Plastic welding creates a strong, permanent bond by melting and fusing plastic parts together, resulting in a seamless joint with high mechanical strength. Plastic adhesion relies on chemical adhesives to join surfaces, which can be faster but may not offer the same durability or resistance to heat and stress. Choosing between plastic welding and plastic adhesion depends on the application requirements, including strength, environmental exposure, and production speed.
Table of Comparison
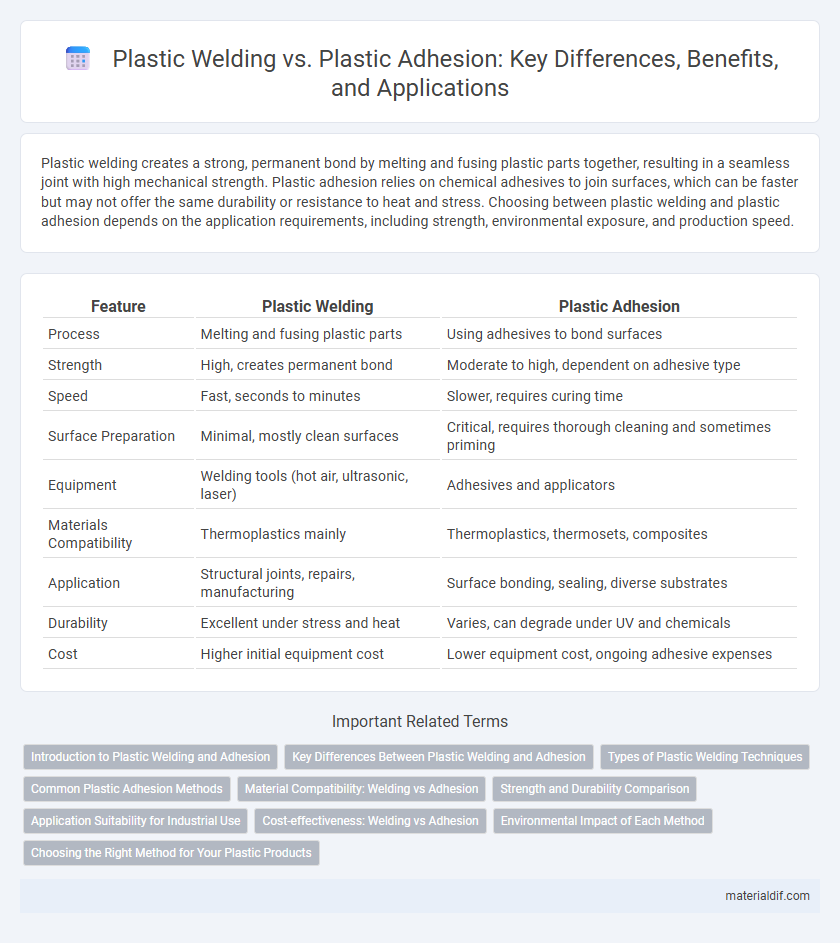
| Feature | Plastic Welding | Plastic Adhesion |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Melting and fusing plastic parts | Using adhesives to bond surfaces |
| Strength | High, creates permanent bond | Moderate to high, dependent on adhesive type |
| Speed | Fast, seconds to minutes | Slower, requires curing time |
| Surface Preparation | Minimal, mostly clean surfaces | Critical, requires thorough cleaning and sometimes priming |
| Equipment | Welding tools (hot air, ultrasonic, laser) | Adhesives and applicators |
| Materials Compatibility | Thermoplastics mainly | Thermoplastics, thermosets, composites |
| Application | Structural joints, repairs, manufacturing | Surface bonding, sealing, diverse substrates |
| Durability | Excellent under stress and heat | Varies, can degrade under UV and chemicals |
| Cost | Higher initial equipment cost | Lower equipment cost, ongoing adhesive expenses |
Introduction to Plastic Welding and Adhesion
Plastic welding involves using heat or ultrasonic vibrations to join thermoplastic surfaces by melting and fusing them together, creating a strong, permanent bond ideal for industrial applications. Plastic adhesion relies on chemical adhesives or solvent-based glues to bond surfaces without altering the plastic's structure, allowing for versatile bonding of dissimilar materials. Both methods are essential in manufacturing, with welding offering durability in structural assemblies and adhesion excelling in precision repairs and lightweight joins.
