Mylar film offers superior tensile strength, clarity, and moisture barrier properties compared to polyethylene film, making it ideal for applications requiring durability and long-lasting protection. While polyethylene film is more flexible and cost-effective, it lacks the heat resistance and dimensional stability that Mylar provides. Choosing between the two depends on whether strength and clarity or affordability and flexibility are the primary concerns.
Table of Comparison
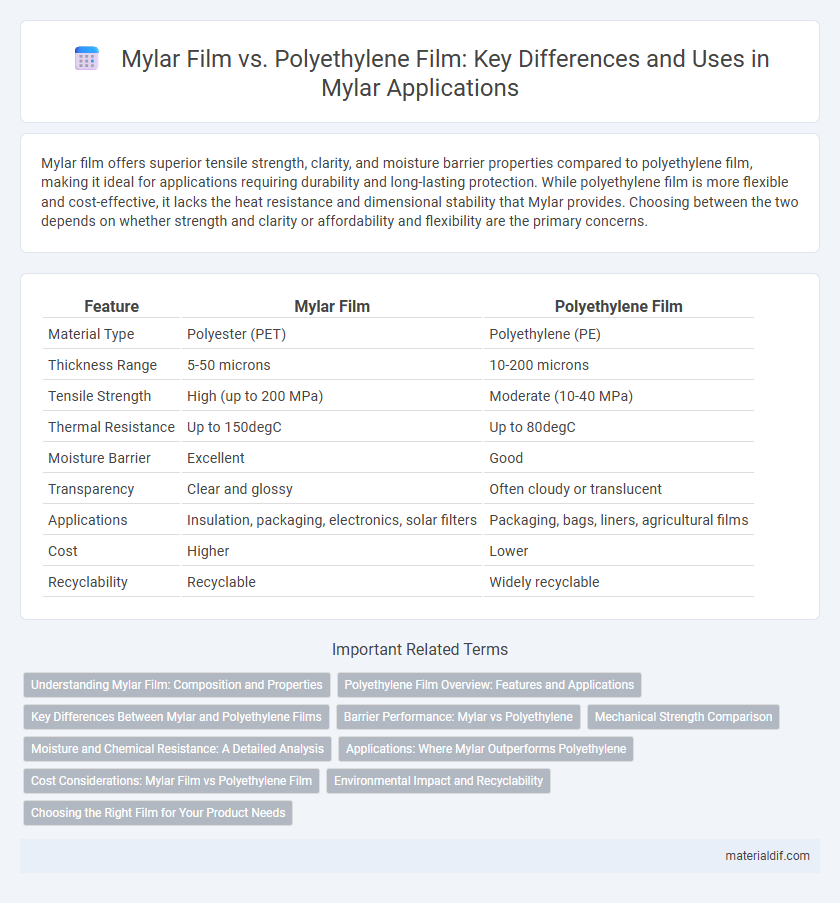
| Feature | Mylar Film | Polyethylene Film |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Polyester (PET) | Polyethylene (PE) |
| Thickness Range | 5-50 microns | 10-200 microns |
| Tensile Strength | High (up to 200 MPa) | Moderate (10-40 MPa) |
| Thermal Resistance | Up to 150degC | Up to 80degC |
| Moisture Barrier | Excellent | Good |
| Transparency | Clear and glossy | Often cloudy or translucent |
| Applications | Insulation, packaging, electronics, solar filters | Packaging, bags, liners, agricultural films |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Recyclability | Recyclable | Widely recyclable |
Understanding Mylar Film: Composition and Properties
Mylar film, composed of stretched polyethylene terephthalate (PET), exhibits superior tensile strength, chemical stability, and dimensional stability compared to polyethylene film, which is made from low-density or high-density polyethylene resins. The biaxial orientation process applied to Mylar enhances its clarity, barrier resistance, and thermal properties, making it ideal for applications requiring durability and resistance to moisture or gases. In contrast, polyethylene films offer flexibility and cost-efficiency but lack the high-temperature resistance and clarity characteristic of Mylar films.
