Plastic lamination involves bonding a thin plastic film to a substrate for enhanced durability and moisture resistance, often used in packaging and printed materials. Plastic coating applies a liquid polymer layer directly onto surfaces, providing protection against corrosion, wear, and chemical exposure. Both methods improve product longevity, but lamination offers a more rigid barrier while coating delivers flexible, often thinner protection.
Table of Comparison
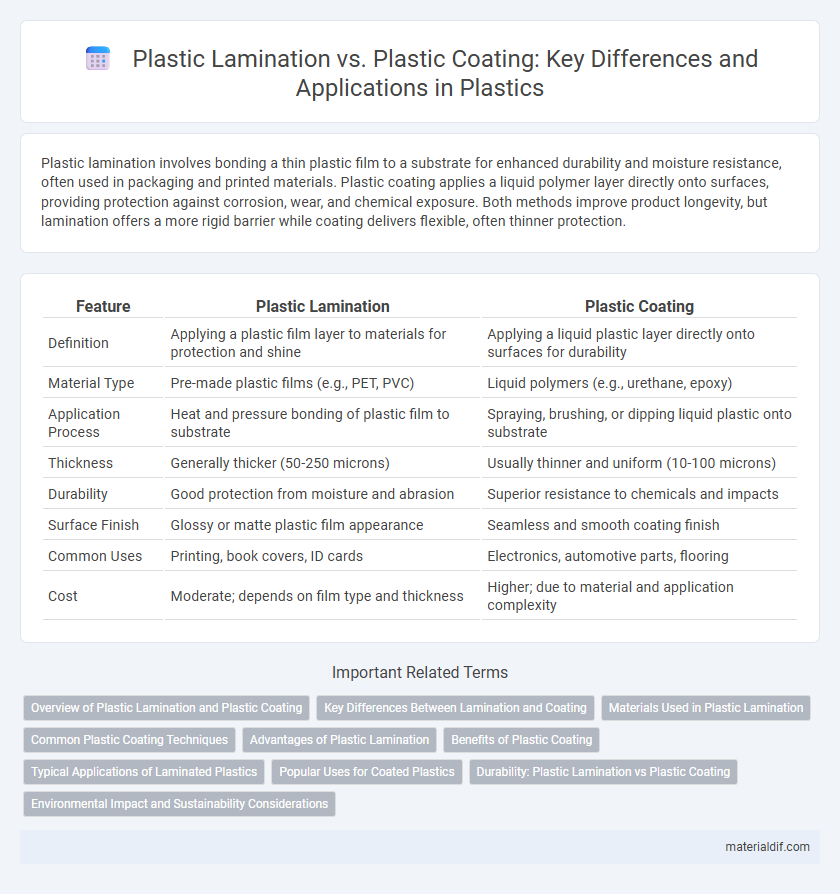
| Feature | Plastic Lamination | Plastic Coating |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Applying a plastic film layer to materials for protection and shine | Applying a liquid plastic layer directly onto surfaces for durability |
| Material Type | Pre-made plastic films (e.g., PET, PVC) | Liquid polymers (e.g., urethane, epoxy) |
| Application Process | Heat and pressure bonding of plastic film to substrate | Spraying, brushing, or dipping liquid plastic onto substrate |
| Thickness | Generally thicker (50-250 microns) | Usually thinner and uniform (10-100 microns) |
| Durability | Good protection from moisture and abrasion | Superior resistance to chemicals and impacts |
| Surface Finish | Glossy or matte plastic film appearance | Seamless and smooth coating finish |
| Common Uses | Printing, book covers, ID cards | Electronics, automotive parts, flooring |
| Cost | Moderate; depends on film type and thickness | Higher; due to material and application complexity |
Overview of Plastic Lamination and Plastic Coating
Plastic lamination involves bonding a thin plastic film to paper or other substrates using heat, pressure, or adhesive, enhancing durability, moisture resistance, and aesthetic appeal. Plastic coating applies a liquid plastic layer directly onto surfaces, providing protective barriers against corrosion, abrasion, and chemical exposure. Both techniques improve product longevity but differ in application methods and flexibility for industrial and consumer uses.
