UV-stabilized plastic offers enhanced resistance to sun damage, preventing discoloration and structural degradation over time, which is crucial for outdoor plastic pet products. Non-UV-stabilized plastic tends to become brittle and fade quickly when exposed to sunlight, reducing its durability and lifespan. Choosing UV-stabilized plastic ensures longer-lasting, safer environments for pets exposed to outdoor elements.
Table of Comparison
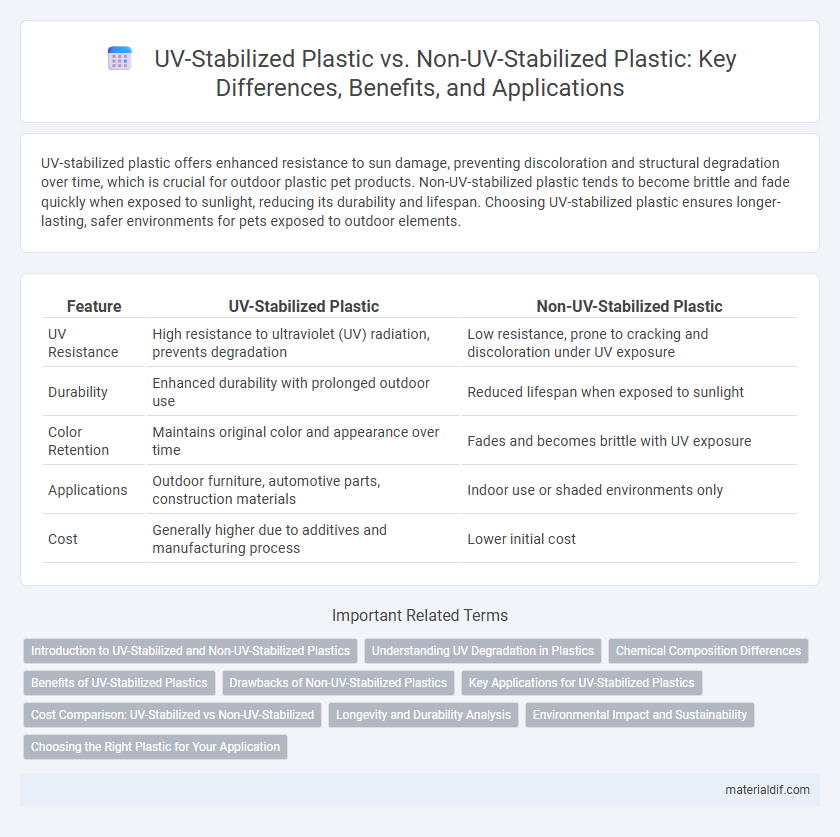
| Feature | UV-Stabilized Plastic | Non-UV-Stabilized Plastic |
|---|---|---|
| UV Resistance | High resistance to ultraviolet (UV) radiation, prevents degradation | Low resistance, prone to cracking and discoloration under UV exposure |
| Durability | Enhanced durability with prolonged outdoor use | Reduced lifespan when exposed to sunlight |
| Color Retention | Maintains original color and appearance over time | Fades and becomes brittle with UV exposure |
| Applications | Outdoor furniture, automotive parts, construction materials | Indoor use or shaded environments only |
| Cost | Generally higher due to additives and manufacturing process | Lower initial cost |
Introduction to UV-Stabilized and Non-UV-Stabilized Plastics
UV-stabilized plastics contain additives that protect polymer chains from degradation caused by ultraviolet radiation, significantly extending their durability and color retention in outdoor applications. Non-UV-stabilized plastics lack these protective compounds, making them susceptible to brittleness, discoloration, and reduced mechanical performance under prolonged UV exposure. Choosing UV-stabilized materials is essential for products exposed to sunlight to ensure longevity and maintain structural integrity.
Understanding UV Degradation in Plastics
UV-stabilized plastic incorporates additives that absorb or block ultraviolet radiation, significantly reducing the rate of polymer chain degradation caused by UV exposure. Non-UV-stabilized plastic suffers from accelerated photo-oxidation, leading to discoloration, brittleness, and loss of mechanical properties over time. Understanding UV degradation in plastics is critical for selecting materials in outdoor applications to ensure longevity and performance stability under sunlight exposure.
