Medical-grade plastic exhibits superior biocompatibility, chemical resistance, and sterilization capabilities compared to consumer-grade plastic, making it essential for applications involving direct contact with the human body or sterile environments. Consumer-grade plastic, while more affordable and versatile for general use, often lacks the strict regulatory standards required for medical safety and performance. Selecting medical-grade plastic ensures enhanced durability, reduced risk of contamination, and compliance with healthcare regulations in critical settings.
Table of Comparison
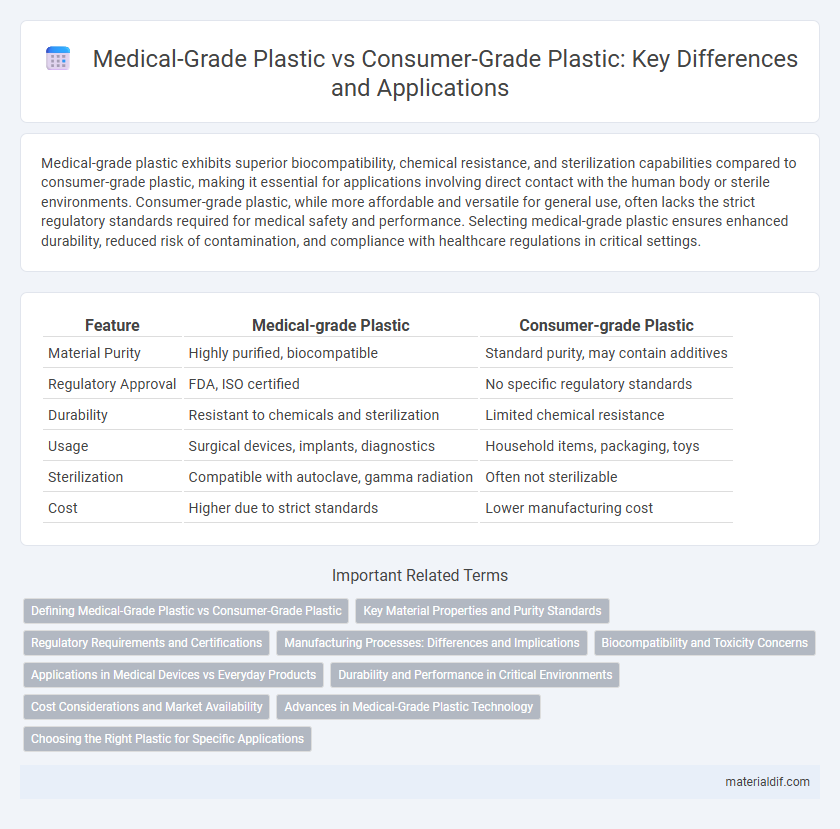
| Feature | Medical-grade Plastic | Consumer-grade Plastic |
|---|---|---|
| Material Purity | Highly purified, biocompatible | Standard purity, may contain additives |
| Regulatory Approval | FDA, ISO certified | No specific regulatory standards |
| Durability | Resistant to chemicals and sterilization | Limited chemical resistance |
| Usage | Surgical devices, implants, diagnostics | Household items, packaging, toys |
| Sterilization | Compatible with autoclave, gamma radiation | Often not sterilizable |
| Cost | Higher due to strict standards | Lower manufacturing cost |
Defining Medical-Grade Plastic vs Consumer-Grade Plastic
Medical-grade plastic is specifically engineered to meet stringent regulatory standards for biocompatibility, sterility, and durability, making it suitable for use in medical devices, implants, and equipment. Consumer-grade plastic, by contrast, is designed for everyday use without the rigorous testing required for medical applications, prioritizing cost-effectiveness and ease of manufacturing. The key distinctions lie in the materials' purity, resistance to chemicals, and compliance with health and safety certifications such as ISO 10993 and FDA guidelines.
Key Material Properties and Purity Standards
Medical-grade plastic exhibits superior biocompatibility, sterilization resistance, and chemical purity compared to consumer-grade plastic, ensuring safety for direct patient contact. These plastics adhere to stringent purity standards such as ISO 10993 for biocompatibility and USP Class VI certification, which govern contamination levels and toxicology criteria. Consumer-grade plastics, while suitable for everyday use, lack the rigorous quality control, sterilization tolerance, and contaminant-free guarantees crucial for medical applications.
