Polyethylene offers superior flexibility and chemical resistance, making it ideal for packaging films and containers, while polystyrene provides higher rigidity and clarity, suitable for disposable cutlery and insulation materials. Polyethylene's low density and toughness contribute to its durability and recyclability, contrasting with polystyrene's brittleness and limited environmental friendliness. Choosing between polyethylene and polystyrene depends on the specific application requirements regarding flexibility, strength, and sustainability.
Table of Comparison
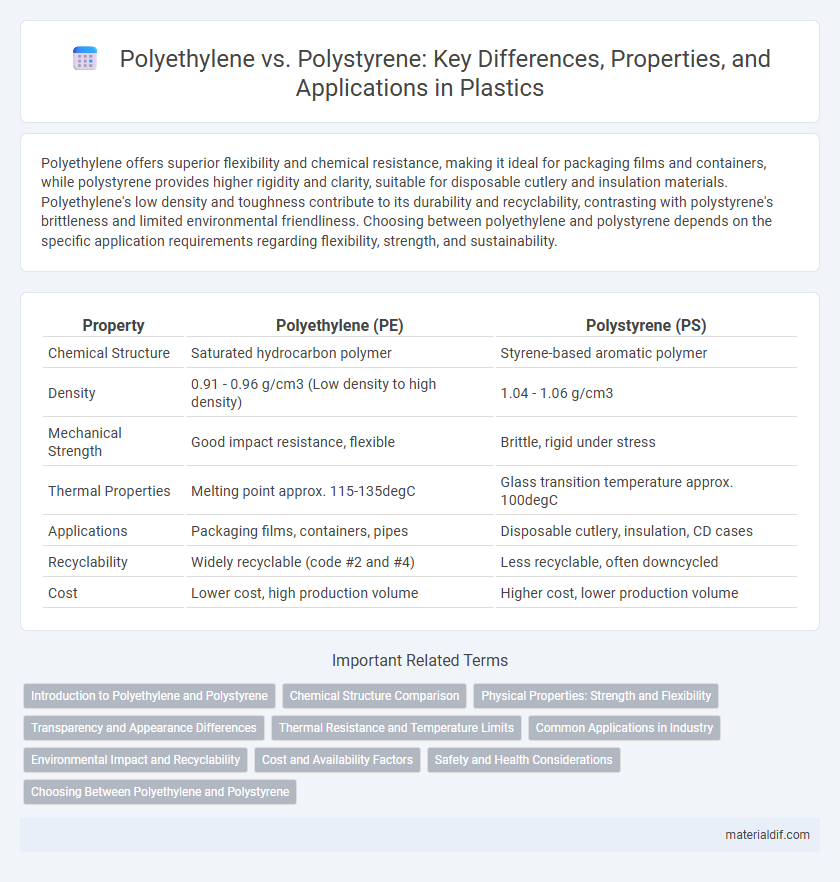
| Property | Polyethylene (PE) | Polystyrene (PS) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Structure | Saturated hydrocarbon polymer | Styrene-based aromatic polymer |
| Density | 0.91 - 0.96 g/cm3 (Low density to high density) | 1.04 - 1.06 g/cm3 |
| Mechanical Strength | Good impact resistance, flexible | Brittle, rigid under stress |
| Thermal Properties | Melting point approx. 115-135degC | Glass transition temperature approx. 100degC |
| Applications | Packaging films, containers, pipes | Disposable cutlery, insulation, CD cases |
| Recyclability | Widely recyclable (code #2 and #4) | Less recyclable, often downcycled |
| Cost | Lower cost, high production volume | Higher cost, lower production volume |
Introduction to Polyethylene and Polystyrene
Polyethylene is a versatile thermoplastic polymer widely used in packaging, containers, and household products due to its chemical resistance and durability. Polystyrene, another common thermoplastic, is valued for its rigidity, clarity, and insulating properties, often found in disposable cutlery, CD cases, and foam packaging. Both polymers originate from petroleum hydrocarbons but differ substantially in molecular structure and application versatility.