Chemical Composition Differences
UV-stabilized plastic contains additives such as UV absorbers, hindered amine light stabilizers (HALS), and benzophenones that absorb or dissipate ultraviolet radiation, preventing polymer chain degradation. Non-UV-stabilized plastic lacks these compounds, making it more susceptible to photodegradation, discoloration, and mechanical property loss under sunlight exposure. The chemical formulation of UV-stabilized plastic enhances durability by chemically intercepting harmful UV radiation that otherwise breaks molecular bonds in conventional plastics.
Benefits of UV-Stabilized Plastics
UV-stabilized plastics contain additives that protect polymers from degrading due to ultraviolet radiation, significantly extending their lifespan when exposed to sunlight. These plastics resist color fading, brittleness, and structural weakening, ensuring durability in outdoor applications such as automotive parts, construction materials, and outdoor furniture. Enhanced UV resistance reduces maintenance costs and environmental waste by minimizing plastic replacement frequency.
Drawbacks of Non-UV-Stabilized Plastics
Non-UV-stabilized plastics degrade rapidly when exposed to sunlight, leading to discoloration, brittleness, and reduced mechanical strength. This degradation shortens the lifespan of plastic products, making them unsuitable for outdoor applications. Additionally, the breakdown of polymers under UV radiation can result in the release of microplastics and harmful chemicals into the environment.
Key Applications for UV-Stabilized Plastics
UV-stabilized plastics are essential for outdoor applications such as automotive parts, roofing materials, and outdoor furniture, where prolonged UV exposure can cause degradation. These plastics incorporate additives that absorb or block ultraviolet radiation, significantly enhancing durability and maintaining mechanical properties under sunlight. Non-UV-stabilized plastics, by contrast, tend to become brittle, discolor, and lose structural integrity when exposed to UV light for extended periods.
Cost Comparison: UV-Stabilized vs Non-UV-Stabilized
UV-stabilized plastic generally incurs a higher initial cost due to the incorporation of additives designed to enhance resistance against ultraviolet radiation and prolong durability. Non-UV-stabilized plastic is typically less expensive upfront but may lead to increased maintenance or replacement costs over time as it degrades faster under sun exposure. Long-term cost-effectiveness favors UV-stabilized plastic for outdoor applications where exposure to UV light is significant.
Longevity and Durability Analysis
UV-stabilized plastic incorporates additives that absorb or block ultraviolet light, significantly enhancing its longevity and resistance to weathering compared to non-UV-stabilized plastic. Non-UV-stabilized plastic tends to degrade quickly when exposed to sunlight, resulting in brittleness, discoloration, and loss of structural integrity. The durability of UV-stabilized plastic makes it ideal for outdoor applications where extended performance and resistance to UV-induced damage are critical.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
UV-stabilized plastic significantly reduces environmental degradation by resisting photodegradation that causes brittleness and fragmentation, thereby extending the product's lifespan and reducing plastic waste accumulation. Non-UV-stabilized plastic breaks down faster under sunlight, leading to microplastic pollution that harms ecosystems and complicates waste management efforts. Opting for UV-stabilized plastics supports sustainability initiatives by enhancing durability and lowering the frequency of replacement, ultimately decreasing the environmental footprint associated with plastic production and disposal.
Choosing the Right Plastic for Your Application
UV-stabilized plastic is engineered with additives that absorb or block ultraviolet radiation, significantly enhancing durability and preventing degradation such as cracking, discoloration, and brittleness, making it ideal for outdoor applications exposed to sunlight. Non-UV-stabilized plastic lacks these protective additives, resulting in faster deterioration under UV exposure, suitable only for indoor or low-UV environments where longevity against sunlight is not critical. Selecting the right plastic involves assessing environmental exposure, expected lifespan, and mechanical stress requirements to ensure material performance aligns with application demands.
UV-Stabilized Plastic vs Non-UV-Stabilized Plastic Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com