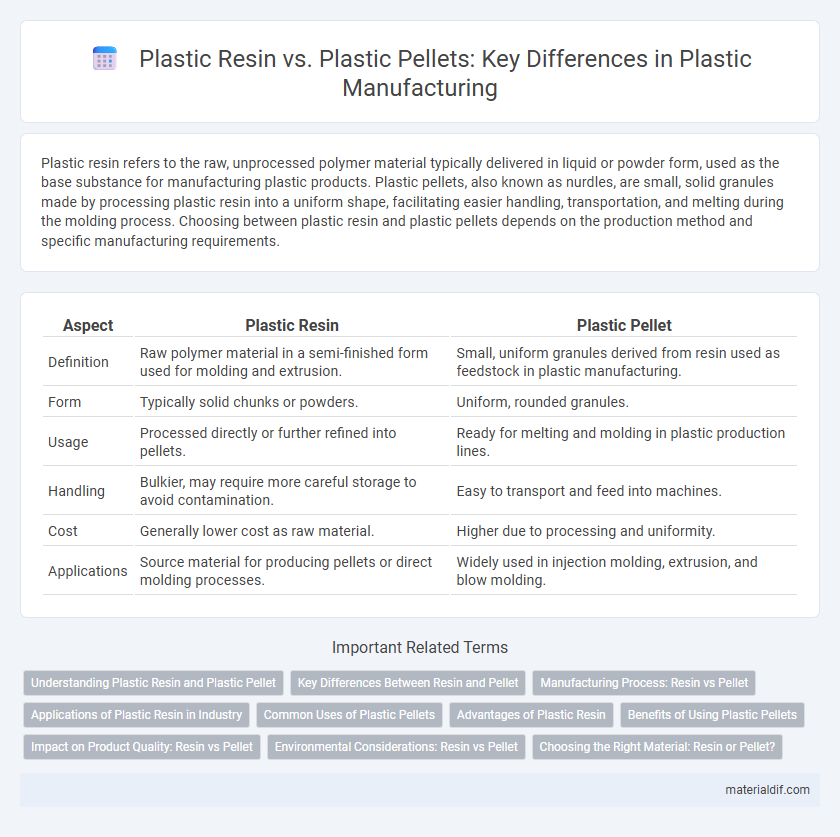
Plastic resin refers to the raw, unprocessed polymer material typically delivered in liquid or powder form, used as the base substance for manufacturing plastic products. Plastic pellets, also known as nurdles, are small, solid granules made by processing plastic resin into a uniform shape, facilitating easier handling, transportation, and melting during the molding process. Choosing between plastic resin and plastic pellets depends on the production method and specific manufacturing requirements.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Plastic Resin | Plastic Pellet |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Raw polymer material in a semi-finished form used for molding and extrusion. | Small, uniform granules derived from resin used as feedstock in plastic manufacturing. |
| Form | Typically solid chunks or powders. | Uniform, rounded granules. |
| Usage | Processed directly or further refined into pellets. | Ready for melting and molding in plastic production lines. |
| Handling | Bulkier, may require more careful storage to avoid contamination. | Easy to transport and feed into machines. |
| Cost | Generally lower cost as raw material. | Higher due to processing and uniformity. |
| Applications | Source material for producing pellets or direct molding processes. | Widely used in injection molding, extrusion, and blow molding. |
Understanding Plastic Resin and Plastic Pellet
Plastic resin refers to the raw polymer material in its pure, granular form, typically used as the primary input in manufacturing processes. Plastic pellets are small, uniformly sized granules derived from plastic resin, designed for ease of handling, melting, and molding during production. Understanding the distinction between plastic resin and pellets is crucial for optimizing processing efficiency and ensuring consistent product quality in plastic fabrication.
