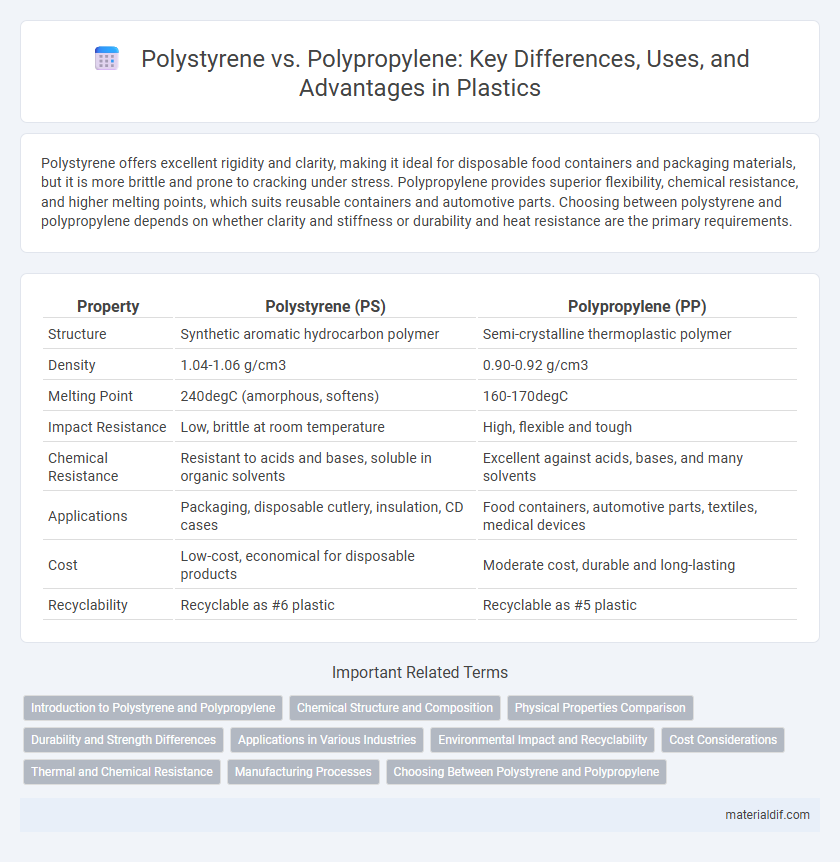
Polystyrene offers excellent rigidity and clarity, making it ideal for disposable food containers and packaging materials, but it is more brittle and prone to cracking under stress. Polypropylene provides superior flexibility, chemical resistance, and higher melting points, which suits reusable containers and automotive parts. Choosing between polystyrene and polypropylene depends on whether clarity and stiffness or durability and heat resistance are the primary requirements.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polystyrene (PS) | Polypropylene (PP) |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Synthetic aromatic hydrocarbon polymer | Semi-crystalline thermoplastic polymer |
| Density | 1.04-1.06 g/cm3 | 0.90-0.92 g/cm3 |
| Melting Point | 240degC (amorphous, softens) | 160-170degC |
| Impact Resistance | Low, brittle at room temperature | High, flexible and tough |
| Chemical Resistance | Resistant to acids and bases, soluble in organic solvents | Excellent against acids, bases, and many solvents |
| Applications | Packaging, disposable cutlery, insulation, CD cases | Food containers, automotive parts, textiles, medical devices |
| Cost | Low-cost, economical for disposable products | Moderate cost, durable and long-lasting |
| Recyclability | Recyclable as #6 plastic | Recyclable as #5 plastic |
Introduction to Polystyrene and Polypropylene
Polystyrene is a versatile thermoplastic polymer widely used in packaging, insulation, and disposable cutlery due to its rigidity and clarity. Polypropylene, a semi-crystalline thermoplastic, features high chemical resistance, elasticity, and fatigue resistance, making it suitable for automotive parts, textiles, and medical devices. Both polymers are significant in the plastic industry, with polystyrene known for its brittleness and ease of molding, while polypropylene is valued for its durability and flexibility.
