Plastic welding creates a strong, permanent join by melting and fusing the plastic materials together, ensuring high durability and structural integrity. Plastic bonding relies on adhesives to chemically bond surfaces, which may be easier to apply but can result in weaker joints prone to failure under stress. Choosing between plastic welding and bonding depends on the required strength, application environment, and material compatibility.
Table of Comparison
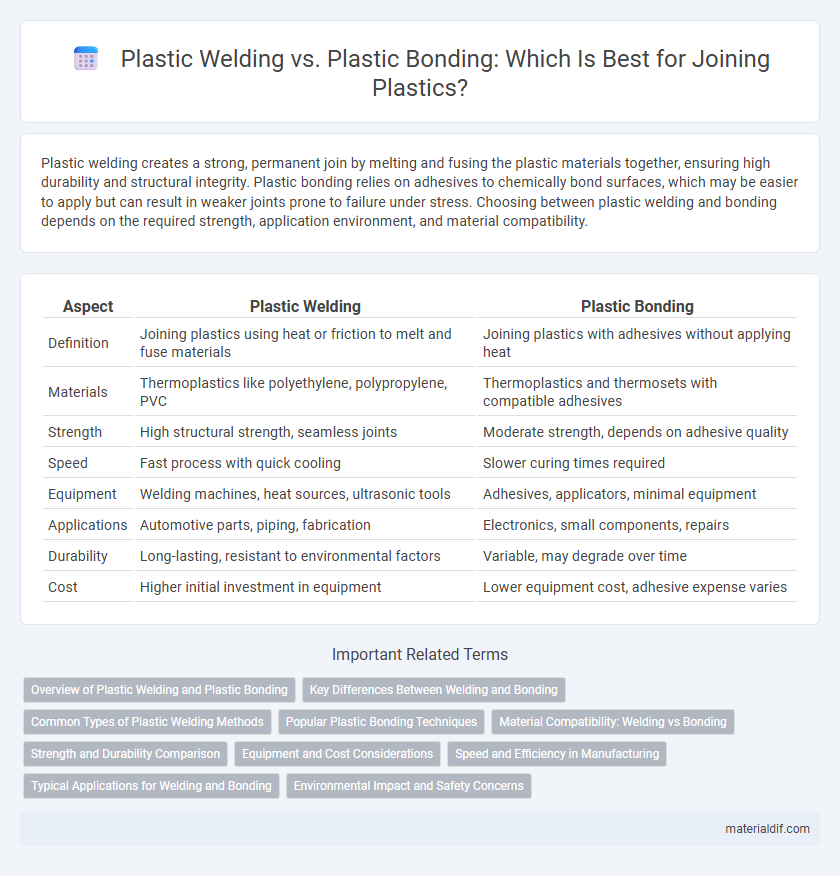
| Aspect | Plastic Welding | Plastic Bonding |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Joining plastics using heat or friction to melt and fuse materials | Joining plastics with adhesives without applying heat |
| Materials | Thermoplastics like polyethylene, polypropylene, PVC | Thermoplastics and thermosets with compatible adhesives |
| Strength | High structural strength, seamless joints | Moderate strength, depends on adhesive quality |
| Speed | Fast process with quick cooling | Slower curing times required |
| Equipment | Welding machines, heat sources, ultrasonic tools | Adhesives, applicators, minimal equipment |
| Applications | Automotive parts, piping, fabrication | Electronics, small components, repairs |
| Durability | Long-lasting, resistant to environmental factors | Variable, may degrade over time |
| Cost | Higher initial investment in equipment | Lower equipment cost, adhesive expense varies |
Overview of Plastic Welding and Plastic Bonding
Plastic welding involves the use of heat or pressure to fuse plastic components, creating a strong, permanent joint by melting the materials at the interface. Plastic bonding, on the other hand, relies on adhesives to chemically or physically adhere surfaces, often providing flexibility in material selection but potentially less mechanical strength. Both methods are essential in manufacturing and repair processes, with plastic welding preferred for high-strength applications and plastic bonding favored for complex or dissimilar material assemblies.
