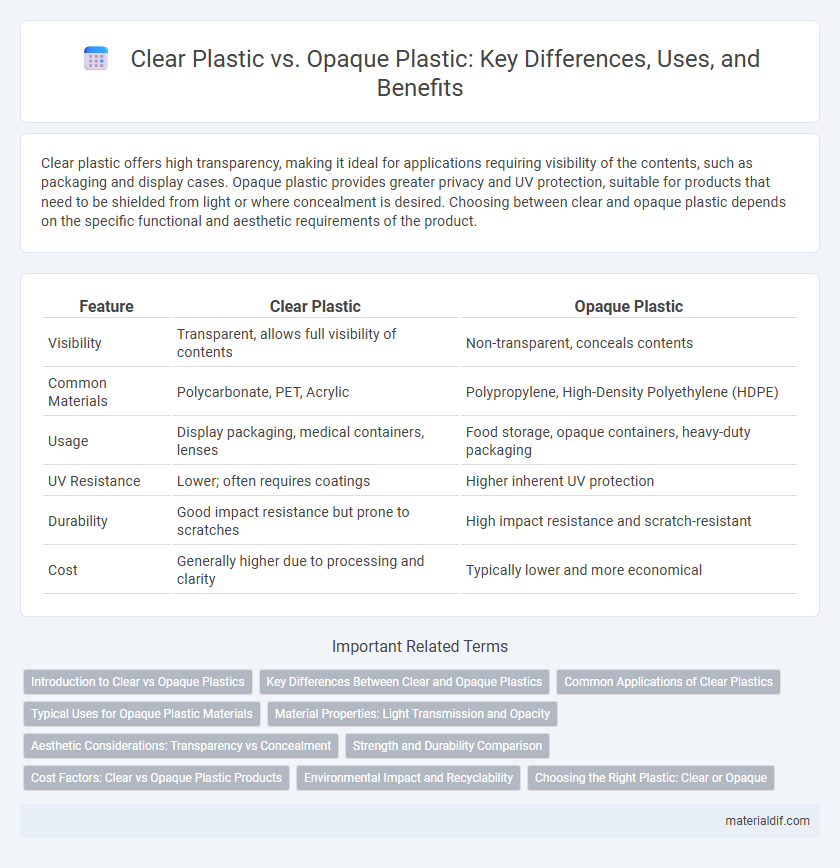
Clear plastic offers high transparency, making it ideal for applications requiring visibility of the contents, such as packaging and display cases. Opaque plastic provides greater privacy and UV protection, suitable for products that need to be shielded from light or where concealment is desired. Choosing between clear and opaque plastic depends on the specific functional and aesthetic requirements of the product.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Clear Plastic | Opaque Plastic |
|---|---|---|
| Visibility | Transparent, allows full visibility of contents | Non-transparent, conceals contents |
| Common Materials | Polycarbonate, PET, Acrylic | Polypropylene, High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) |
| Usage | Display packaging, medical containers, lenses | Food storage, opaque containers, heavy-duty packaging |
| UV Resistance | Lower; often requires coatings | Higher inherent UV protection |
| Durability | Good impact resistance but prone to scratches | High impact resistance and scratch-resistant |
| Cost | Generally higher due to processing and clarity | Typically lower and more economical |
Introduction to Clear vs Opaque Plastics
Clear plastic offers transparency, allowing light and objects to be seen through the material, making it ideal for packaging, protective covers, and optical applications. Opaque plastic, in contrast, blocks light completely, providing privacy, UV protection, and a more solid aesthetic, commonly used in containers, automotive parts, and construction materials. Understanding the differences between clear and opaque plastics is essential for selecting the right type based on visibility, durability, and functional requirements in various industries.
Key Differences Between Clear and Opaque Plastics
Clear plastics, such as polycarbonate and acrylic, offer transparency and high light transmission, making them ideal for applications requiring visibility or aesthetics. Opaque plastics, like polypropylene and polyethylene, provide better UV resistance, chemical durability, and privacy, often used in packaging and automotive parts. The key differences lie in their optical properties, mechanical strength, and typical applications based on transparency versus opacity.
Common Applications of Clear Plastics
Clear plastics such as polycarbonate, acrylic, and PET are extensively used in applications requiring transparency and durability, including eyewear lenses, food packaging, and greenhouse panels. These materials allow for high light transmission, making them ideal for display cases, protective barriers, and medical devices where visibility is crucial. Their resistance to impact and UV stability further enhances their suitability for automotive components and electronic screens.
Typical Uses for Opaque Plastic Materials
Opaque plastic materials are commonly used in packaging for products that require protection from light, such as pharmaceuticals and food items, to preserve freshness and prevent degradation. These plastics are favored in manufacturing household goods, automotive parts, and electronic casings due to their durability and ability to hide internal components. Industrial applications also rely on opaque plastics for insulation and structural purposes where transparency is unnecessary.
Material Properties: Light Transmission and Opacity
Clear plastic offers high light transmission, allowing up to 90% of visible light to pass through, making it ideal for applications requiring transparency like packaging and display cases. Opaque plastic blocks light completely, enhancing privacy and protecting contents from UV radiation and light-induced degradation. The choice between clear and opaque plastics depends on the balance needed between visibility and protection in end-use applications.
Aesthetic Considerations: Transparency vs Concealment
Clear plastic offers superior transparency, allowing full visibility of the enclosed product, which enhances aesthetic appeal through vibrant color display and intricate design details. Opaque plastic provides concealment, hiding contents to create a sleek, uniform appearance ideal for branding that emphasizes mystery or minimalism. Choosing between clear and opaque plastics depends on desired consumer engagement, with transparency promoting product showcase and concealment focusing on design consistency.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Clear plastic often exhibits slightly lower impact resistance compared to opaque plastic due to its molecular structure, which prioritizes transparency over strength. Opaque plastics such as high-density polyethylene (HDPE) or polypropylene (PP) typically demonstrate superior durability and resistance to environmental stress cracking, making them ideal for heavy-duty applications. Both types offer distinct advantages, but opaque plastics consistently provide greater toughness and longevity under harsh conditions.
Cost Factors: Clear vs Opaque Plastic Products
Clear plastic products generally incur higher production costs due to the use of purified raw materials and more precise manufacturing processes that ensure transparency and optical clarity. Opaque plastics often utilize a broader range of fillers and colorants, reducing material expenses and allowing for less stringent processing conditions, resulting in lower overall costs. The cost difference between clear and opaque plastic items is further influenced by factors such as the required quality standards, application-specific performance, and production scale.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Clear plastic typically offers higher recyclability rates due to better sorting and processing compatibility in recycling facilities, while opaque plastic often presents challenges because pigments and additives can contaminate the recycling stream. The environmental impact of clear plastic tends to be lower when recycled properly, as it reduces the demand for virgin plastic production and associated carbon emissions. Conversely, opaque plastics, which are less frequently recycled, contribute more significantly to landfill waste and environmental pollution.
Choosing the Right Plastic: Clear or Opaque
Clear plastic offers superior visibility for packaging and display purposes, allowing consumers to see the product inside and enhancing aesthetic appeal. Opaque plastic provides better protection from light, which is essential for preserving sensitive contents such as pharmaceuticals and food items. Selecting between clear or opaque plastic depends on factors like product protection requirements, marketing needs, and environmental considerations.
Clear Plastic vs Opaque Plastic Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com