Key Differences Between Lamination and Coating
Plastic lamination involves bonding a transparent plastic film to paper or other materials for added protection and durability, while plastic coating applies a liquid polymer layer directly onto the surface, creating a thin, protective film. Lamination typically offers enhanced resistance to moisture, tearing, and UV damage, making it ideal for documents and packaging, whereas coating provides a smooth finish and can improve resistance to scratches and chemical exposure. The key differences lie in application methods, thickness, and the level of protection each technique offers to the underlying material.
Materials Used in Plastic Lamination
Plastic lamination primarily uses polyethylene terephthalate (PET), polypropylene (PP), and oriented polypropylene (OPP) films as base materials, chosen for their durability and clarity. These materials are combined with layer adhesives such as thermal or pressure-sensitive adhesives to enhance protection and aesthetic appeal. This process creates a barrier against moisture, UV rays, and physical abrasion, extending the lifespan of printed materials and packaging.
Common Plastic Coating Techniques
Common plastic coating techniques include powder coating, dip coating, spray coating, and vacuum deposition, each providing distinct protective and aesthetic benefits. Powder coating offers a durable, uniform finish ideal for metal substrates, while dip coating ensures complete coverage for complex shapes. Spray coating allows for controlled application of thin layers, and vacuum deposition applies ultra-thin films with enhanced adhesion and barrier properties, making them widely used in packaging, automotive, and electronics industries.
Advantages of Plastic Lamination
Plastic lamination offers superior protection against moisture, UV rays, and physical wear, significantly extending the lifespan of printed materials. It enhances visual appeal by providing a smooth, glossy, or matte finish that improves color vibrancy and print clarity. This process also adds rigidity and durability, making laminated items more resistant to tearing and creasing compared to plastic coating.
Benefits of Plastic Coating
Plastic coating offers enhanced protection against moisture, chemicals, and abrasion, significantly extending the lifespan of the underlying material. It provides a flexible, durable barrier that maintains clarity and resists yellowing better than lamination. The application of plastic coating also improves surface texture and adhesion, enabling better print quality and overall product durability.
Typical Applications of Laminated Plastics
Laminated plastics are commonly used in packaging, automotive interiors, and electronics due to their enhanced durability, moisture resistance, and improved aesthetic appeal. Their multilayer structure provides superior barrier properties, making them ideal for food packaging, medical device covers, and protective films. Industrial applications also benefit from laminated plastics' ability to combine different material properties, such as strength and flexibility, in a single product.
Popular Uses for Coated Plastics
Plastic coating is widely used in automotive parts to enhance durability and resistance to corrosion, while laminated plastics find frequent application in packaging for moisture barrier and strength. Coated plastics are popular in electronics for insulating components and providing water resistance. The versatility of plastic coatings in protective outer layers makes them ideal for household appliances, medical devices, and outdoor furniture.
Durability: Plastic Lamination vs Plastic Coating
Plastic lamination offers superior durability by providing a thick protective layer that resists scratches, moisture, and UV damage, significantly extending the lifespan of printed materials. Plastic coating, while enhancing surface protection, typically provides a thinner barrier primarily guarding against minor abrasions and spills but may wear faster under heavy use. For high-impact applications requiring long-term durability, plastic lamination is generally the preferred choice over plastic coating.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability Considerations
Plastic lamination uses multiple layers of plastic films, often complicating recycling processes due to mixed materials, whereas plastic coating typically involves a single polymer layer, improving recyclability. The environmental impact of lamination is higher, with increased energy consumption and waste generation compared to coating, which tends to be more resource-efficient. Sustainability considerations favor plastic coating for its easier end-of-life processing and reduced contribution to landfill accumulation.
Plastic Lamination vs Plastic Coating Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com