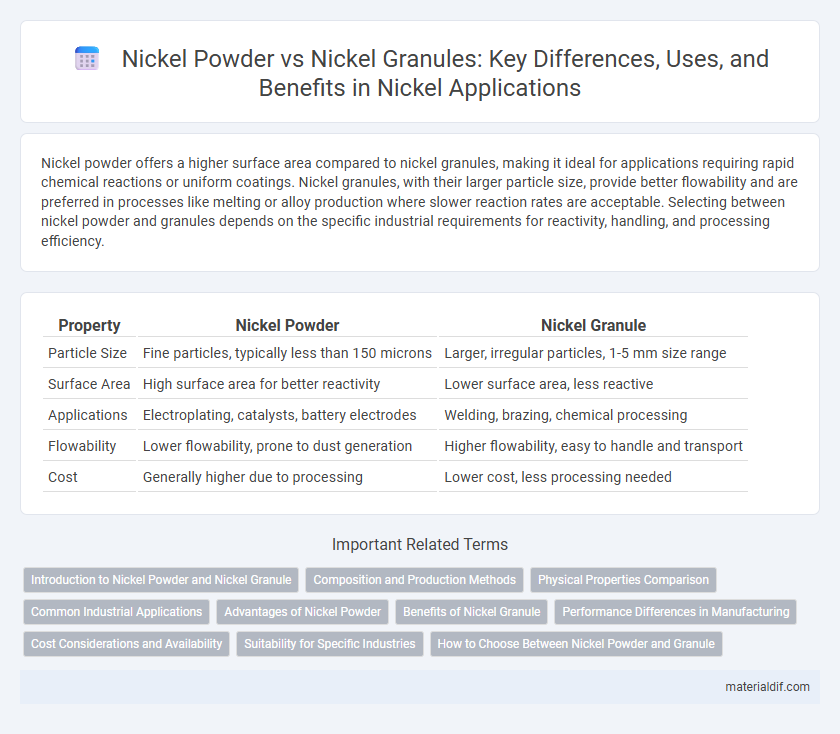
Nickel powder offers a higher surface area compared to nickel granules, making it ideal for applications requiring rapid chemical reactions or uniform coatings. Nickel granules, with their larger particle size, provide better flowability and are preferred in processes like melting or alloy production where slower reaction rates are acceptable. Selecting between nickel powder and granules depends on the specific industrial requirements for reactivity, handling, and processing efficiency.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Nickel Powder | Nickel Granule |
|---|---|---|
| Particle Size | Fine particles, typically less than 150 microns | Larger, irregular particles, 1-5 mm size range |
| Surface Area | High surface area for better reactivity | Lower surface area, less reactive |
| Applications | Electroplating, catalysts, battery electrodes | Welding, brazing, chemical processing |
| Flowability | Lower flowability, prone to dust generation | Higher flowability, easy to handle and transport |
| Cost | Generally higher due to processing | Lower cost, less processing needed |
Introduction to Nickel Powder and Nickel Granule
Nickel powder consists of fine particles typically below 150 microns, offering high surface area and reactivity, ideal for applications like catalysis, battery electrodes, and metal additive manufacturing. Nickel granules are larger, irregularly shaped particles providing better flow characteristics, commonly used in metallurgical processes, alloy production, and chemical manufacturing. The choice between nickel powder and granules depends on the desired surface area, reactivity, and processing requirements.
Composition and Production Methods
Nickel powder consists of fine particles produced primarily through atomization or chemical reduction processes, ensuring high surface area and uniform composition mainly of pure nickel or nickel alloys. Nickel granules are larger, irregularly shaped particles typically created by granulation or crushing methods, exhibiting slightly varied composition due to surface oxidation. Both forms maintain a base of high-purity nickel but differ significantly in particle size, morphology, and production techniques, influencing their suitability for applications like catalysts, batteries, or metallic coatings.
Physical Properties Comparison
Nickel powder exhibits a higher surface area and finer particle size compared to nickel granules, resulting in greater reactivity and improved sintering properties for catalytic and battery applications. Nickel granules possess coarser particles, enhancing flowability and ease of handling in metallurgical and chemical processes. Both forms share high melting points around 1455degC and excellent corrosion resistance, but their distinct morphologies influence their specific physical performance in industrial uses.
Common Industrial Applications
Nickel powder is extensively used in battery electrodes, catalysts, and conductive coatings due to its high surface area and reactivity, making it ideal for energy storage and chemical processes. Nickel granules find common application in metallurgical processes, alloy production, and chemical manufacturing where controlled melting and consistent particle size enable uniform alloy composition and enhanced process efficiency. Both forms are crucial in stainless steel production and electroplating industries, with the choice depending on the specific industrial requirements for particle morphology and surface characteristics.
Advantages of Nickel Powder
Nickel powder offers a higher surface area compared to nickel granules, enabling faster chemical reactions and improved catalytic performance in industrial applications. Its fine particle size allows for uniform mixing and enhanced sintering in metal injection molding and battery production. The increased reactivity and consistent particle distribution of nickel powder provide superior efficiency in coatings and electroplating processes.
Benefits of Nickel Granule
Nickel granules offer enhanced surface area and improved flowability compared to nickel powder, making them ideal for consistent melting and alloy production. Their larger particle size reduces oxidation risks during high-temperature processes, ensuring higher purity and better mechanical properties in end products. The granule form also minimizes dust generation, enhancing safety and cleanliness in industrial handling environments.
Performance Differences in Manufacturing
Nickel powder offers a finer particle size and higher surface area compared to nickel granules, resulting in improved homogeneity and reactivity during manufacturing processes like electroplating and alloy production. The superior flowability and packing density of nickel powder enhance sintering performance, leading to denser and stronger final products. In contrast, nickel granules, with their larger particle size, provide slower reaction rates and are better suited for applications requiring lower surface energy and reduced oxidation risk.
Cost Considerations and Availability
Nickel powder typically incurs higher costs than nickel granules due to its finer particle size requiring more complex manufacturing processes, which enhance its reactivity and surface area for specialized applications. Nickel granules offer better availability and lower price points, making them more suitable for bulk industrial uses where surface area is less critical. Market demand fluctuations and production methods directly influence the cost and supply consistency of both nickel powder and granules.
Suitability for Specific Industries
Nickel powder offers superior surface area and reactivity, making it highly suitable for industries like electronics, catalysts, and battery manufacturing where fine particle consistency enhances performance. Nickel granules, due to their larger size and ease of handling, are preferred in metallurgy and chemical industries for use as raw material in alloy production and plating processes. The choice between nickel powder and granule depends on specific industry requirements for particle size, reactivity, and processing methods.
How to Choose Between Nickel Powder and Granule
When deciding between nickel powder and nickel granule, consider the specific application requirements such as surface area, particle size, and reactivity; nickel powder offers a greater surface area for faster reactions and better sintering in metallurgical processes. Nickel granules, with their larger particle size, provide easier handling, reduced dust hazards, and are ideal for applications requiring slower dissolution or reduced oxidation rates. Selecting the appropriate form involves balancing processing efficiency, safety, and desired physicochemical characteristics to optimize performance in catalysts, batteries, or plating.
Nickel Powder vs Nickel Granule Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com