Plastic pets made with plasticizers offer enhanced flexibility and durability, making them less prone to cracking or breaking under pressure. In contrast, plastic pets without plasticizers tend to be more rigid and brittle, which can compromise their longevity and safety. Choosing plasticizer-infused materials ensures a softer, more resilient product ideal for both play and display.
Table of Comparison
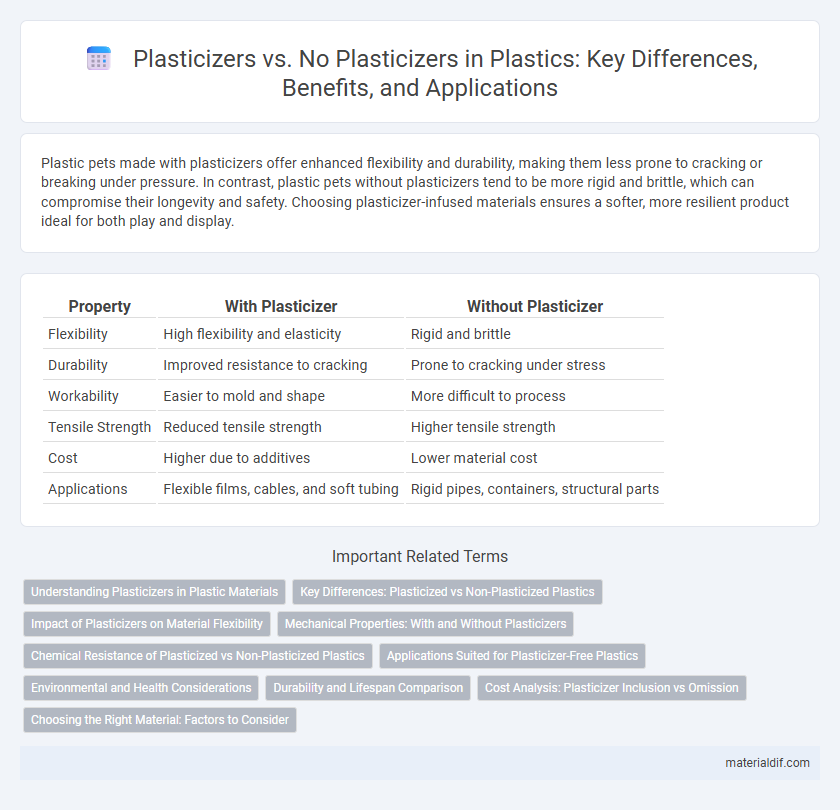
| Property | With Plasticizer | Without Plasticizer |
|---|---|---|
| Flexibility | High flexibility and elasticity | Rigid and brittle |
| Durability | Improved resistance to cracking | Prone to cracking under stress |
| Workability | Easier to mold and shape | More difficult to process |
| Tensile Strength | Reduced tensile strength | Higher tensile strength |
| Cost | Higher due to additives | Lower material cost |
| Applications | Flexible films, cables, and soft tubing | Rigid pipes, containers, structural parts |
Understanding Plasticizers in Plastic Materials
Plasticizers are additives used in plastic materials to enhance flexibility, durability, and workability by reducing intermolecular forces between polymer chains. Without plasticizers, plastics tend to be rigid, brittle, and less resistant to impact, limiting their applications in flexible products like cables, flooring, and packaging films. Understanding the role of plasticizers helps optimize material properties for specific uses while balancing environmental and health concerns associated with some types of chemical additives.
Key Differences: Plasticized vs Non-Plasticized Plastics
Plasticized plastics contain additives called plasticizers that enhance flexibility, softness, and workability by reducing intermolecular forces, making them ideal for applications requiring pliability and impact resistance. Non-plasticized plastics maintain rigidity and higher tensile strength, offering better dimensional stability and resistance to deformation under stress, often used in structural and load-bearing components. Choosing between plasticized and non-plasticized plastics depends on the specific requirements for elasticity, durability, and environmental factors such as temperature and chemical exposure.
Impact of Plasticizers on Material Flexibility
Plasticizers significantly enhance the flexibility and elasticity of polymers by reducing intermolecular forces, allowing polymer chains to move more freely. Materials with plasticizers exhibit improved softness, increased elongation at break, and better impact resistance compared to rigid, brittle polymers without plasticizers. The absence of plasticizers typically results in stiffer, less flexible plastics that are prone to cracking under stress or low temperatures.
Mechanical Properties: With and Without Plasticizers
Plasticizers significantly enhance the mechanical properties of plastics by increasing flexibility, tensile strength, and impact resistance, making materials more durable and less brittle. Without plasticizers, plastics tend to be rigid, with higher brittleness and lower elongation at break, limiting their applications where flexibility is crucial. The selection of plasticizers directly influences the polymer's elasticity and mechanical performance, tailoring materials for specific industrial uses.
Chemical Resistance of Plasticized vs Non-Plasticized Plastics
Plasticized plastics typically exhibit reduced chemical resistance compared to non-plasticized plastics due to the presence of plasticizers, which can leach out or degrade when exposed to aggressive chemicals. Non-plasticized plastics maintain stronger molecular interactions, providing enhanced resistance against solvents, oils, and other corrosive substances. The choice between plasticized and non-plasticized materials depends on the balance required between flexibility and chemical durability for specific applications.
Applications Suited for Plasticizer-Free Plastics
Plasticizer-free plastics are ideal for medical and food packaging applications due to their enhanced chemical stability and lower risk of contaminant leaching. These materials exhibit improved durability and resistance to environmental stress cracking, making them suitable for automotive and electronic components that require consistent performance under varying conditions. Their rigid structure also benefits construction materials where long-term mechanical strength and dimensional stability are critical.
Environmental and Health Considerations
Plasticizers enhance the flexibility and durability of plastics but often contain phthalates, which have been linked to environmental pollution and adverse health effects such as endocrine disruption. Plastics without plasticizers reduce the risk of chemical leaching and bioaccumulation, promoting safer disposal and recycling processes. Choosing non-plasticized materials supports sustainability goals by minimizing toxic chemical release into ecosystems and human exposure.
Durability and Lifespan Comparison
Plasticizers enhance the flexibility and durability of plastics by reducing brittleness, leading to an extended lifespan in products subjected to mechanical stress and environmental factors. Plastics without plasticizers tend to be more rigid and prone to cracking, which can significantly shorten their functional lifespan under continuous use or exposure to varying temperatures. Therefore, incorporating plasticizers improves long-term performance in applications where flexibility and impact resistance are critical.
Cost Analysis: Plasticizer Inclusion vs Omission
Including plasticizers in plastic manufacturing increases initial production costs by 10-15% due to raw material expenses but enhances flexibility and durability, potentially reducing long-term maintenance and replacement costs by up to 20%. Omitting plasticizers lowers upfront costs but results in stiffer, more brittle products that may require more frequent repairs or early replacement, increasing lifecycle expenses. A thorough cost-benefit analysis shows plasticizer inclusion is more economical for applications demanding flexibility and longevity, while omission suits low-cost, short-term use products.
Choosing the Right Material: Factors to Consider
Selecting the right material involves evaluating the impact of plasticizers on flexibility, durability, and chemical stability. Plasticized plastics offer enhanced softness and pliability, while non-plasticized versions provide greater rigidity and resistance to leaching. Consider application-specific factors such as temperature range, exposure to chemicals, and desired mechanical properties to determine the optimal choice.
Plasticizer vs No Plasticizer Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com