Polycarbonate offers superior impact resistance and clarity compared to polypropylene, making it ideal for applications requiring durability and transparency such as eyewear lenses and protective gear. Polypropylene is valued for its chemical resistance, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness, commonly used in packaging, automotive parts, and consumer goods. Selecting between polycarbonate and polypropylene depends on the specific mechanical properties, temperature tolerance, and budget requirements of the intended application.
Table of Comparison
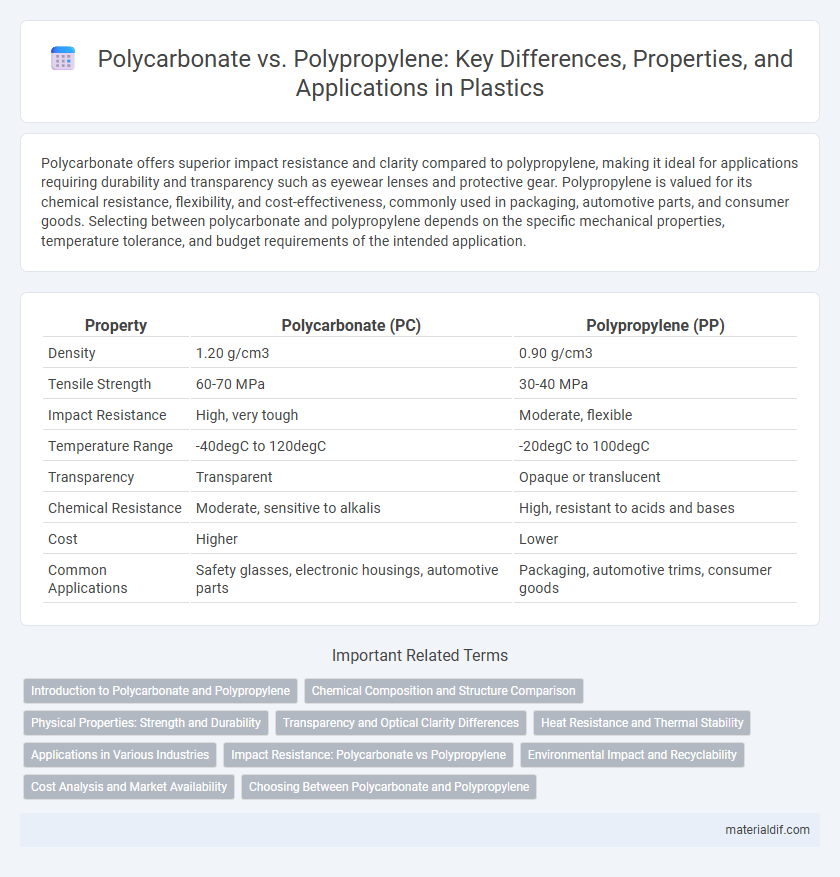
| Property | Polycarbonate (PC) | Polypropylene (PP) |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 1.20 g/cm3 | 0.90 g/cm3 |
| Tensile Strength | 60-70 MPa | 30-40 MPa |
| Impact Resistance | High, very tough | Moderate, flexible |
| Temperature Range | -40degC to 120degC | -20degC to 100degC |
| Transparency | Transparent | Opaque or translucent |
| Chemical Resistance | Moderate, sensitive to alkalis | High, resistant to acids and bases |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Common Applications | Safety glasses, electronic housings, automotive parts | Packaging, automotive trims, consumer goods |
Introduction to Polycarbonate and Polypropylene
Polycarbonate is a durable, impact-resistant thermoplastic known for its high transparency and heat resistance, widely used in eyewear lenses, automotive components, and electronic housings. Polypropylene is a lightweight, chemically resistant polymer favored for packaging, textiles, automotive parts, and consumer goods due to its flexibility and moisture resistance. Both materials offer distinct advantages depending on the application requirements for strength, clarity, and environmental exposure.
