Flame retardant plastic contains additives that inhibit or resist the spread of fire, enhancing safety in applications requiring high fire resistance. Non-flame retardant plastic lacks these additives, making it more susceptible to ignition and rapid flame propagation. Choosing between the two depends on the specific fire safety regulations and performance requirements of the intended use.
Table of Comparison
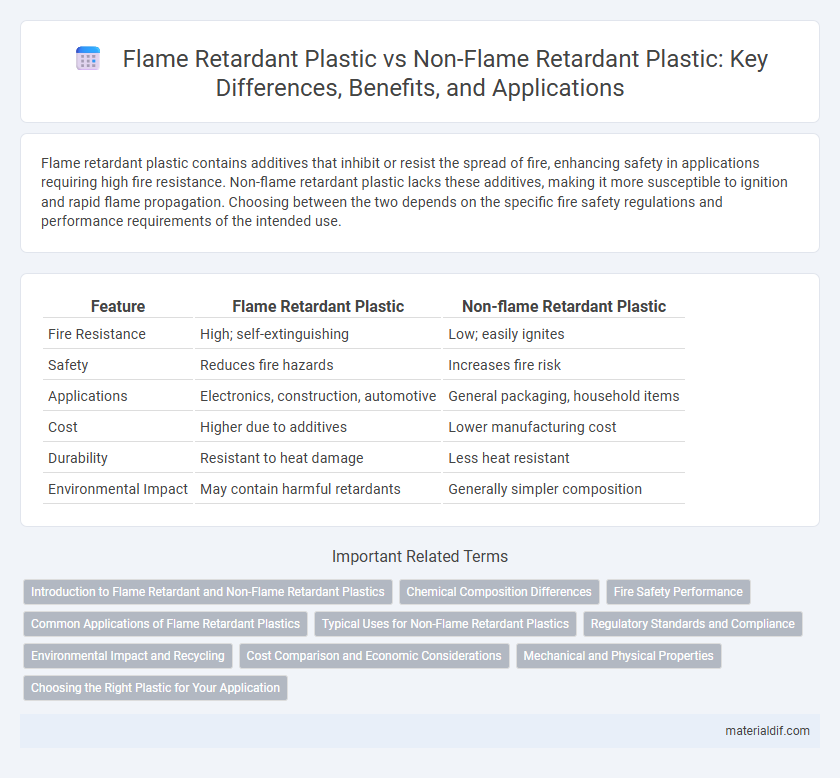
| Feature | Flame Retardant Plastic | Non-flame Retardant Plastic |
|---|---|---|
| Fire Resistance | High; self-extinguishing | Low; easily ignites |
| Safety | Reduces fire hazards | Increases fire risk |
| Applications | Electronics, construction, automotive | General packaging, household items |
| Cost | Higher due to additives | Lower manufacturing cost |
| Durability | Resistant to heat damage | Less heat resistant |
| Environmental Impact | May contain harmful retardants | Generally simpler composition |
Introduction to Flame Retardant and Non-Flame Retardant Plastics
Flame retardant plastics contain additives that inhibit or resist the spread of fire, enhancing safety in applications such as electronics, construction, and automotive components. Non-flame retardant plastics lack these fire-resistant properties, making them more susceptible to ignition and combustion under high heat or flame exposure. Understanding the distinction is crucial for selecting materials that meet specific fire safety standards and regulatory requirements.
Chemical Composition Differences
Flame retardant plastics contain specific chemical additives such as brominated compounds, phosphorus-based compounds, or metal hydroxides like aluminum trihydrate, which inhibit or resist ignition and slow down combustion. Non-flame retardant plastics lack these additives, making them more susceptible to catching fire and propagating flames rapidly. The presence of these flame retardant chemicals modifies the polymer matrix, enhancing thermal stability and reducing flammability compared to standard plastics.
Fire Safety Performance
Flame retardant plastics exhibit significantly enhanced fire safety performance compared to non-flame retardant plastics due to their ability to resist ignition, slow down flame spread, and reduce heat release during combustion. These specialized polymers contain additives like brominated compounds, phosphorus-based agents, or mineral fillers that interrupt the chemical reactions in fire, thereby minimizing fire hazards. Non-flame retardant plastics lack these protective additives, making them more combustible and increasing the risk of fire-related damage and safety concerns in various applications.
Common Applications of Flame Retardant Plastics
Flame retardant plastics are extensively used in electrical and electronic housings, building materials, automotive components, and aerospace parts to enhance fire safety and comply with strict regulatory standards. These plastics contain additives that inhibit or resist the spread of fire, making them essential in environments with high fire risk. Their application ensures protection of equipment and personnel by reducing fire hazards compared to non-flame retardant plastics.
Typical Uses for Non-Flame Retardant Plastics
Non-flame retardant plastics are commonly used in applications where fire resistance is not a primary requirement, such as packaging materials, consumer goods, and automotive interior components. These plastics offer excellent moldability, durability, and cost-effectiveness, making them ideal for manufacturing everyday items like containers, toys, and electronic housings. Their widespread use is driven by the need for lightweight and versatile materials in industries prioritizing mechanical performance over fire safety.
Regulatory Standards and Compliance
Flame retardant plastics comply with strict regulatory standards such as UL 94, EN 13501, and RoHS, ensuring enhanced fire resistance and safety in various applications. Non-flame retardant plastics typically do not meet these fire safety regulations, limiting their use in environments requiring stringent compliance. Compliance with standards like REACH and FAR 25.853 is critical for flame retardant plastics in aerospace, electronics, and construction industries to prevent fire hazards and meet legal requirements.
Environmental Impact and Recycling
Flame retardant plastics contain chemical additives designed to inhibit or resist the spread of fire, often making them less environmentally friendly due to the potential release of toxic substances during disposal or recycling processes. Non-flame retardant plastics typically pose fewer challenges in recycling and generate fewer harmful emissions, but they lack the enhanced fire safety benefits crucial in many applications. The presence of flame retardants can complicate polymer recovery and reduce the efficiency of recycling streams, contributing to greater environmental impact compared to non-flame retardant counterparts.
Cost Comparison and Economic Considerations
Flame retardant plastics typically incur higher costs due to the incorporation of specialized additives that enhance fire resistance, impacting raw material expenses and processing requirements. Non-flame retardant plastics offer a more economical choice, especially for applications with lower fire safety demands, reducing overall production and material costs. Economic considerations must balance initial investment against potential savings from regulatory compliance, insurance premiums, and risk mitigation associated with flame retardant properties.
Mechanical and Physical Properties
Flame retardant plastics exhibit enhanced mechanical strength and thermal stability compared to non-flame retardant plastics, making them ideal for applications requiring fire resistance and durability. These materials often maintain their physical integrity under high temperatures, preventing deformation and maintaining dimensional stability. Non-flame retardant plastics typically have lower heat resistance and are more prone to melting or warping when exposed to flames or elevated temperatures.
Choosing the Right Plastic for Your Application
Flame retardant plastics contain chemical additives that significantly reduce their flammability, making them ideal for applications requiring strict fire safety standards, such as electronics and automotive parts. Non-flame retardant plastics are generally more cost-effective and suitable for applications where fire resistance is not a critical factor, such as packaging or consumer goods. Selecting the right plastic depends on balancing safety requirements, performance needs, and regulatory compliance specific to your industry.
Flame Retardant Plastic vs Non-flame Retardant Plastic Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com