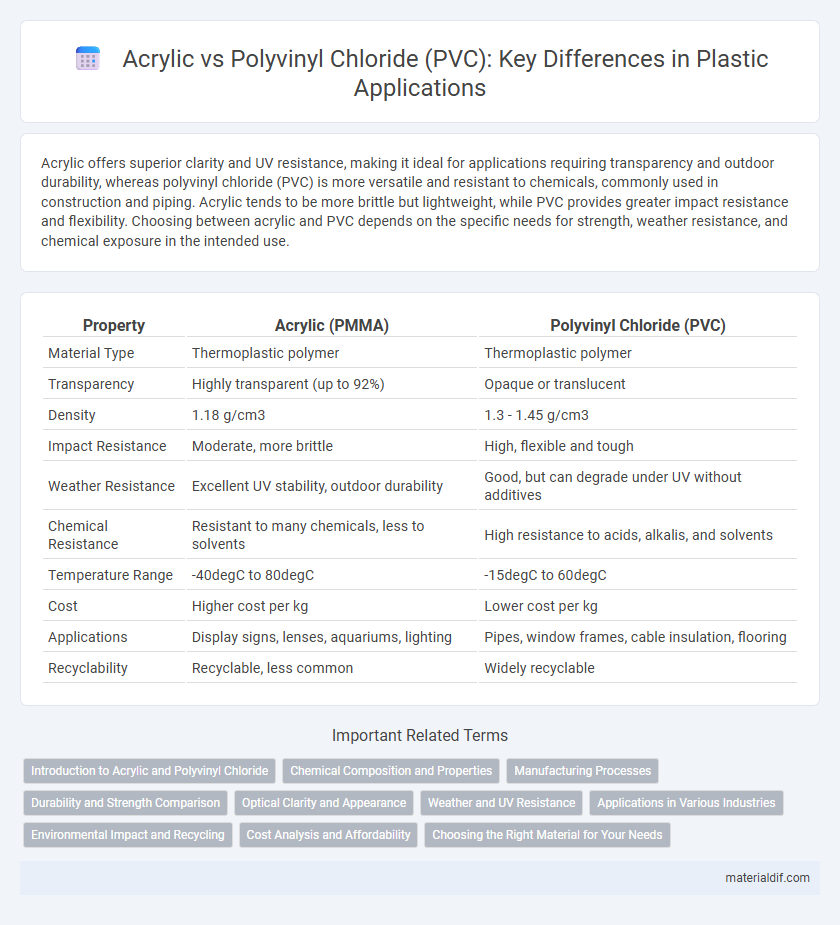
| Property | Acrylic (PMMA) | Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic polymer | Thermoplastic polymer |
| Transparency | Highly transparent (up to 92%) | Opaque or translucent |
| Density | 1.18 g/cm3 | 1.3 - 1.45 g/cm3 |
| Impact Resistance | Moderate, more brittle | High, flexible and tough |
| Weather Resistance | Excellent UV stability, outdoor durability | Good, but can degrade under UV without additives |
| Chemical Resistance | Resistant to many chemicals, less to solvents | High resistance to acids, alkalis, and solvents |
| Temperature Range | -40degC to 80degC | -15degC to 60degC |
| Cost | Higher cost per kg | Lower cost per kg |
| Applications | Display signs, lenses, aquariums, lighting | Pipes, window frames, cable insulation, flooring |
| Recyclability | Recyclable, less common | Widely recyclable |
Introduction to Acrylic and Polyvinyl Chloride
Acrylic, known chemically as polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA), is a transparent thermoplastic often used as a lightweight and shatter-resistant alternative to glass in applications like windows, displays, and signage. Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) is a versatile plastic polymer widely utilized for its durability, chemical resistance, and flame retardancy in construction materials, pipes, and electrical cable insulation. Both materials offer unique properties: acrylic excels in optical clarity and weather resistance, while PVC provides excellent mechanical strength and cost-effectiveness.