Key Differences Between Plastic Welding and Adhesion
Plastic welding involves melting and fusing plastic materials together using heat or ultrasonic energy, creating a strong, seamless joint ideal for structural applications. Plastic adhesion relies on chemical or physical bonding agents like adhesives to join surfaces without melting, offering flexibility in bonding dissimilar plastics or complex shapes. Welding typically provides superior mechanical strength and durability, while adhesion enables versatility and ease of application for lightweight or delicate assemblies.
Types of Plastic Welding Techniques
Plastic welding techniques include ultrasonic welding, which uses high-frequency vibrations to join thermoplastics; hot plate welding, where heated plates soften materials for fusion; and laser welding, employing focused laser beams for precise bonds in complex shapes. Spin welding rotates one plastic part against another under pressure and heat, commonly used for cylindrical components. Each method suits specific thermoplastic types and applications, enhancing joint strength and durability compared to traditional plastic adhesion.
Common Plastic Adhesion Methods
Common plastic adhesion methods include solvent bonding, where a chemical solvent temporarily dissolves the plastic surfaces to fuse them upon evaporation, and hot melt adhesion using thermoplastic adhesives that solidify upon cooling. Epoxy adhesives provide strong bonding for dissimilar plastics by forming cross-linked molecular networks, while acrylic adhesives offer fast curing and high resistance to environmental factors. These methods differ from plastic welding, which typically involves melting and fusing plastic parts directly through heat or pressure, resulting in a more homogeneous joint.
Material Compatibility: Welding vs Adhesion
Plastic welding offers superior material compatibility for thermoplastics by fusing polymers at the molecular level, creating strong, homogeneous joints. Plastic adhesion relies on chemical bonding agents and is effective across a broader range of materials, including some thermosets and composites, but may require surface treatments for optimal results. Selecting welding or adhesion depends on the plastic type, desired joint strength, and environmental resistance requirements.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Plastic welding creates a stronger, more durable bond by melting and fusing materials at the molecular level, resulting in a seamless joint with high resistance to mechanical stress and environmental factors. Plastic adhesion relies on chemical bonding through adhesives, which can offer flexibility but generally leads to weaker joints susceptible to failure under heavy loads or exposure to moisture and heat. For applications demanding maximum strength and long-term durability, plastic welding is the preferred method over plastic adhesion.
Application Suitability for Industrial Use
Plastic welding offers superior strength and durability for high-stress industrial applications, making it ideal for structural components and load-bearing assemblies. Plastic adhesion provides versatility and ease of use for bonding dissimilar materials or complex geometries where mechanical strength requirements are moderate. Industries such as automotive, aerospace, and electronics often select plastic welding for reliability and chemical resistance, while plastic adhesion suits rapid prototyping and lightweight enclosures.
Cost-effectiveness: Welding vs Adhesion
Plastic welding offers a cost-effective solution for joining thermoplastics by creating strong, permanent bonds with minimal material waste and faster processing times, reducing labor and production expenses. In contrast, plastic adhesion often requires additional adhesives, curing times, and surface preparation, which can increase overall costs and complicate automation. Welding proves more economical in high-volume manufacturing, while adhesion may be suitable for applications requiring flexibility or disassembly.
Environmental Impact of Each Method
Plastic welding typically produces fewer harmful emissions compared to plastic adhesion, which often relies on chemical solvents that can release volatile organic compounds (VOCs) harmful to the environment. Welding creates strong, durable bonds through heat or ultrasonic methods, reducing the need for additional materials and minimizing waste. Adhesion methods may involve toxic substances and generate more hazardous waste, making plastic welding a more eco-friendly option in many industrial applications.
Choosing the Right Method for Your Plastic Products
Plastic welding creates a strong, permanent bond by melting and fusing materials, ideal for high-strength applications like automotive parts and medical devices. Plastic adhesion uses adhesives to join surfaces, offering versatility and suitability for complex geometries or mixed-material assemblies. Selecting the right method depends on factors such as material type, load requirements, environmental conditions, and production volume.
Plastic Welding vs Plastic Adhesion Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com