Chemical Composition and Structure Comparison
Polycarbonate (PC) is a thermoplastic polymer composed of bisphenol A and phosgene, characterized by its rigid aromatic carbonate groups that provide high impact resistance and thermal stability. Polypropylene (PP) is a polyolefin made from propylene monomers, featuring a semi-crystalline structure with a saturated hydrocarbon chain that offers excellent chemical resistance and flexibility. The molecular structure of PC includes polar carbonate linkages enhancing durability, while PP's non-polar, hydrocarbon backbone contributes to its low density and corrosion resistance.
Physical Properties: Strength and Durability
Polycarbonate exhibits superior strength and impact resistance compared to polypropylene, making it ideal for high-stress applications requiring toughness and durability. Polypropylene offers good chemical resistance and flexibility but has lower tensile strength and is more prone to fatigue under continuous stress. The choice between these plastics depends on the required balance between mechanical performance and environmental resistance.
Transparency and Optical Clarity Differences
Polycarbonate exhibits superior transparency and optical clarity compared to polypropylene, making it ideal for applications requiring clear, glass-like materials such as eyewear lenses and protective barriers. Polycarbonate allows approximately 90% light transmission with excellent impact resistance, while polypropylene is more opaque, with light transmission typically below 70%, limiting its use where high transparency is critical. The molecular structure of polycarbonate contributes to its high refractive index and minimal haze, whereas polypropylene's semi-crystalline nature results in lower clarity and a more matte appearance.
Heat Resistance and Thermal Stability
Polycarbonate exhibits superior heat resistance with a melting point around 267degC and retains dimensional stability at temperatures up to 150degC, making it ideal for high-temperature applications. Polypropylene has a lower melting point near 160degC and shows less thermal stability, softening at temperatures above 100degC, which limits its use in heat-intensive environments. The high glass transition temperature of polycarbonate provides enhanced thermal durability compared to the semi-crystalline structure of polypropylene that is prone to deformation under heat.
Applications in Various Industries
Polycarbonate is widely used in automotive parts, medical devices, and electronic components due to its high impact resistance and transparency. Polypropylene is favored in packaging, textiles, and consumer goods for its chemical resistance, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness. Both plastics serve distinct applications: polycarbonate excels in optical clarity and toughness, while polypropylene is preferred for lightweight, moisture-resistant solutions.
Impact Resistance: Polycarbonate vs Polypropylene
Polycarbonate exhibits superior impact resistance compared to polypropylene, making it the preferred choice for applications requiring high durability and toughness. Polycarbonate can withstand significant force without cracking or breaking, which is why it is commonly used in safety gear and automotive components. In contrast, polypropylene offers moderate impact resistance but excels in flexibility and chemical resistance, suitable for less demanding impact scenarios.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Polycarbonate exhibits a higher environmental impact due to its energy-intensive production process and limited recyclability, often resulting in downcycling rather than closed-loop recycling. Polypropylene is more eco-friendly with a lower carbon footprint and widespread recyclability, supported by established mechanical recycling systems that improve resource recovery. The choice between polycarbonate and polypropylene significantly influences sustainability outcomes in plastic applications based on end-of-life processing and environmental emissions.
Cost Analysis and Market Availability
Polycarbonate generally incurs higher costs than polypropylene due to its superior strength and impact resistance, which justify its premium pricing in high-performance applications. Polypropylene offers a more cost-effective solution with widespread availability, making it a preferred choice for large-scale manufacturing and everyday consumer products. Market demand for polypropylene remains robust, driven by its affordability and versatility, while polycarbonate retains strong niche market presence in electronics and automotive sectors.
Choosing Between Polycarbonate and Polypropylene
Polycarbonate offers superior impact resistance and clarity, making it ideal for applications requiring durability and transparency like eyewear lenses and electronic components. Polypropylene provides excellent chemical resistance and flexibility, commonly used in packaging, automotive parts, and household goods. Selection depends on the need for strength and optical clarity versus chemical resistance and cost-effectiveness.
Polycarbonate vs Polypropylene Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com