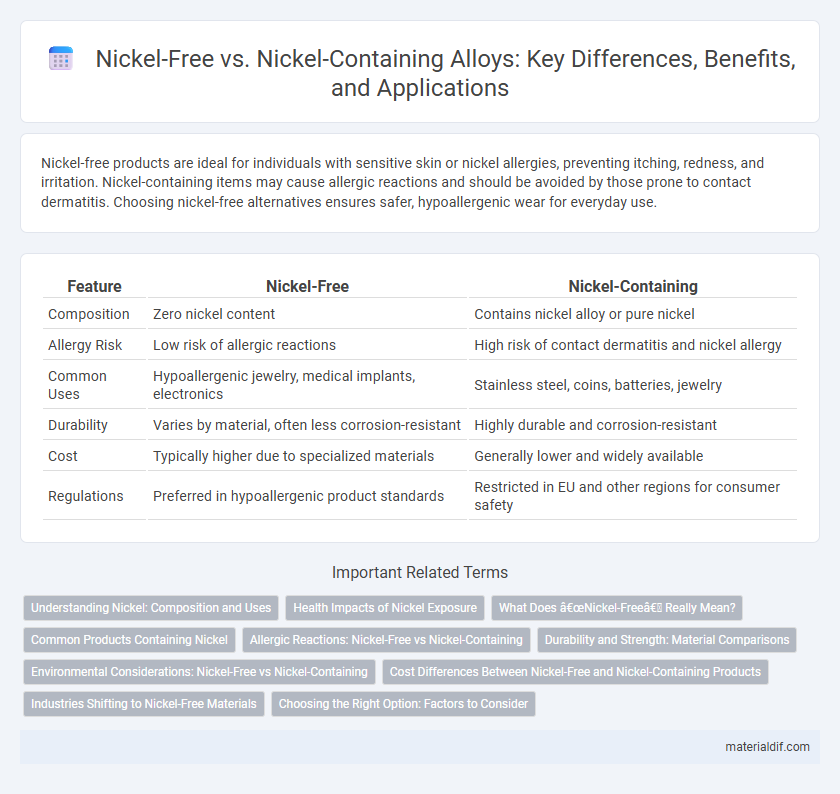
Nickel-free products are ideal for individuals with sensitive skin or nickel allergies, preventing itching, redness, and irritation. Nickel-containing items may cause allergic reactions and should be avoided by those prone to contact dermatitis. Choosing nickel-free alternatives ensures safer, hypoallergenic wear for everyday use.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Nickel-Free | Nickel-Containing |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Zero nickel content | Contains nickel alloy or pure nickel |
| Allergy Risk | Low risk of allergic reactions | High risk of contact dermatitis and nickel allergy |
| Common Uses | Hypoallergenic jewelry, medical implants, electronics | Stainless steel, coins, batteries, jewelry |
| Durability | Varies by material, often less corrosion-resistant | Highly durable and corrosion-resistant |
| Cost | Typically higher due to specialized materials | Generally lower and widely available |
| Regulations | Preferred in hypoallergenic product standards | Restricted in EU and other regions for consumer safety |
Understanding Nickel: Composition and Uses
Nickel-free products eliminate nickel metal to prevent allergic reactions, making them ideal for sensitive skin, whereas nickel-containing items incorporate nickel alloys prized for corrosion resistance and durability. Nickel's composition primarily includes blends with iron, chromium, and copper, enhancing strength and magnetic properties across industries like stainless steel manufacturing and electronics. Understanding the distinction aids consumers in selecting materials based on biocompatibility requirements and functional performance.
Health Impacts of Nickel Exposure
Nickel-free products significantly reduce the risk of allergic contact dermatitis, especially for individuals with nickel sensitivity, which affects approximately 10-20% of the population. Exposure to nickel-containing items can trigger skin irritation, itching, and inflammation due to the metal's potential to release ions that penetrate the skin. Long-term or high-level exposure to nickel compounds is also associated with respiratory problems and has been classified as a carcinogen by the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC).
What Does “Nickel-Free” Really Mean?
"Nickel-free" typically means the item contains less than 0.05% nickel, reducing the risk of allergic reactions for sensitive individuals. Nickel-containing products may release nickel ions through perspiration or friction, provoking skin irritation or dermatitis. Regulatory standards in many countries set strict limits on permissible nickel release to protect consumers with nickel allergies.
Common Products Containing Nickel
Common products containing nickel include jewelry, watches, eyeglass frames, coins, and kitchen utensils, as well as electronic devices like smartphones and laptops. Nickel-free alternatives are prevalent in hypoallergenic jewelry, medical implants, and certain types of stainless steel cookware designed to minimize allergic reactions. Identifying nickel content in everyday items is essential for individuals with nickel allergies to prevent contact dermatitis and related skin irritations.
Allergic Reactions: Nickel-Free vs Nickel-Containing
Nickel-containing products often trigger allergic reactions such as contact dermatitis, characterized by redness, itching, and swelling, due to nickel ions interacting with skin proteins and triggering an immune response. Nickel-free alternatives significantly reduce the risk of hypersensitivity, making them ideal for individuals with nickel allergy, the most common metal allergy worldwide. Choosing nickel-free materials in jewelry and medical devices minimizes exposure to nickel allergens, preventing chronic skin irritation and improving patient outcomes.
Durability and Strength: Material Comparisons
Nickel-containing alloys typically offer superior durability and strength compared to nickel-free alternatives due to their enhanced corrosion resistance and hardness. Nickel-free materials, such as certain stainless steels or titanium alloys, may sacrifice some tensile strength and wear resistance for hypoallergenic properties. Choosing between nickel-containing and nickel-free options depends on balancing the need for mechanical performance against biocompatibility requirements.
Environmental Considerations: Nickel-Free vs Nickel-Containing
Nickel-free products significantly reduce environmental risks by eliminating nickel mining and refining processes that contribute to soil degradation, water pollution, and high energy consumption. Nickel-containing materials require intensive extraction methods that release greenhouse gases and toxic byproducts, impacting ecosystems and human health. Choosing nickel-free options supports sustainable manufacturing practices and lowers the ecological footprint associated with metal production.
Cost Differences Between Nickel-Free and Nickel-Containing Products
Nickel-containing products generally cost less due to the metal's abundant availability and established manufacturing processes, making them a budget-friendly choice for many applications. In contrast, nickel-free products often require alternative materials such as titanium or stainless steel, which can increase production costs and retail prices. This cost difference reflects the premium associated with hypoallergenic materials designed to reduce allergic reactions in sensitive individuals.
Industries Shifting to Nickel-Free Materials
Industries such as electronics, medical devices, and jewelry manufacturing are increasingly shifting to nickel-free materials to address allergy concerns and regulatory restrictions like the EU Nickel Directive. Nickel-free alternatives, including stainless steel alloys and titanium, offer comparable durability and corrosion resistance without causing contact dermatitis. This trend drives innovation in material science, reducing nickel exposure while maintaining product performance in sensitive applications.
Choosing the Right Option: Factors to Consider
Choosing between nickel-free and nickel-containing products depends on individual skin sensitivity and potential allergic reactions, with nickel allergies affecting approximately 10-20% of the population. Nickel-free options are essential for individuals prone to contact dermatitis or eczema, as exposure to nickel ions can trigger inflammation and discomfort. In contrast, nickel-containing items may offer greater durability and cost-effectiveness but pose risks for those with nickel hypersensitivity, making patch testing a critical step in selecting safe materials.
Nickel-Free vs Nickel-Containing Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com