Key Differences Between Resin and Pellet
Plastic resin refers to the raw, unprocessed polymer material typically supplied in powder or granule form, serving as the base for manufacturing various plastic products. Plastic pellets are small, uniformly shaped granules produced by processing resin into a standardized size for easier handling, melting, and molding in manufacturing processes. The key difference lies in resin being the initial polymer substance, while pellets represent a processed, ready-to-use intermediate form optimized for consistent feeding in plastic production equipment.
Manufacturing Process: Resin vs Pellet
Plastic resin is the initial, raw form of polymer produced directly from the polymerization process, typically in liquid or powder form, which requires further processing to transform into usable plastic products. Plastic pellets, on the other hand, are small, cylindrical granules created by melting and cooling resin, serving as a standardized intermediate material that improves handling, transportation, and feeding into manufacturing equipment such as injection molding or extrusion machines. The manufacturing process from resin to pellet involves extrusion, where the molten polymer is shaped into strands and then cut into uniform pellets, optimizing consistency and quality for downstream plastic fabrication.
Applications of Plastic Resin in Industry
Plastic resin serves as the primary raw material in manufacturing processes such as injection molding, extrusion, and blow molding, enabling the production of diverse industrial components like automotive parts, packaging materials, and consumer goods. Its versatility and customizable properties allow for applications in sectors including electronics, medical devices, and construction. Plastic pellets, by contrast, are the processed form of resin, prepared for ease of handling and feeding into molding machines, emphasizing the foundational role of plastic resin in industrial manufacturing workflows.
Common Uses of Plastic Pellets
Plastic pellets serve as the primary raw material in manufacturing processes such as injection molding, extrusion, and blow molding, enabling the creation of a wide range of products from packaging films to automotive parts. These small, uniform granules offer consistent melting properties that ensure precision and efficiency in producing consumer goods, electronics casings, and medical devices. Their versatility and ease of handling make plastic pellets essential for standardizing production across industries utilizing plastic resin.
Advantages of Plastic Resin
Plastic resin offers superior purity and consistency compared to plastic pellets, making it ideal for high-precision manufacturing processes. Its molecular structure ensures enhanced mechanical properties and improved chemical resistance, which results in stronger, more durable end products. Additionally, plastic resin facilitates easier customization in terms of color and additives, optimizing performance for specific applications.
Benefits of Using Plastic Pellets
Plastic pellets offer enhanced consistency and ease of handling compared to plastic resin, resulting in more uniform melting and molding processes. Their small, granular form improves feeding accuracy in extrusion and injection molding machines, reducing manufacturing waste and improving efficiency. Utilizing plastic pellets also facilitates better blending with additives and colorants, optimizing the final product's physical properties and appearance.
Impact on Product Quality: Resin vs Pellet
Plastic resin offers superior consistency in molecular structure, resulting in enhanced product strength and uniformity compared to plastic pellets, which may contain varying sizes and impurities affecting the final product's integrity. Resin's controlled formulation reduces the risk of defects such as warping and brittleness, while pellets require additional processing steps that can introduce variability in melt quality. Choosing resin over pellets directly impacts the durability, surface finish, and dimensional accuracy of plastic products, making resin ideal for high-performance applications demanding strict quality standards.
Environmental Considerations: Resin vs Pellet
Plastic resin, typically in liquid or powder form, offers faster processing times but requires careful handling to minimize spills and airborne particulate pollution. Plastic pellets, solid granules used as raw material for molding, pose significant environmental risks due to their potential to become microplastic pollutants in marine ecosystems if spilled during transport or manufacturing. Both forms demand stringent environmental management practices to reduce waste, prevent contamination, and support sustainability efforts in plastic production.
Choosing the Right Material: Resin or Pellet?
Plastic resin offers a purer form of polymer ideal for precise molding and high-quality end products, while plastic pellets provide ease of handling and consistent melting rates for efficient manufacturing. Selecting between resin and pellets depends on the specific production requirements, including processing methods such as injection molding or extrusion. Understanding the differences in form, processing behavior, and application compatibility ensures optimal material choice for durability, cost-efficiency, and product performance.
Plastic Resin vs Plastic Pellet Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com