ABS offers superior impact resistance and rigidity compared to polypropylene, making it ideal for applications requiring durability and structural strength. Polypropylene excels in chemical resistance and flexibility, providing lightweight solutions suitable for packaging and automotive parts. Choosing between ABS and polypropylene depends on the specific requirements for toughness, flexibility, and environmental exposure.
Table of Comparison
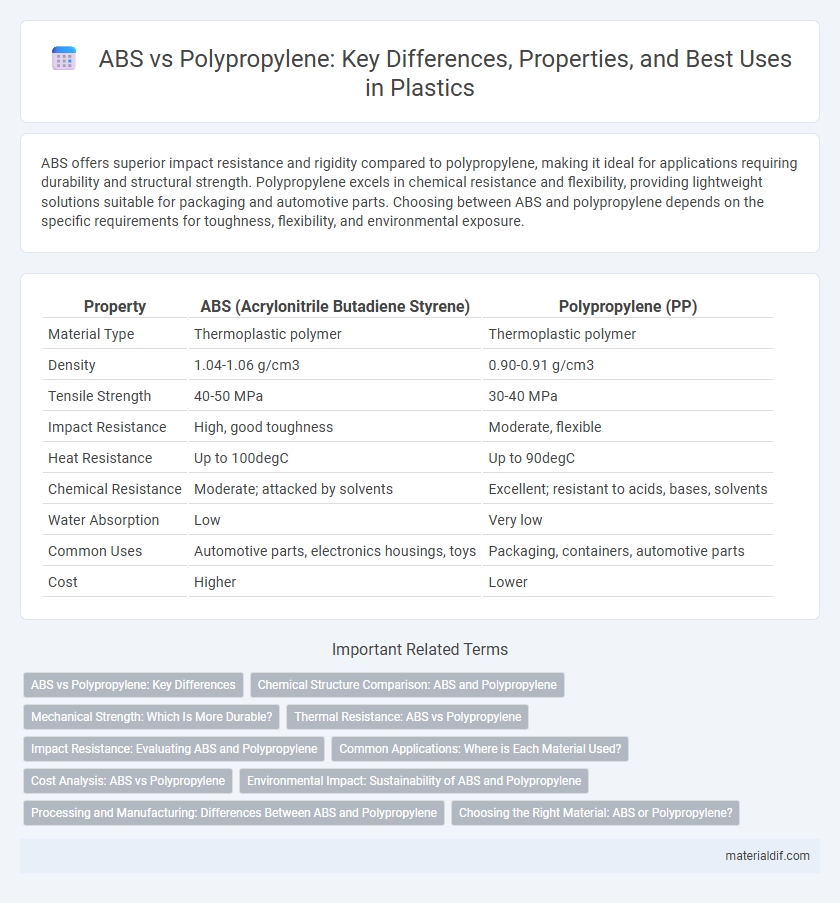
| Property | ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene) | Polypropylene (PP) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic polymer | Thermoplastic polymer |
| Density | 1.04-1.06 g/cm3 | 0.90-0.91 g/cm3 |
| Tensile Strength | 40-50 MPa | 30-40 MPa |
| Impact Resistance | High, good toughness | Moderate, flexible |
| Heat Resistance | Up to 100degC | Up to 90degC |
| Chemical Resistance | Moderate; attacked by solvents | Excellent; resistant to acids, bases, solvents |
| Water Absorption | Low | Very low |
| Common Uses | Automotive parts, electronics housings, toys | Packaging, containers, automotive parts |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
ABS vs Polypropylene: Key Differences
ABS offers superior impact resistance and rigidity compared to polypropylene, making it ideal for applications requiring durability and strength. Polypropylene excels in chemical resistance and flexibility, often preferred for packaging, automotive components, and consumer goods where lightweight and moisture resistance are critical. The choice between ABS and polypropylene depends on specific requirements such as mechanical performance, thermal stability, and environmental exposure.
