Thermoplastic elastomers (TPE) and thermoplastic polyurethanes (TPU) both offer flexibility and durability but differ in their mechanical properties and applications. TPE is generally softer, more cost-effective, and easier to process, making it ideal for consumer goods and flexible seals. TPU provides superior abrasion resistance, tensile strength, and chemical resistance, making it suitable for demanding industrial uses like automotive parts and protective covers.
Table of Comparison
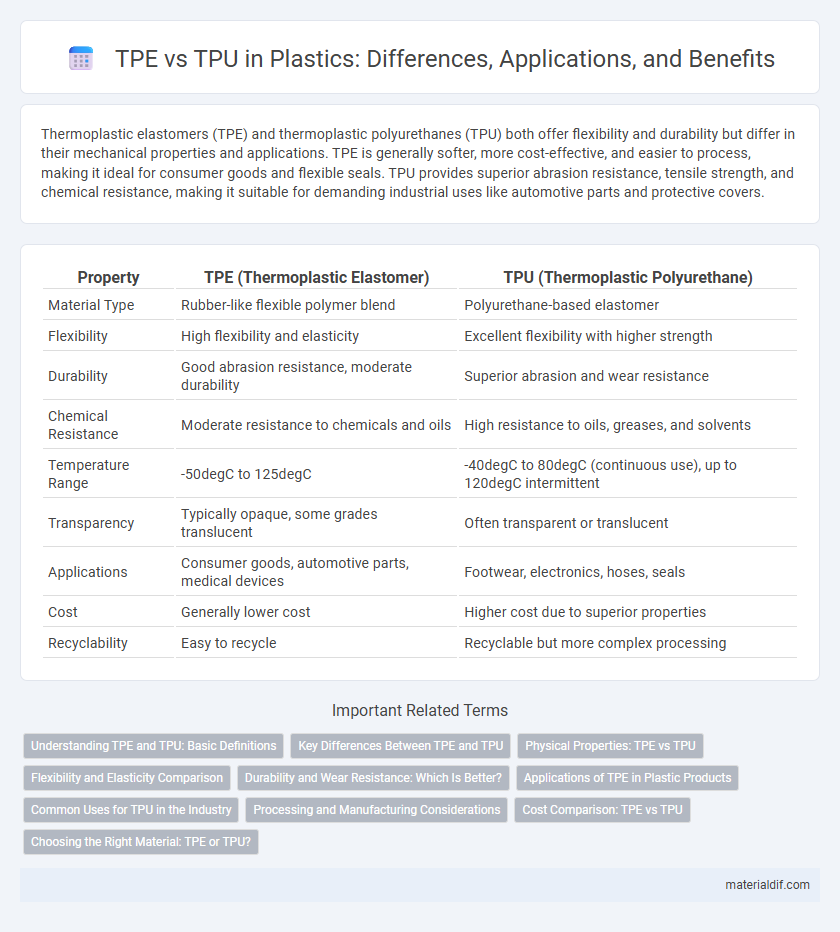
| Property | TPE (Thermoplastic Elastomer) | TPU (Thermoplastic Polyurethane) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Rubber-like flexible polymer blend | Polyurethane-based elastomer |
| Flexibility | High flexibility and elasticity | Excellent flexibility with higher strength |
| Durability | Good abrasion resistance, moderate durability | Superior abrasion and wear resistance |
| Chemical Resistance | Moderate resistance to chemicals and oils | High resistance to oils, greases, and solvents |
| Temperature Range | -50degC to 125degC | -40degC to 80degC (continuous use), up to 120degC intermittent |
| Transparency | Typically opaque, some grades translucent | Often transparent or translucent |
| Applications | Consumer goods, automotive parts, medical devices | Footwear, electronics, hoses, seals |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Higher cost due to superior properties |
| Recyclability | Easy to recycle | Recyclable but more complex processing |
Understanding TPE and TPU: Basic Definitions
Thermoplastic elastomers (TPE) combine the elastic properties of rubber with the processing ease of plastics, characterized by their ability to be melted and reshaped multiple times. Thermoplastic polyurethanes (TPU) represent a specific class of TPE known for superior abrasion resistance, flexibility, and chemical stability, making them ideal for demanding applications. Understanding the molecular structure differences, with TPEs generally encompassing various block copolymers and TPUs specifically based on urethane linkages, is essential for selecting the right material in product design.