Chemical Composition and Properties
Acrylic, or polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA), is a transparent thermoplastic known for its high clarity, UV resistance, and rigidity, derived from the polymerization of methyl methacrylate monomers. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC), a synthetic plastic polymer produced from vinyl chloride monomers, exhibits excellent chemical resistance, durability, and versatility, but tends to be less transparent and more rigid unless plasticizers are added. The chemical composition of acrylic gives it superior optical clarity and weather resistance, whereas PVC's chlorine content contributes to its flame retardancy and sturdiness in construction and piping applications.
Manufacturing Processes
Acrylic is manufactured through a polymerization process involving methyl methacrylate monomers, typically via bulk or suspension polymerization, resulting in clear, rigid sheets widely used in signage and glazing. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) is produced by polymerizing vinyl chloride monomers through suspension or emulsion polymerization, followed by mixing with plasticizers and stabilizers to create flexible or rigid forms for pipes, fittings, and profiles. Both materials require precise temperature and catalyst control during polymerization to achieve desired physical properties and product performance.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Acrylic offers superior impact resistance and maintains clarity over time, making it highly durable for both indoor and outdoor applications. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) exhibits excellent chemical resistance and toughness but tends to become brittle with prolonged UV exposure. While acrylic excels in strength and weather resistance, PVC remains favored for its cost-effectiveness and versatility in construction and piping systems.
Optical Clarity and Appearance
Acrylic exhibits superior optical clarity with light transmission up to 92%, making it highly transparent and ideal for applications requiring excellent visibility. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) offers lower clarity, typically around 80% light transmission, resulting in a more opaque and less visually appealing finish. Acrylic's glass-like appearance and resistance to yellowing enhance its aesthetic value compared to the duller, often hazy look of PVC.
Weather and UV Resistance
Acrylic offers superior weather and UV resistance compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC), maintaining clarity and structural integrity under prolonged sun exposure without yellowing or becoming brittle. PVC tends to degrade faster when exposed to ultraviolet light, leading to discoloration and loss of mechanical properties over time. For outdoor applications requiring long-term durability, acrylic is the preferred material due to its enhanced resistance to environmental stressors.
Applications in Various Industries
Acrylic is widely utilized in automotive and architectural applications due to its clarity, UV resistance, and weatherability, making it ideal for windows, displays, and signage. Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) is preferred in construction, healthcare, and electrical industries for its durability, chemical resistance, and flame retardancy, commonly used in pipes, medical devices, and cable insulation. Both plastics offer versatile solutions tailored to industry-specific needs, with acrylic excelling in optical uses and PVC dominating structural and protective applications.
Environmental Impact and Recycling
Acrylic (PMMA) typically has lower environmental toxicity during production compared to Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC), which releases harmful dioxins and chlorine-based compounds when manufactured or incinerated. Acrylic is more readily recyclable through mechanical recycling processes, while PVC recycling is more complex due to its chlorine content and additives, often resulting in landfill disposal or energy recovery. The environmental impact of PVC is considerably higher due to persistent pollutants and challenges in safe recycling practices.
Cost Analysis and Affordability
Acrylic typically costs more than polyvinyl chloride (PVC) due to its higher clarity and durability, with prices ranging from $3 to $6 per square foot, while PVC generally falls between $1 to $3 per square foot. Despite the higher upfront cost, acrylic offers better long-term value in applications requiring impact resistance and UV stability. PVC remains the most affordable choice for budget-conscious projects, especially in non-structural uses where cost is a critical factor.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Needs
Acrylic offers superior clarity, UV resistance, and is ideal for applications requiring transparency and outdoor durability, while polyvinyl chloride (PVC) excels in chemical resistance, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness for piping, signage, and construction uses. When choosing the right material, consider acrylic for aesthetic appeal and weather resistance, and PVC for impact resistance and versatility in industrial settings. Evaluating the specific environmental exposure and mechanical demands ensures optimal performance and longevity of your plastic product.
Acrylic vs Polyvinyl Chloride Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com