Chemical Structure and Composition
Polystyrene is a polymer composed of repeating styrene monomers characterized by a benzene ring attached to the carbon backbone, which imparts rigidity and clarity. Polypropylene consists of propylene monomers with a methyl group attached to every other carbon atom in the polymer chain, resulting in a semi-crystalline structure that offers flexibility and chemical resistance. The aromatic ring in polystyrene contributes to its brittleness, whereas the saturated hydrocarbon structure of polypropylene enhances its toughness and thermal stability.
Physical Properties Comparison
Polystyrene (PS) is a rigid, brittle thermoplastic with a low melting point around 240degC, offering excellent clarity and stiffness but limited impact resistance. Polypropylene (PP) demonstrates higher flexibility, toughness, and a higher melting point near 160-170degC, making it more suitable for applications requiring durability and heat resistance. PS has a higher density of approximately 1.05 g/cm3 compared to PP's lower density of around 0.90-0.92 g/cm3, contributing to PP's lighter weight in packaging and automotive uses.
Durability and Strength Differences
Polystyrene offers rigidity and impact resistance but tends to be more brittle and prone to cracking under stress compared to polypropylene. Polypropylene excels in flexibility, tensile strength, and resistance to fatigue, making it more durable for applications involving repeated use or bending. The molecular structure of polypropylene grants superior chemical resistance and resilience, resulting in better long-term strength and durability.
Applications in Various Industries
Polystyrene is widely used in packaging, disposable cutlery, and insulation due to its rigidity and clarity, making it ideal for product protection and food service applications. Polypropylene excels in automotive parts, textiles, and medical devices thanks to its chemical resistance, flexibility, and high melting point. Industries leverage polystyrene for lightweight containers and polypropylpentene for durable, reusable components, optimizing performance based on material properties.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Polystyrene generates substantial environmental concerns due to its slow degradation and tendency to fragment into microplastics, which persist in ecosystems and pose risks to wildlife. Polypropylene offers better recyclability with higher recovery rates and more efficient processing in recycling facilities, reducing landfill accumulation. Both plastics contribute to environmental pollution, but polypropylene's lower carbon footprint and greater recycling potential make it a more sustainable option in plastic manufacturing and waste management.
Cost Considerations
Polystyrene generally has a lower material cost compared to polypropylene, making it a preferred choice for budget-sensitive applications such as disposable cutlery and packaging. Polypropylene offers greater durability and chemical resistance, which can justify its higher price in long-term use or industrial settings. The overall cost-effectiveness depends on the product lifecycle and specific application requirements, with polypropylene often favored for reusable items despite its initial expense.
Thermal and Chemical Resistance
Polystyrene exhibits lower thermal resistance with a melting point around 240degC and tends to degrade when exposed to high temperatures, whereas polypropylene withstands higher temperatures up to 260degC, making it more suitable for heat-exposed applications. Chemically, polypropylene offers superior resistance to acids, bases, and organic solvents compared to polystyrene, which is more prone to chemical attack and swelling. These differences influence their use in packaging, automotive parts, and household goods where thermal and chemical stability is critical.
Manufacturing Processes
Polystyrene is typically produced through a suspension or bulk polymerization process, allowing for transparent and rigid plastic products commonly used in packaging and insulation. Polypropylene manufacturing involves a chain-growth polymerization catalyzed by Ziegler-Natta or metallocene catalysts, resulting in a versatile thermoplastic known for its toughness and chemical resistance. Both polymers require precise temperature control and catalyst selection to optimize polymer chain structure and achieve desired physical properties.
Choosing Between Polystyrene and Polypropylene
Polystyrene offers rigidity and clarity, making it ideal for packaging and disposable cutlery, but it lacks flexibility and impact resistance compared to polypropylene. Polypropylene provides greater durability, chemical resistance, and flexibility, which suits applications like automotive parts, reusable containers, and textiles. Selecting between polystyrene and polypropylene depends on factors like desired strength, transparency, temperature tolerance, and environmental impact.
Polystyrene vs Polypropylene Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com