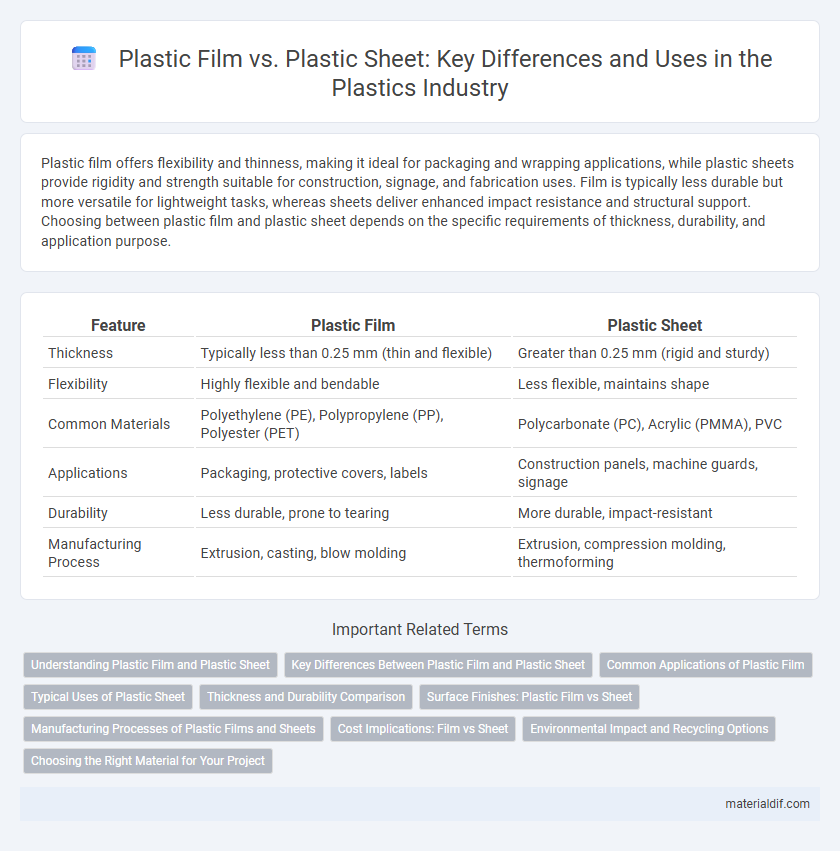
Plastic film offers flexibility and thinness, making it ideal for packaging and wrapping applications, while plastic sheets provide rigidity and strength suitable for construction, signage, and fabrication uses. Film is typically less durable but more versatile for lightweight tasks, whereas sheets deliver enhanced impact resistance and structural support. Choosing between plastic film and plastic sheet depends on the specific requirements of thickness, durability, and application purpose.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Plastic Film | Plastic Sheet |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | Typically less than 0.25 mm (thin and flexible) | Greater than 0.25 mm (rigid and sturdy) |
| Flexibility | Highly flexible and bendable | Less flexible, maintains shape |
| Common Materials | Polyethylene (PE), Polypropylene (PP), Polyester (PET) | Polycarbonate (PC), Acrylic (PMMA), PVC |
| Applications | Packaging, protective covers, labels | Construction panels, machine guards, signage |
| Durability | Less durable, prone to tearing | More durable, impact-resistant |
| Manufacturing Process | Extrusion, casting, blow molding | Extrusion, compression molding, thermoforming |
Understanding Plastic Film and Plastic Sheet
Plastic film is a thin, flexible material typically less than 0.25 mm in thickness, used primarily for packaging, covering, and wrapping applications due to its lightweight and transparent properties. Plastic sheets are thicker, rigid or semi-rigid flat pieces generally exceeding 0.25 mm in thickness, suitable for structural and industrial uses such as signage, fabrication, and protective barriers. Understanding the differences in thickness, flexibility, and application helps determine the appropriate choice between plastic film and plastic sheet for specific manufacturing or consumer needs.