Key Differences Between TPE and TPU
Thermoplastic elastomers (TPE) offer superior flexibility and easier processability, making them ideal for applications requiring soft touch and elasticity, whereas thermoplastic polyurethanes (TPU) provide higher abrasion resistance, tensile strength, and durability suitable for heavy-duty and high-performance environments. TPE materials typically have a lower melting point, enabling faster cycle times in injection molding, while TPU maintains mechanical properties at a broader range of temperatures and exhibits excellent resistance to oils and chemicals. The key differences between TPE and TPU lie in their molecular structure, with TPE being a blend of rubber and plastic phases, and TPU being a copolymer with hard and soft segments, impacting their performance characteristics and application suitability.
Physical Properties: TPE vs TPU
TPE (Thermoplastic Elastomers) and TPU (Thermoplastic Polyurethanes) display distinct physical properties, with TPU offering superior abrasion resistance, higher tensile strength, and better elasticity compared to TPE. TPE generally provides greater flexibility and softer textures, making it ideal for applications requiring more cushioning and comfort. TPU's enhanced durability and chemical resistance suit demanding environments, while TPE excels in lightweight and flexible uses.
Flexibility and Elasticity Comparison
Thermoplastic elastomers (TPE) exhibit superior flexibility due to their softer polymer chains, allowing greater elongation and bending without permanent deformation. Thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU) offers higher elasticity, enabling it to return to its original shape quickly after stretching, thanks to its segmented block copolymer structure. While TPE excels in softness and flexibility for applications like soft-touch coatings, TPU is preferred in uses demanding durability, abrasion resistance, and rapid elastic recovery.
Durability and Wear Resistance: Which Is Better?
Thermoplastic Polyurethane (TPU) exhibits superior durability and wear resistance compared to Thermoplastic Elastomers (TPE), making it ideal for applications involving high abrasion and mechanical stress. TPU maintains excellent resistance to oils, chemicals, and environmental factors, leading to a longer lifespan in demanding conditions. TPE offers flexibility and softer textures but generally falls short of TPU's robust performance in heavy-duty wear scenarios.
Applications of TPE in Plastic Products
Thermoplastic elastomers (TPE) are widely used in automotive parts, medical devices, and consumer goods due to their flexibility, durability, and ease of processing. Unlike thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU), TPE offers superior elasticity and softer touch, making it ideal for seals, gaskets, and grips. Its recyclability and ability to be colored enhance design versatility in various plastic product applications.
Common Uses for TPU in the Industry
Thermoplastic Polyurethane (TPU) is widely used in industries for its exceptional abrasion resistance, flexibility, and durability. Common applications include automotive parts, footwear, medical devices, and electronic cases, where impact resistance and elasticity are critical. TPU's versatility also extends to industrial hoses, films, and flexible tubing due to its superior chemical and wear resistance compared to other thermoplastic elastomers.
Processing and Manufacturing Considerations
TPE offers ease of processing with lower melting points, enabling faster cycle times and energy efficiency in injection molding, while TPU requires precise temperature control due to its higher melting range to prevent degradation. TPU provides superior mechanical properties and durability but demands more complex processing equipment and longer mold cooling times. Manufacturers must weigh TPE's cost-effective and flexible processing advantages against TPU's performance benefits in applications requiring abrasion resistance and elasticity.
Cost Comparison: TPE vs TPU
TPE (Thermoplastic Elastomers) generally offers a lower cost compared to TPU (Thermoplastic Polyurethane) due to simpler manufacturing processes and raw material composition. TPU provides higher durability and chemical resistance but comes at an increased price point, making it more suitable for applications requiring enhanced performance. For budget-sensitive projects, TPE is the preferred option, while TPU is favored where longevity and toughness justify the additional expense.
Choosing the Right Material: TPE or TPU?
Thermoplastic elastomers (TPE) offer flexibility, excellent weather resistance, and ease of processing, making them ideal for consumer goods and soft-touch applications. Thermoplastic polyurethanes (TPU) provide superior abrasion resistance, high tensile strength, and chemical resistance, which suits industrial parts, automotive components, and protective gear. Selecting between TPE and TPU depends on application requirements for durability, elasticity, and environmental exposure.
TPE vs TPU Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com