Polyethylene Film Overview: Features and Applications
Polyethylene film is a versatile, lightweight plastic known for its flexibility, chemical resistance, and moisture barrier properties. Commonly used in packaging, agriculture, and construction, it provides effective protection for food products, greenhouse covers, and vapor barriers. Its cost-effectiveness and ease of processing make polyethylene film a preferred choice over Mylar film in applications requiring stretchability and impact resistance.
Key Differences Between Mylar and Polyethylene Films
Mylar film, a polyester resin film known for its exceptional tensile strength, dimensional stability, and high resistance to moisture and chemicals, contrasts with polyethylene film, which offers superior flexibility and cost-effectiveness but lower durability and barrier properties. Mylar's superior clarity and ability to withstand high temperatures make it ideal for applications requiring long-lasting transparency and thermal resistance, whereas polyethylene is commonly used for everyday packaging due to its lightweight and ease of sealing. The key differences lie in their chemical composition, thermal resistance, mechanical strength, and application suitability, with Mylar excelling in industrial, electrical, and insulation uses while polyethylene dominates in basic packaging and protective coverings.
Barrier Performance: Mylar vs Polyethylene
Mylar film offers superior barrier performance compared to polyethylene film, providing excellent resistance to moisture, oxygen, and chemical permeation due to its polyester composition. Its dense molecular structure significantly reduces gas transmission rates, making it ideal for applications requiring long-term preservation and protection. In contrast, polyethylene has higher permeability, which limits its effectiveness in maintaining product integrity against environmental factors.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
Mylar film exhibits superior mechanical strength compared to polyethylene film, with tensile strength typically ranging from 100 to 250 MPa, whereas polyethylene films generally fall between 10 to 30 MPa. The enhanced durability and resistance to tearing make Mylar ideal for applications requiring high-performance materials such as insulation, packaging, and electrical insulation. Polyethylene film's lower strength offers greater flexibility but limits its use in structurally demanding environments.
Moisture and Chemical Resistance: A Detailed Analysis
Mylar film offers superior moisture resistance compared to polyethylene film, with a lower water vapor transmission rate that effectively protects sensitive products from humidity damage. Chemically, Mylar's polyethylene terephthalate (PET) composition provides enhanced resistance to oils, solvents, and acids, making it more durable in harsh environments. In contrast, polyethylene film exhibits limited chemical resistance and higher permeability to moisture, reducing its suitability for applications requiring stringent barrier properties.
Applications: Where Mylar Outperforms Polyethylene
Mylar film excels in applications requiring high tensile strength, superior dimensional stability, and excellent chemical resistance, making it ideal for electrical insulation, packaging sensitive electronics, and reflective surfaces in solar energy equipment. Unlike polyethylene film, Mylar maintains clarity and strength under extreme temperatures, enabling its use in aerospace and medical device sterilization packaging. These attributes ensure Mylar's dominance in precision-demanding industries where polyethylene film's flexibility and lower durability are insufficient.
Cost Considerations: Mylar Film vs Polyethylene Film
Mylar film typically costs more than polyethylene film due to its superior tensile strength, dimensional stability, and heat resistance, making it ideal for high-performance applications. Polyethylene film remains a budget-friendly option for general packaging or low-stress uses where cost-efficiency is prioritized over durability. Evaluating application requirements against material properties helps determine whether the higher initial investment in Mylar translates to long-term cost savings.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Mylar film, made from biaxially-oriented polyethylene terephthalate (BoPET), offers superior recyclability compared to polyethylene film, which is typically sourced from low-density polyethylene (LDPE). Mylar's higher melting point and chemical stability allow for easier processing in recycling facilities, reducing environmental pollution. In contrast, polyethylene films often contribute to landfill accumulation due to limited recycling infrastructure and slower degradation rates in natural environments.
Choosing the Right Film for Your Product Needs
Mylar film, a polyester-based material, offers superior tensile strength, dimensional stability, and excellent barrier properties compared to polyethylene film, making it ideal for applications requiring durability and protection against moisture and gases. Polyethylene film, known for its flexibility and cost-effectiveness, suits packaging needs where lightweight and sealability are prioritized over high strength. Evaluating your product's required barrier performance, mechanical strength, and environmental resistance will guide you to select the appropriate film that balances performance and budget effectively.
Mylar Film vs Polyethylene Film Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com