Chemical Structure Comparison: ABS and Polypropylene
ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene) is a terpolymer composed of acrylonitrile, butadiene, and styrene, combining rigidity, impact resistance, and chemical stability due to its distinct phases of rubbery butadiene and rigid styrene-acrylonitrile copolymer. Polypropylene is a semi-crystalline polyolefin made from propylene monomers, characterized by a simple hydrocarbon chain with methyl groups, providing balance between toughness, flexibility, and chemical resistance. The chemical structure of ABS includes polar nitrile groups enhancing adhesion and solvent resistance, while polypropylene's nonpolar, saturated hydrocarbon backbone offers superior resistance to acids and bases but lower UV stability.
Mechanical Strength: Which Is More Durable?
ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene) offers superior mechanical strength compared to polypropylene, with higher impact resistance and rigidity that make it suitable for demanding applications like automotive parts and protective gear. Polypropylene, while more flexible and resistant to fatigue, generally exhibits lower tensile strength and is better suited for less mechanically stressed uses such as packaging and consumer goods. The superior durability of ABS under mechanical stress results from its sturdy molecular structure combining rigidity and toughness.
Thermal Resistance: ABS vs Polypropylene
ABS offers higher thermal resistance with a heat deflection temperature around 100degC, making it suitable for applications requiring durability under moderate heat. Polypropylene has a lower thermal resistance, typically deforming above 80degC, which limits its use in high-temperature environments. The choice between ABS and polypropylene depends significantly on the specific thermal demands of the intended application.
Impact Resistance: Evaluating ABS and Polypropylene
ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene) offers superior impact resistance compared to polypropylene, making it ideal for applications requiring durability under stress. Polypropylene exhibits good impact resistance but tends to become brittle at lower temperatures, limiting its performance in cold environments. The rubber component in ABS absorbs shocks effectively, enhancing its toughness in demanding structural uses.
Common Applications: Where is Each Material Used?
ABS is commonly used in automotive components, electronic housings, and consumer goods like LEGO bricks due to its strength, rigidity, and excellent impact resistance. Polypropylene is widely utilized in packaging, automotive parts, and household containers because of its chemical resistance, flexibility, and fatigue resistance. Both materials serve diverse industries, with ABS favored for structural applications and polypropylene preferred for flexible, lightweight products.
Cost Analysis: ABS vs Polypropylene
ABS typically costs more than polypropylene due to its higher impact resistance and superior aesthetic qualities, making it a preferred choice for applications requiring durability and a polished finish. Polypropylene offers a lower material cost and excellent chemical resistance, providing an economical option for large-scale manufacturing where cost efficiency is critical. Manufacturing expenses for ABS are generally higher due to its processing temperatures and tooling requirements, whereas polypropylene's lower melting point contributes to reduced energy consumption and faster cycle times.
Environmental Impact: Sustainability of ABS and Polypropylene
Polypropylene demonstrates superior environmental sustainability compared to ABS due to its higher recyclability rate and lower carbon footprint during production. ABS plastic, derived from petroleum-based sources, contributes more significantly to environmental pollution and challenges in biodegradability. Polypropylene's versatility in recycling processes significantly reduces landfill waste and supports circular economy initiatives.
Processing and Manufacturing: Differences Between ABS and Polypropylene
ABS offers excellent dimensional stability and impact resistance, making it ideal for injection molding processes that demand precision and durability. Polypropylene is favored for its chemical resistance and ease of processing, allowing for faster cycle times in extrusion and thermoforming applications. The choice between ABS and polypropylene hinges on specific manufacturing requirements, with ABS suited for complex, high-strength parts and polypropylene preferred for flexible, cost-effective production.
Choosing the Right Material: ABS or Polypropylene?
ABS offers high impact resistance, rigidity, and excellent surface finish, making it ideal for automotive parts, consumer electronics, and appliances. Polypropylene provides superior chemical resistance, flexibility, and fatigue endurance, suitable for packaging, automotive components, and medical devices. Selecting ABS or Polypropylene depends on specific application requirements such as mechanical strength, environmental exposure, and cost-effectiveness.
ABS vs Polypropylene Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com