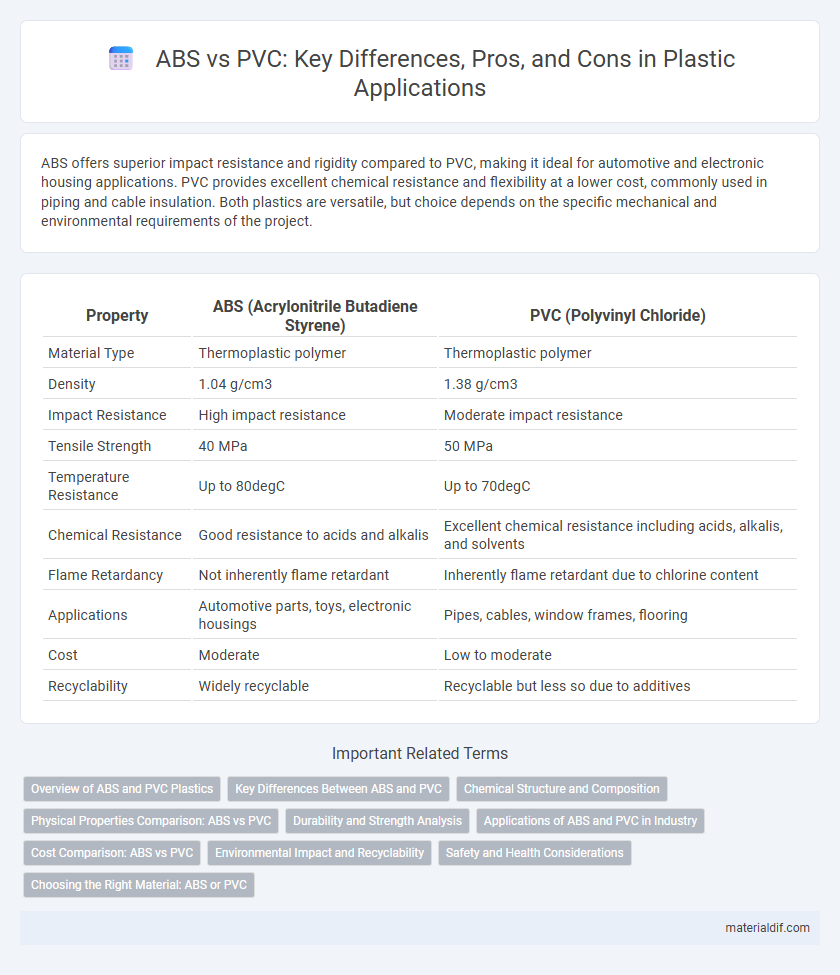
ABS offers superior impact resistance and rigidity compared to PVC, making it ideal for automotive and electronic housing applications. PVC provides excellent chemical resistance and flexibility at a lower cost, commonly used in piping and cable insulation. Both plastics are versatile, but choice depends on the specific mechanical and environmental requirements of the project.
Table of Comparison
| Property | ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene) | PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic polymer | Thermoplastic polymer |
| Density | 1.04 g/cm3 | 1.38 g/cm3 |
| Impact Resistance | High impact resistance | Moderate impact resistance |
| Tensile Strength | 40 MPa | 50 MPa |
| Temperature Resistance | Up to 80degC | Up to 70degC |
| Chemical Resistance | Good resistance to acids and alkalis | Excellent chemical resistance including acids, alkalis, and solvents |
| Flame Retardancy | Not inherently flame retardant | Inherently flame retardant due to chlorine content |
| Applications | Automotive parts, toys, electronic housings | Pipes, cables, window frames, flooring |
| Cost | Moderate | Low to moderate |
| Recyclability | Widely recyclable | Recyclable but less so due to additives |
Overview of ABS and PVC Plastics
ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene) is a strong, impact-resistant thermoplastic commonly used in automotive parts, electronics, and consumer goods due to its toughness and ease of machining. PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) is a versatile, rigid or flexible plastic widely utilized in construction, piping, and medical devices because of its chemical resistance and flame retardant properties. Both ABS and PVC offer durability and performance, with ABS excelling in impact strength and aesthetic finish, while PVC provides superior chemical and weather resistance.