Key Differences Between Welding and Bonding
Plastic welding creates a permanent joint by melting and fusing materials together using heat, resulting in high strength and durability ideal for load-bearing applications. Plastic bonding relies on adhesives to join surfaces without melting, offering flexibility in material combinations but generally lower mechanical strength. Welding suits thermoplastics with thermal compatibility, while bonding applies broadly to various plastics and is preferred for delicate or dissimilar materials.
Common Types of Plastic Welding Methods
Common types of plastic welding methods include ultrasonic welding, which uses high-frequency vibrations to join thermoplastics; hot plate welding, where heated plates soften plastic surfaces before pressing them together; and laser welding, employing focused laser beams to create strong, precise joints. These methods are preferred for their strong bond strength, speed, and suitability for various plastic materials such as polyethylene, polypropylene, and PVC. Each technique offers specific advantages depending on the application, plastic type, and desired joint characteristics.
Popular Plastic Bonding Techniques
Popular plastic bonding techniques include solvent bonding, which chemically softens surfaces for a strong join, and adhesive bonding using epoxies or cyanoacrylates tailored for specific plastic types like ABS or PVC. Ultrasonic welding and hot plate welding provide precise, heat-based alternatives but fall under welding rather than bonding methods. Selecting the optimal technique depends on plastic compatibility, required joint strength, and application environment.
Material Compatibility: Welding vs Bonding
Plastic welding offers superior material compatibility for thermoplastics by melting and fusing similar polymers, creating a strong, homogeneous joint ideal for load-bearing applications. Plastic bonding relies on adhesives that can accommodate a broader range of materials, including dissimilar plastics and composites, but may face limitations with certain low-energy surfaces. Selecting welding or bonding hinges on the specific polymers involved, surface energy, and the mechanical demands of the application.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Plastic welding creates a stronger and more durable joint by melting and fusing the base materials together, resulting in a seamless bond that withstands high stress and environmental exposure. Plastic bonding relies on adhesives, which may degrade over time under heat, chemicals, or mechanical loads, typically producing weaker bonds compared to welded joints. For applications requiring maximum strength and long-term durability, plastic welding is generally preferred over plastic bonding.
Equipment and Cost Considerations
Plastic welding utilizes specialized equipment such as ultrasonic welders, hot plate welders, and laser welders, often requiring higher initial investment but delivering strong, permanent joints suitable for industrial applications. Plastic bonding involves adhesives and primers, typically demanding less expensive equipment but incurring ongoing costs for consumables and longer curing times. Cost considerations should balance upfront equipment expenses against long-term material costs and production speed to determine the most effective joining method for specific plastic fabrication needs.
Speed and Efficiency in Manufacturing
Plastic welding offers superior speed and efficiency in manufacturing by creating strong, seamless joints through heat and pressure, significantly reducing assembly time compared to plastic bonding. Plastic bonding relies on adhesives, which require longer curing times and may involve surface preparation to achieve optimal strength. Industries prioritize plastic welding for high-volume production due to its rapid processing and enhanced durability of welded components.
Typical Applications for Welding and Bonding
Plastic welding is commonly used in automotive manufacturing, medical device assembly, and packaging industries where strong, durable joints are essential. Plastic bonding suits applications in electronics, consumer goods, and decorative items where precision and surface finish are critical. Welding provides high-strength, structural connections, while bonding excels in joining dissimilar plastics and delicate components.
Environmental Impact and Safety Concerns
Plastic welding creates strong joints by melting substrates, reducing the need for adhesives that may contain harmful solvents, thus minimizing VOC emissions and environmental toxicity. Plastic bonding relies on chemical adhesives that often include volatile organic compounds, posing greater health risks and environmental pollution potential during application and disposal. Safety concerns favor plastic welding for reducing exposure to hazardous fumes and offering more durable, recyclable bonds critical for sustainable plastic manufacturing.
Plastic Welding vs Plastic Bonding Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com