Key Differences Between Plastic Film and Plastic Sheet
Plastic film is a thin, flexible material typically less than 0.008 inches thick, used for packaging, wrapping, and protective covers, while plastic sheet is thicker, rigid or semi-rigid, and employed in applications like signage, construction, and fabrication. Key differences include thickness, flexibility, and durability, with plastic sheets providing greater structural support compared to the lightweight, bendable nature of plastic films. Surface texture and transparency can also vary, influencing their suitability for specific industrial or consumer uses.
Common Applications of Plastic Film
Plastic film is widely used in packaging industries due to its flexibility, lightweight nature, and transparency, making it ideal for wrapping food products, protecting goods, and creating shrink wraps. It also plays a crucial role in agriculture as greenhouse covers and mulch films, enhancing crop growth and moisture retention. Furthermore, plastic films are essential in industrial applications such as lamination, insulation, and printing substrates, providing durability and protection.
Typical Uses of Plastic Sheet
Plastic sheets are commonly used in construction for vapor barriers, insulation, and protective coverings due to their rigidity and durability. They serve as panels for signage, partitions, and machine guards in industrial settings, offering structural strength and easy fabrication. Unlike plastic films, plastic sheets provide enhanced thickness and stability, making them ideal for applications requiring impact resistance and long-term use.
Thickness and Durability Comparison
Plastic films typically range from less than 0.05 mm to 0.3 mm in thickness, offering flexibility and lightweight properties but lower durability compared to plastic sheets. Plastic sheets, usually thicker than 0.3 mm and up to several millimeters, provide enhanced rigidity, impact resistance, and long-term durability suitable for structural and protective applications. The selection between plastic film and sheet depends on balancing thickness requirements with mechanical strength and endurance for specific uses.
Surface Finishes: Plastic Film vs Sheet
Plastic film typically features a smooth, glossy surface finish designed for flexibility and clarity, ideal for packaging and labeling applications. In contrast, plastic sheets offer a wider range of surface finishes, including matte, textured, or embossed options, providing enhanced durability and aesthetic versatility in construction and signage. Surface finish choice directly impacts functionality, with films prioritizing transparency and sheets emphasizing strength and visual appeal.
Manufacturing Processes of Plastic Films and Sheets
Plastic films are produced through extrusion processes such as blown film extrusion and cast film extrusion, where molten polymer is stretched into thin, flexible layers. Plastic sheets are manufactured using methods like extrusion, calendering, and compression molding to create thicker, rigid or semi-rigid flat products. The key distinction lies in film production's emphasis on thinness and flexibility, while sheet manufacturing targets thickness and structural strength.
Cost Implications: Film vs Sheet
Plastic film generally offers a lower cost per square foot compared to plastic sheet due to its thinner gauge and reduced material usage, making it ideal for applications requiring flexibility and lightweight properties. Plastic sheets, while typically more expensive, provide greater durability and structural integrity, which can justify the higher upfront investment in projects demanding long-term strength and rigidity. Cost efficiency depends largely on the specific application, with film favored for budget-sensitive, disposable, or protective uses, and sheet preferred for heavy-duty, load-bearing tasks.
Environmental Impact and Recycling Options
Plastic film, typically thin and flexible, poses significant environmental challenges due to its high potential for pollution and difficulty in recycling through conventional curbside programs. Plastic sheets are thicker, more durable, and generally accepted by most recycling facilities, resulting in better recyclability and reduced environmental footprint. Proper sorting and specialized recycling methods for plastic films, such as drop-off programs, can mitigate their negative impact compared to plastic sheets' broader recycling acceptance.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Project
Plastic film offers flexibility and lightweight protection, making it ideal for packaging and insulation tasks, while plastic sheets provide greater rigidity and structural support suitable for construction and fabrication projects. Selecting the right material depends on factors such as thickness, durability, and application requirements, with films generally ranging from 0.5 to 10 mils and sheets starting at 0.010 inches and thicker. Consider environmental exposure, mechanical stress, and cost efficiency when deciding between plastic film and plastic sheet to ensure optimal performance for your specific project.
Plastic Film vs Plastic Sheet Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com