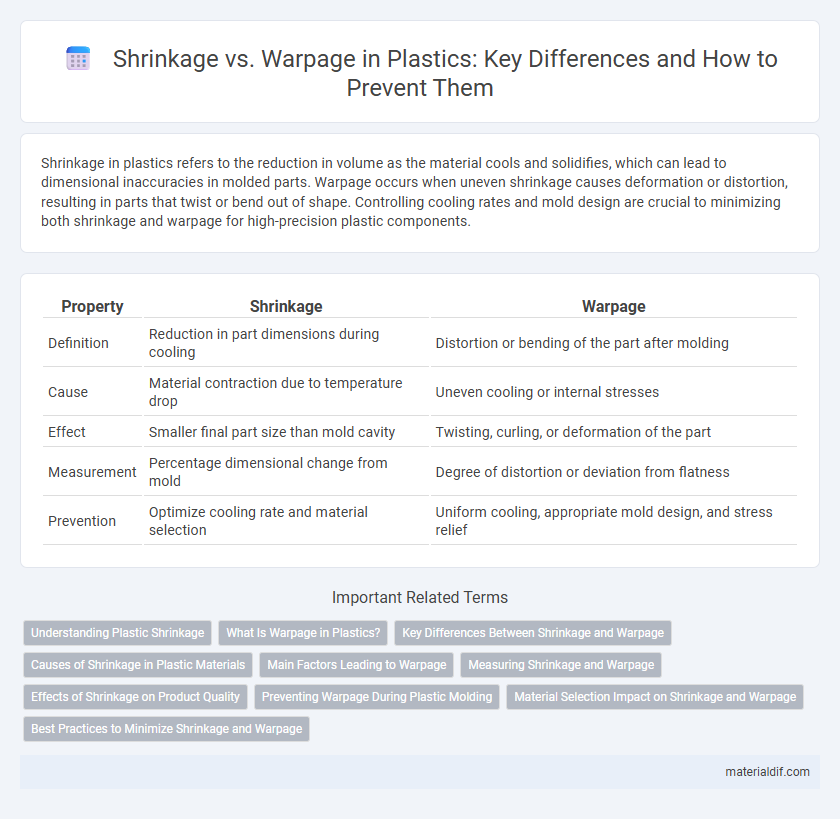
Shrinkage in plastics refers to the reduction in volume as the material cools and solidifies, which can lead to dimensional inaccuracies in molded parts. Warpage occurs when uneven shrinkage causes deformation or distortion, resulting in parts that twist or bend out of shape. Controlling cooling rates and mold design are crucial to minimizing both shrinkage and warpage for high-precision plastic components.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Shrinkage | Warpage |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Reduction in part dimensions during cooling | Distortion or bending of the part after molding |
| Cause | Material contraction due to temperature drop | Uneven cooling or internal stresses |
| Effect | Smaller final part size than mold cavity | Twisting, curling, or deformation of the part |
| Measurement | Percentage dimensional change from mold | Degree of distortion or deviation from flatness |
| Prevention | Optimize cooling rate and material selection | Uniform cooling, appropriate mold design, and stress relief |
Understanding Plastic Shrinkage
Plastic shrinkage refers to the reduction in volume as molten plastic cools and solidifies, typically ranging from 0.5% to 7% depending on the polymer type and processing conditions. Accurate prediction of shrinkage is critical to ensure dimensional stability and proper mold design, as improper allowance can lead to defects such as warpage and internal stresses. Factors influencing shrinkage include polymer crystallinity, mold temperature, injection speed, and cooling time, which must be optimized for efficient manufacturing and product quality.
What Is Warpage in Plastics?
Warpage in plastics refers to the deformation or distortion of a molded part as it cools and solidifies unevenly, causing it to bend, twist, or warp out of its intended shape. This issue arises from differential shrinkage rates within the plastic material, inconsistent cooling, or internal stresses during the molding process. Understanding warpage is critical for optimizing mold design, material selection, and processing parameters to achieve dimensional accuracy and structural integrity in plastic components.
Key Differences Between Shrinkage and Warpage
Shrinkage in plastics refers to the reduction in volume as the material cools and solidifies, typically measured as a percentage of the original part dimensions, while warpage involves the distortion or bending of the molded part caused by uneven cooling or internal stresses during solidification. Shrinkage primarily affects dimensional accuracy and fit, whereas warpage impacts the structural integrity and functionality by causing deviations from the intended shape. Key differences lie in their causative factors--shrinkage results from material contraction, whereas warpage stems from differential shrinkage and residual stresses within the molded component.
Causes of Shrinkage in Plastic Materials
Shrinkage in plastic materials primarily occurs due to molecular alignment and cooling rates during the solidification process. Factors such as polymer type, mold temperature, and cooling time critically influence the degree of shrinkage by affecting the density and crystallinity of the material. Uneven cooling or high mold temperatures often exacerbate shrinkage, leading to dimensional inaccuracies in molded plastic parts.
Main Factors Leading to Warpage
Warpage in plastic components primarily results from uneven shrinkage during the cooling phase, influenced by factors such as material type, mold design, and processing conditions. Variations in wall thickness and inconsistent cooling rates cause differential contraction, leading to internal stresses that deform the part. Proper control of mold temperature, injection speed, and cooling time is essential to minimize warpage and maintain dimensional accuracy.
Measuring Shrinkage and Warpage
Measuring shrinkage in plastics involves calculating the dimensional changes by comparing the mold cavity size with the finished part, often using calipers or micrometers for precision. Warpage measurement requires assessing the degree of deformation on the molded part's surface, typically with optical or laser scanning techniques to detect distortions. Accurate quantification of both shrinkage and warpage is essential for optimizing mold design and material selection in injection molding processes.
Effects of Shrinkage on Product Quality
Shrinkage in plastic molding causes dimensional inaccuracies, leading to parts that may not fit as intended in assemblies. Excessive shrinkage can result in internal stresses, compromising the mechanical strength and durability of the final product. Controlling shrinkage is essential to maintain tight tolerances and ensure consistent product quality in injection-molded components.
Preventing Warpage During Plastic Molding
Controlling cooling rates and uniform mold temperature significantly reduces warpage in plastic molding by minimizing uneven shrinkage. Utilizing optimized mold design and selecting appropriate materials with low shrinkage coefficients also help maintain dimensional stability. Applying controlled injection pressure ensures consistent fill and packing, preventing internal stresses that lead to warpage.
Material Selection Impact on Shrinkage and Warpage
Material selection critically influences shrinkage and warpage in plastic molding, with polymers like polypropylene exhibiting higher shrinkage rates compared to polycarbonate, leading to dimensional inaccuracies. The inherent thermal expansion coefficients and crystallinity levels of materials dictate the extent and uniformity of shrinkage, directly impacting warpage severity. Using materials with low moisture absorption and stable thermal properties minimizes internal stresses, thereby reducing warpage and ensuring precision in molded plastic components.
Best Practices to Minimize Shrinkage and Warpage
To minimize shrinkage and warpage in plastic manufacturing, precise control of mold temperature and uniform cooling rates are essential to reduce internal stresses and ensure dimensional stability. Selecting materials with low shrinkage rates and optimizing part wall thickness can significantly decrease the likelihood of deformation during cooling. Implementing proper gate design and consistent injection pressure further enhances flow uniformity, preventing uneven shrinkage and warpage in molded plastic parts.
Shrinkage vs Warpage Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com