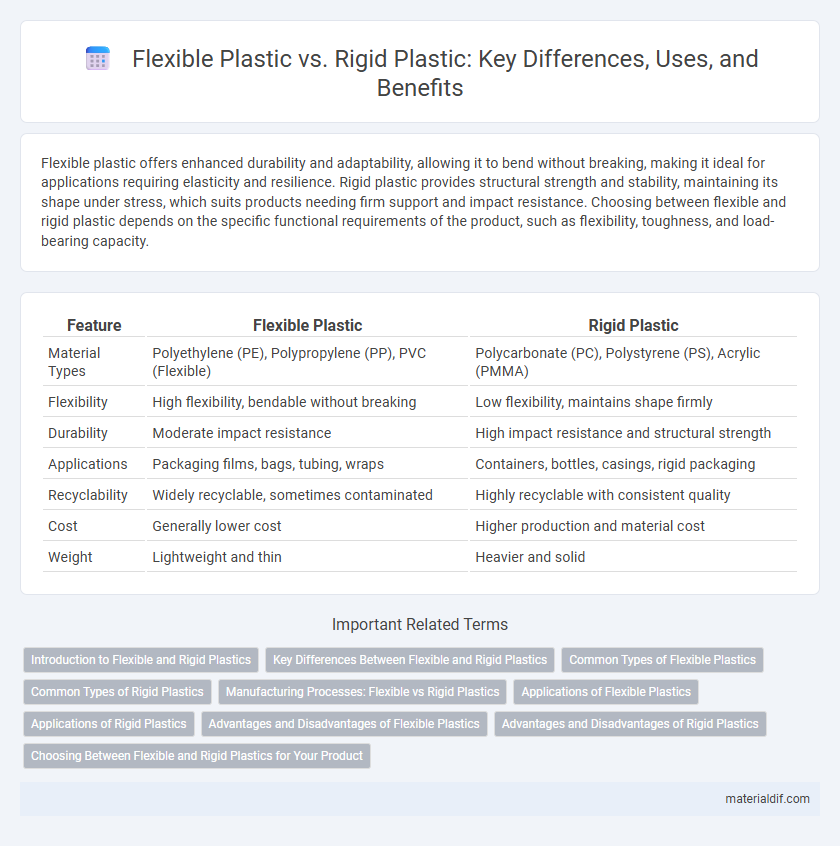
Flexible plastic offers enhanced durability and adaptability, allowing it to bend without breaking, making it ideal for applications requiring elasticity and resilience. Rigid plastic provides structural strength and stability, maintaining its shape under stress, which suits products needing firm support and impact resistance. Choosing between flexible and rigid plastic depends on the specific functional requirements of the product, such as flexibility, toughness, and load-bearing capacity.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Flexible Plastic | Rigid Plastic |
|---|---|---|
| Material Types | Polyethylene (PE), Polypropylene (PP), PVC (Flexible) | Polycarbonate (PC), Polystyrene (PS), Acrylic (PMMA) |
| Flexibility | High flexibility, bendable without breaking | Low flexibility, maintains shape firmly |
| Durability | Moderate impact resistance | High impact resistance and structural strength |
| Applications | Packaging films, bags, tubing, wraps | Containers, bottles, casings, rigid packaging |
| Recyclability | Widely recyclable, sometimes contaminated | Highly recyclable with consistent quality |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Higher production and material cost |
| Weight | Lightweight and thin | Heavier and solid |
Introduction to Flexible and Rigid Plastics
Flexible plastics, such as polyethylene and polypropylene, are characterized by their ability to bend and stretch without breaking, making them ideal for packaging, films, and hoses. Rigid plastics like polystyrene and polycarbonate maintain their shape under stress and are commonly used in containers, automotive parts, and construction materials. Understanding the fundamental differences in mechanical properties and applications between flexible and rigid plastics is essential for selecting the appropriate material for specific industrial or consumer needs.
