Polycarbonate offers superior durability and impact resistance compared to polystyrene, making it ideal for applications requiring toughness and longevity. Polystyrene, while more cost-effective and lightweight, tends to be more brittle and less heat resistant, limiting its use in high-stress environments. Choosing between these plastics depends on balancing the need for strength and clarity against budget constraints and specific functional requirements.
Table of Comparison
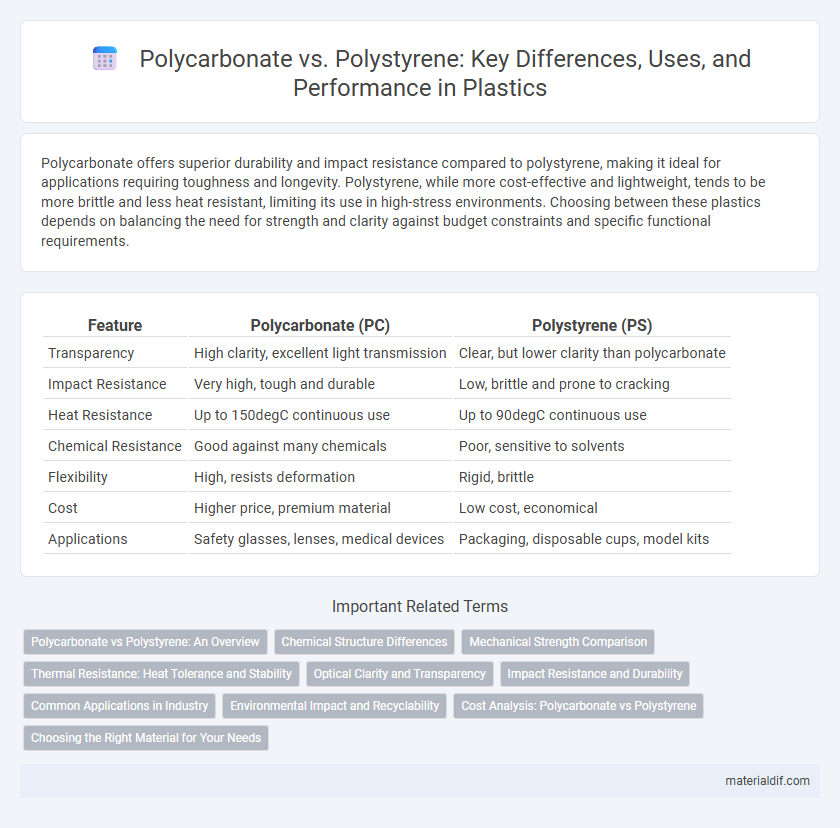
| Feature | Polycarbonate (PC) | Polystyrene (PS) |
|---|---|---|
| Transparency | High clarity, excellent light transmission | Clear, but lower clarity than polycarbonate |
| Impact Resistance | Very high, tough and durable | Low, brittle and prone to cracking |
| Heat Resistance | Up to 150degC continuous use | Up to 90degC continuous use |
| Chemical Resistance | Good against many chemicals | Poor, sensitive to solvents |
| Flexibility | High, resists deformation | Rigid, brittle |
| Cost | Higher price, premium material | Low cost, economical |
| Applications | Safety glasses, lenses, medical devices | Packaging, disposable cups, model kits |
Polycarbonate vs Polystyrene: An Overview
Polycarbonate offers higher impact resistance and thermal stability compared to polystyrene, making it ideal for durable applications such as eyewear lenses and automotive parts. Polystyrene, while more cost-effective and easier to mold, is more brittle and less heat resistant, commonly used in packaging and disposable cutlery. Polycarbonate's superior clarity and resistance to UV radiation provide longer-lasting optical properties, whereas polystyrene may yellow and degrade under prolonged sunlight exposure.
Chemical Structure Differences
Polycarbonate features a carbonate group linking aromatic rings, providing high impact resistance and thermal stability, while polystyrene consists of a long chain of styrene monomers with a phenyl group attached, resulting in rigidity but lower heat resistance. The presence of carbonate groups in polycarbonate enhances its toughness and transparency compared to the simpler hydrocarbon backbone of polystyrene. This structural difference significantly influences their mechanical properties and applications in industries such as automotive and packaging.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
Polycarbonate exhibits significantly higher mechanical strength than polystyrene, offering superior impact resistance and durability under stress. Its tensile strength ranges between 60-70 MPa, while polystyrene typically measures around 40-50 MPa. This makes polycarbonate the preferred choice for applications requiring toughness and structural integrity, such as protective gear and durable containers.
Thermal Resistance: Heat Tolerance and Stability
Polycarbonate exhibits superior thermal resistance compared to polystyrene, with a heat tolerance typically up to 135degC, enabling it to maintain stability under higher temperature conditions. Polystyrene has a lower heat tolerance, generally around 90-100degC, and is more prone to deformation and thermal degradation at elevated temperatures. This makes polycarbonate the preferred choice for applications requiring enhanced heat resistance and dimensional stability.
Optical Clarity and Transparency
Polycarbonate offers superior optical clarity and transparency compared to polystyrene, making it ideal for applications requiring high impact resistance and clear visibility, such as eyewear lenses and protective screens. Polystyrene, while transparent, tends to have lower clarity due to its brittleness and susceptibility to yellowing over time. The enhanced light transmittance and durability of polycarbonate contribute to its preference in high-performance optical and display technologies.
Impact Resistance and Durability
Polycarbonate exhibits significantly higher impact resistance compared to polystyrene, making it ideal for applications requiring shock absorption and toughness. Its durability under prolonged stress and varying environmental conditions surpasses that of polystyrene, which tends to become brittle over time. This superior mechanical performance positions polycarbonate as a preferred material for protective gear, eyewear lenses, and automotive components.
Common Applications in Industry
Polycarbonate is widely used in industries requiring high impact resistance and optical clarity, such as automotive headlamp lenses, protective gear, and electronic housings. Polystyrene finds common applications in packaging, disposable cutlery, and insulation materials due to its rigidity and ease of molding. Both plastics serve distinct industrial needs, with polycarbonate favored for durability and polystyrene for cost-effective, lightweight solutions.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Polycarbonate exhibits higher durability and strength than polystyrene, resulting in longer product life cycles that reduce overall waste generation. Its recyclability is moderate but limited by the presence of bisphenol A (BPA), which can pose environmental and health risks if improperly processed. Polystyrene, especially in its expanded foam form, is less environmentally sustainable due to its low degradation rate and challenges in recycling, often contributing to persistent pollution and landfill accumulation.
Cost Analysis: Polycarbonate vs Polystyrene
Polycarbonate typically has a higher upfront cost compared to polystyrene due to its superior durability and impact resistance. Polystyrene is more cost-effective for applications requiring lightweight and low-strength materials, making it ideal for disposable products and packaging. Long-term savings with polycarbonate arise from its longevity and reduced replacement frequency, balancing initial expenses in high-performance uses.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Needs
Polycarbonate offers superior impact resistance and heat tolerance, making it ideal for applications requiring durability and safety, such as eyewear lenses and automotive parts. Polystyrene, while more cost-effective and easier to mold, provides excellent clarity and rigidity, suitable for packaging and disposable cutlery. Selecting between these plastics depends on prioritizing strength and longevity versus affordability and ease of fabrication.
Polycarbonate vs Polystyrene Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com