Key Differences Between ABS and PVC
ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene) offers superior impact resistance and temperature tolerance compared to PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride), making it ideal for automotive parts and piping under dynamic stress. PVC excels in chemical resistance and weatherability, commonly used in plumbing, electrical insulation, and outdoor applications due to its durability in harsh environments. Both plastics differ significantly in rigidity, with ABS being more rigid and easier to machine, while PVC provides better flexibility and cost-effectiveness for large-scale construction projects.
Chemical Structure and Composition
ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene) consists of a copolymer combining acrylonitrile, butadiene, and styrene monomers, offering a balance of strength, toughness, and rigidity due to its unique chemical structure. PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) is a polymer primarily composed of vinyl chloride units, characterized by its chlorine content which provides chemical resistance and flame retardancy. The key distinction lies in ABS's rubbery butadiene phase enhancing impact resistance, while PVC's chlorine atoms influence its chemical stability and versatility in applications.
Physical Properties Comparison: ABS vs PVC
ABS plastic offers superior impact resistance and higher tensile strength compared to PVC, making it more suitable for applications requiring durability under mechanical stress. PVC provides better chemical resistance and flame retardancy, which is advantageous in environments exposed to corrosive substances or fire hazards. Both materials exhibit different hardness levels, with ABS being more rigid and PVC offering greater flexibility depending on the formulation.
Durability and Strength Analysis
ABS plastic demonstrates superior impact resistance and toughness compared to PVC, making it ideal for applications requiring high durability under stress. PVC offers excellent chemical resistance and weatherability but tends to be more brittle and less resilient under mechanical strain. When comparing strength, ABS maintains its structural integrity better in dynamic environments, while PVC performs well in static settings without heavy load demands.
Applications of ABS and PVC in Industry
ABS is widely used in automotive parts, consumer electronics housings, and 3D printing due to its toughness and impact resistance. PVC finds extensive applications in construction for pipes, window frames, and electrical cable insulation because of its chemical resistance and durability. Both polymers serve critical roles in manufacturing, with ABS favored for structural components and PVC preferred for flexible and corrosion-resistant solutions.
Cost Comparison: ABS vs PVC
ABS plastic typically costs more than PVC due to its higher impact resistance and better temperature tolerance, making it suitable for demanding applications. PVC is generally more affordable and offers excellent chemical resistance and ease of processing, which reduces fabrication expenses. Overall, the choice between ABS and PVC hinges on balancing initial material costs against performance requirements and long-term durability.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene) generally exhibits lower environmental toxicity during production compared to PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride), which releases harmful chlorine-based compounds and dioxins when manufactured or incinerated. ABS is more readily recyclable through mechanical recycling processes, while PVC poses recycling challenges due to its chlorine content and the presence of additives requiring specialized treatment. PVC waste often contributes to persistent environmental pollution, whereas ABS's recyclability helps reduce landfill accumulation and resource depletion.
Safety and Health Considerations
ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene) is generally safer for indoor air quality as it emits fewer volatile organic compounds (VOCs) compared to PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride), which can release harmful chemicals like dioxins during combustion or decomposition. PVC contains chlorine and additives such as phthalates that pose health risks through off-gassing, potentially causing respiratory and endocrine issues. Choosing ABS over PVC reduces exposure to toxic compounds, making it a preferable option for applications requiring enhanced safety and health standards.
Choosing the Right Material: ABS or PVC
ABS offers superior impact resistance and thermal stability, making it ideal for components exposed to mechanical stress or higher temperatures. PVC provides excellent chemical resistance and cost-effectiveness, favored in applications requiring durability against corrosive substances and electrical insulation. Selecting ABS or PVC depends on the specific environmental conditions, mechanical demands, and budget constraints of the project.
ABS vs PVC Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com