Chemical Structure Comparison
Polyethylene consists of long chains of ethylene monomers with a simple, non-polar hydrocarbon backbone, making it highly flexible and chemically resistant. Polystyrene's chemical structure includes a phenyl group attached to every other carbon atom in the hydrocarbon chain, which introduces rigidity and reduces chemical resistance. The presence of aromatic rings in polystyrene significantly alters its thermal and mechanical properties compared to the saturated alkane structure of polyethylene.
Physical Properties: Strength and Flexibility
Polyethylene exhibits superior flexibility and impact resistance due to its long-chain polymer structure, making it ideal for applications requiring durability and pliability. In contrast, polystyrene is rigid and brittle, offering higher tensile strength but lower flexibility, which suits it for rigid containers and insulation materials. The differences in crystallinity and molecular arrangement directly influence their strength-to-flexibility ratio, impacting their respective performance in packaging and consumer products.
Transparency and Appearance Differences
Polyethylene typically exhibits a translucent appearance with limited clarity, while polystyrene offers superior transparency and a glass-like finish, making it ideal for applications requiring clear visibility. The molecular structure of polystyrene allows for less light scattering, resulting in higher optical clarity compared to the more opaque and waxy texture of polyethylene. This distinction in transparency and appearance significantly influences their use in packaging, consumer goods, and display cases.
Thermal Resistance and Temperature Limits
Polyethylene offers moderate thermal resistance with a melting point around 115-135degC, making it suitable for applications requiring flexibility under moderate heat. Polystyrene has a lower thermal resistance, with a heat distortion temperature near 95degC, which limits its use in high-temperature environments. The temperature limits of polyethylene provide greater durability for heat exposure compared to polystyrene's more brittle nature under thermal stress.
Common Applications in Industry
Polyethylene is widely used in packaging materials, plastic bags, containers, and piping due to its flexibility and chemical resistance. Polystyrene finds common applications in insulation, disposable cutlery, and packaging foam because of its rigidity and thermal insulation properties. Industries select polyethylene for durability in flexible products and polystyrene for lightweight, structurally stable items requiring insulation.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Polyethylene exhibits higher recyclability rates compared to polystyrene, as it is widely accepted by recycling programs due to its simpler polymer structure and lower contamination risk. Polystyrene poses significant environmental challenges because it degrades slowly, occupies considerable landfill space, and often ends up as marine pollutant due to its lightweight and brittle nature. The environmental impact of polyethylene is comparatively lower, with emerging bioplastic alternatives and improved recycling technologies further reducing its ecological footprint.
Cost and Availability Factors
Polyethylene is widely available and generally less expensive than polystyrene, making it a cost-effective choice for mass production in packaging and plastic products. Polystyrene, while offering better rigidity and insulation properties, tends to be pricier and less accessible due to more complex manufacturing processes and higher material costs. Market demand and regional production capacities further influence the cost and availability differences between these two polymers.
Safety and Health Considerations
Polyethylene (PE) is considered safer for food packaging and household products due to its chemical inertness and low toxicity, making it less likely to leach harmful substances. Polystyrene (PS), particularly in foam form, can release styrene monomers, suspected carcinogens that pose potential health risks with prolonged exposure or improper use. Handling and disposal guidelines emphasize minimizing PS exposure to reduce inhalation and ingestion hazards, while PE's more stable structure presents fewer health concerns.
Choosing Between Polyethylene and Polystyrene
Choosing between polyethylene and polystyrene depends on application requirements such as flexibility, durability, and thermal resistance. Polyethylene offers high impact resistance and excellent chemical stability, making it ideal for packaging, containers, and plastic bags. Polystyrene provides superior rigidity and insulation properties, commonly used in disposable cups, insulation panels, and food packaging.
Polyethylene vs Polystyrene Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com