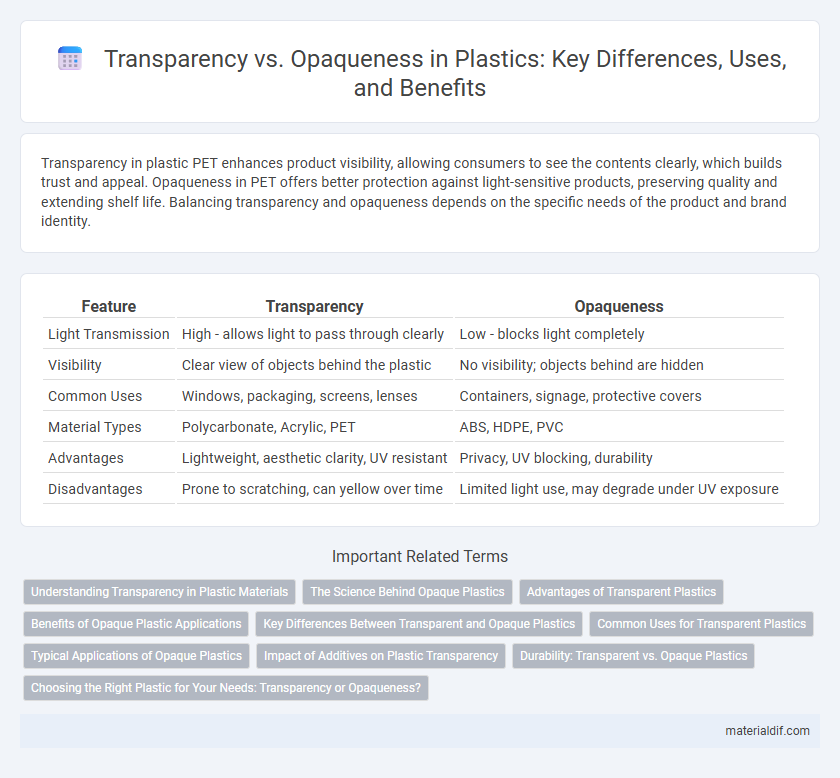
Transparency in plastic PET enhances product visibility, allowing consumers to see the contents clearly, which builds trust and appeal. Opaqueness in PET offers better protection against light-sensitive products, preserving quality and extending shelf life. Balancing transparency and opaqueness depends on the specific needs of the product and brand identity.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Transparency | Opaqueness |
|---|---|---|
| Light Transmission | High - allows light to pass through clearly | Low - blocks light completely |
| Visibility | Clear view of objects behind the plastic | No visibility; objects behind are hidden |
| Common Uses | Windows, packaging, screens, lenses | Containers, signage, protective covers |
| Material Types | Polycarbonate, Acrylic, PET | ABS, HDPE, PVC |
| Advantages | Lightweight, aesthetic clarity, UV resistant | Privacy, UV blocking, durability |
| Disadvantages | Prone to scratching, can yellow over time | Limited light use, may degrade under UV exposure |
Understanding Transparency in Plastic Materials
Transparency in plastic materials is determined by the polymer's molecular structure and the presence of additives, which influence light transmission and clarity. Highly transparent plastics, such as acrylic and polycarbonate, allow visible light to pass through with minimal scattering, making them ideal for applications requiring clear visibility. Opaque plastics, like polypropylene or high-impact polystyrene, scatter or absorb light due to crystallinity or fillers, resulting in reduced transparency for privacy or aesthetic purposes.
The Science Behind Opaque Plastics
Opaque plastics owe their lack of transparency to the scattering of light caused by microscopic fillers or polymer crystallinity within the material. The presence of pigments, additives, or high-density polymer chains disrupts the transmission of light waves, preventing them from passing through evenly. These structural variations at the molecular level create an opaque surface by diffusing and absorbing incoming light, which is critical for applications requiring light blockage or added durability.
Advantages of Transparent Plastics
Transparent plastics offer superior clarity, allowing for optimal light transmission and enhanced product visibility, which is crucial in packaging and consumer goods. Their ability to provide aesthetic appeal while maintaining durability and impact resistance makes them ideal for applications requiring both protection and visual inspection. Moreover, transparent plastics facilitate better quality control, as defects and contamination can be easily detected without dismantling the packaging or enclosure.
Benefits of Opaque Plastic Applications
Opaque plastics offer enhanced UV protection, preventing material degradation and extending product lifespan in packaging and automotive industries. Their ability to hide contents or internal components ensures better aesthetic appeal and privacy for consumer goods. Increased mechanical strength and resistance to stains make opaque plastics ideal for durable household items and industrial applications.
Key Differences Between Transparent and Opaque Plastics
Transparent plastics like acrylic and polycarbonate allow light to pass through clearly, offering high clarity and visibility, ideal for applications requiring optical precision. Opaque plastics such as polypropylene and ABS block light transmission, providing better UV protection and structural concealment, often used for aesthetic or functional coverings. Key differences include light transmission properties, mechanical strength, and suitability for specific uses based on visual requirements and durability.
Common Uses for Transparent Plastics
Transparent plastics, such as polycarbonate and acrylic, are widely used in applications requiring clear visibility and durability, including eyewear lenses, protective barriers, and medical devices. These materials offer excellent optical clarity, UV resistance, and impact strength, making them ideal for automotive windows, smartphone screens, and aquarium tanks. The ability to maintain transparency while providing structural integrity enables their extensive use in packaging, allowing consumers to see product contents clearly.
Typical Applications of Opaque Plastics
Opaque plastics are widely used in packaging for products requiring light protection, such as pharmaceuticals, food containers, and cosmetics, to preserve quality and shelf life. They are essential in automotive parts and electrical housings, where visual concealment and durability are critical. Industrial applications benefit from opaque plastics due to their ability to provide insulation and structural strength while masking internal components.
Impact of Additives on Plastic Transparency
Additives such as plasticizers, UV stabilizers, and colorants significantly influence plastic transparency by altering the polymer's light transmission properties. The incorporation of pigments or fillers increases opacity by scattering and absorbing light, reducing clarity. Conversely, carefully selected additives can enhance transparency by improving polymer chain alignment and minimizing light diffusion.
Durability: Transparent vs. Opaque Plastics
Transparent plastics like polycarbonate and acrylic offer moderate durability with excellent visibility, making them ideal for applications requiring clarity and impact resistance. Opaque plastics such as ABS and polypropylene generally provide higher durability and better resistance to UV degradation, chemicals, and wear, suited for structural and protective uses. Choosing between transparency and opaquer materials depends on balancing the need for visual clarity against environmental resistance and mechanical strength.
Choosing the Right Plastic for Your Needs: Transparency or Opaqueness?
Selecting the appropriate plastic hinges on the desired transparency or opaqueness required for the application. Transparent plastics like polycarbonate and acrylic offer clarity and light transmission, ideal for display cases and protective shields. Opaque plastics such as ABS and HDPE provide durability and concealing properties, suitable for structural components and packaging that demand privacy or UV resistance.
Transparency vs Opaqueness Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com