Regulatory Requirements and Certifications
Medical-grade plastic complies with stringent regulatory requirements such as FDA, ISO 13485, and USP Class VI certifications, ensuring biocompatibility, sterility, and safety for medical applications. Consumer-grade plastic lacks these rigorous certifications, making it unsuitable for use in critical healthcare environments where contamination risks and toxicity must be minimized. Regulatory oversight for medical-grade plastic mandates traceability, stringent quality control, and adherence to specific chemical composition standards not required for consumer-grade materials.
Manufacturing Processes: Differences and Implications
Medical-grade plastic undergoes stringent manufacturing processes that comply with regulatory standards such as ISO 13485 and FDA CFR 21 Part 820, ensuring biocompatibility, sterilization capability, and contaminant-free production. Consumer-grade plastic manufacturing prioritizes cost-efficiency and mass production, often using additives and fillers that may not meet medical safety requirements. These process differences impact product reliability, safety in medical applications, and the scope of use in sterile environments.
Biocompatibility and Toxicity Concerns
Medical-grade plastic undergoes rigorous testing to ensure biocompatibility, minimizing adverse reactions when in contact with human tissues, unlike consumer-grade plastic which usually lacks such certification. The controlled composition of medical-grade plastics limits toxic additives, reducing the risk of harmful leachates that can cause inflammation or toxicity in medical applications. Consumer-grade plastics often contain stabilizers and plasticizers that may release toxic substances, posing safety concerns for prolonged or internal exposure.
Applications in Medical Devices vs Everyday Products
Medical-grade plastic is engineered for biocompatibility, sterilizability, and resistance to chemicals, making it ideal for critical medical devices such as surgical instruments, implants, and diagnostic equipment. Consumer-grade plastic, in contrast, is designed primarily for cost-efficiency and versatility, used extensively in everyday products like packaging, household items, and disposable containers. The stringent regulatory requirements and superior performance properties of medical-grade plastics ensure safety and reliability in healthcare settings, whereas consumer-grade plastics prioritize accessibility and convenience in daily use.
Durability and Performance in Critical Environments
Medical-grade plastics exhibit superior durability and performance compared to consumer-grade plastics, especially in critical environments such as hospitals and laboratories. These materials are engineered to withstand repeated sterilization, chemical exposure, and mechanical stress without degrading or leaching harmful substances. Their enhanced properties ensure reliability and safety in medical devices and equipment where precision and contamination control are paramount.
Cost Considerations and Market Availability
Medical-grade plastic commands a higher price due to stringent manufacturing standards, certifications, and biocompatibility testing required for healthcare applications. Consumer-grade plastic is more widely available and cost-effective, catering to mass production for everyday use without the need for specialized compliance. Market availability of medical-grade plastic is limited to certified suppliers, whereas consumer-grade plastic benefits from extensive distribution channels and economies of scale.
Advances in Medical-Grade Plastic Technology
Medical-grade plastics have undergone significant advancements, incorporating biocompatible materials such as polyetheretherketone (PEEK) and medical-grade silicone that offer superior strength, sterilization resistance, and chemical stability compared to consumer-grade plastics like polyethylene and polypropylene. Innovations in antimicrobial coatings and enhanced polymer formulations enable medical-grade plastics to meet stringent regulatory standards from the FDA and ISO, ensuring safety during prolonged human contact. These technological improvements facilitate the production of medical devices with improved durability, reduced risks of infection, and optimized performance in critical healthcare applications.
Choosing the Right Plastic for Specific Applications
Medical-grade plastic offers superior biocompatibility, sterilization tolerance, and chemical resistance, making it ideal for implantable devices, surgical instruments, and diagnostic equipment. Consumer-grade plastic, while cost-effective and versatile, lacks the rigorous testing and certification required for medical use, rendering it suitable only for non-critical applications like packaging and household items. Selecting the right plastic hinges on the specific application's safety requirements, regulatory standards, and performance criteria to ensure optimal functionality and patient safety.
Medical-grade Plastic vs Consumer-grade Plastic Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com