Key Differences Between Flexible and Rigid Plastics
Flexible plastics like polyethylene and polypropylene exhibit elasticity and can bend without breaking, making them ideal for packaging, films, and bags. Rigid plastics such as ABS, polycarbonate, and polystyrene maintain a solid structure and provide high impact resistance, suitable for products like containers, automotive parts, and electronic housings. The key differences lie in flexibility, durability, and application, with flexible plastics offering pliability and lightweight properties, while rigid plastics deliver strength and structural support.
Common Types of Flexible Plastics
Common types of flexible plastics include polyethylene (PE), polypropylene (PP), and polyvinyl chloride (PVC), widely used in packaging, tubing, and consumer goods due to their durability and adaptability. Low-density polyethylene (LDPE) is popular for its softness and flexibility, making it ideal for plastic bags and squeeze bottles. Thermoplastic elastomers (TPE) combine rubber-like properties with recyclability, finding applications in flexible hoses and seals.
Common Types of Rigid Plastics
Common types of rigid plastics include polyethylene terephthalate (PET), high-density polyethylene (HDPE), polyvinyl chloride (PVC), and polystyrene (PS), each known for durability and structural integrity. PET is widely used in beverage bottles and food packaging due to its strength and clarity, while HDPE finds applications in containers and piping because of its high tensile strength. PVC and PS serve in construction materials and disposable cutlery respectively, offering rigidity and resistance to impact.
Manufacturing Processes: Flexible vs Rigid Plastics
Flexible plastics are typically manufactured using processes such as extrusion, blow molding, and casting, which allow the material to retain its pliability and elasticity. Rigid plastics are produced through injection molding, thermoforming, and compression molding, focusing on creating durable, stable structures with high strength and rigidity. The choice of manufacturing process directly influences the mechanical properties, with flexible plastics offering adaptability and rigid plastics providing structural integrity for diverse applications.
Applications of Flexible Plastics
Flexible plastics are extensively used in packaging applications such as bags, pouches, and shrink wraps due to their lightweight and conformability, offering superior protection for food and consumer goods. Medical devices and tubing also leverage flexible plastics like PVC and silicone for their durability and ability to withstand sterilization. Furthermore, flexible plastics find applications in textiles, automotive interiors, and wearable electronics because they combine elasticity with strength and moisture resistance.
Applications of Rigid Plastics
Rigid plastics are extensively used in applications requiring durability and structural integrity, such as automotive parts, medical devices, and packaging containers. Their resistance to impact and ability to maintain shape under stress make them ideal for product casings, construction materials, and electronic housings. Materials like polycarbonate, ABS, and PVC dominate these sectors due to their strength and versatility.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Flexible Plastics
Flexible plastics offer advantages such as lightweight properties, cost-effectiveness in production, and enhanced adaptability for packaging applications requiring contour fitting and easy sealing. They provide excellent barrier properties against moisture and oxygen, extending product shelf life, but have disadvantages including lower structural strength and reduced durability compared to rigid plastics. Disposal and recycling processes for flexible plastics are often more challenging due to material blends and thin film forms, impacting environmental sustainability.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Rigid Plastics
Rigid plastics offer high strength, durability, and excellent resistance to impact, making them ideal for structural applications and long-term use in containers, automotive parts, and construction materials. Their disadvantages include brittleness under extreme cold, difficulty in molding complex shapes, and higher production costs compared to flexible plastics. Despite limited flexibility, rigid plastics provide superior protection and stability, essential for packaging sensitive products and heavy-duty applications.
Choosing Between Flexible and Rigid Plastics for Your Product
Flexible plastics offer superior shock absorption and bending capabilities, making them ideal for products requiring durability and adaptability such as packaging films and squeeze bottles. Rigid plastics provide structural strength and protection, suitable for containers, automotive parts, and electronic housings. Selecting between the two depends on product design, usage conditions, and cost-efficiency requirements to optimize performance and user experience.
Flexible Plastic vs Rigid Plastic Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com