Seamless tubes offer superior strength and corrosion resistance due to their uniform structure without any welding seams, making them ideal for high-pressure applications. Welded tubes are more cost-effective and available in larger diameters, but their weld joints can be potential points of weakness under stress. Choosing between seamless and welded tubes depends on the specific mechanical requirements and budget constraints of the project.
Table of Comparison
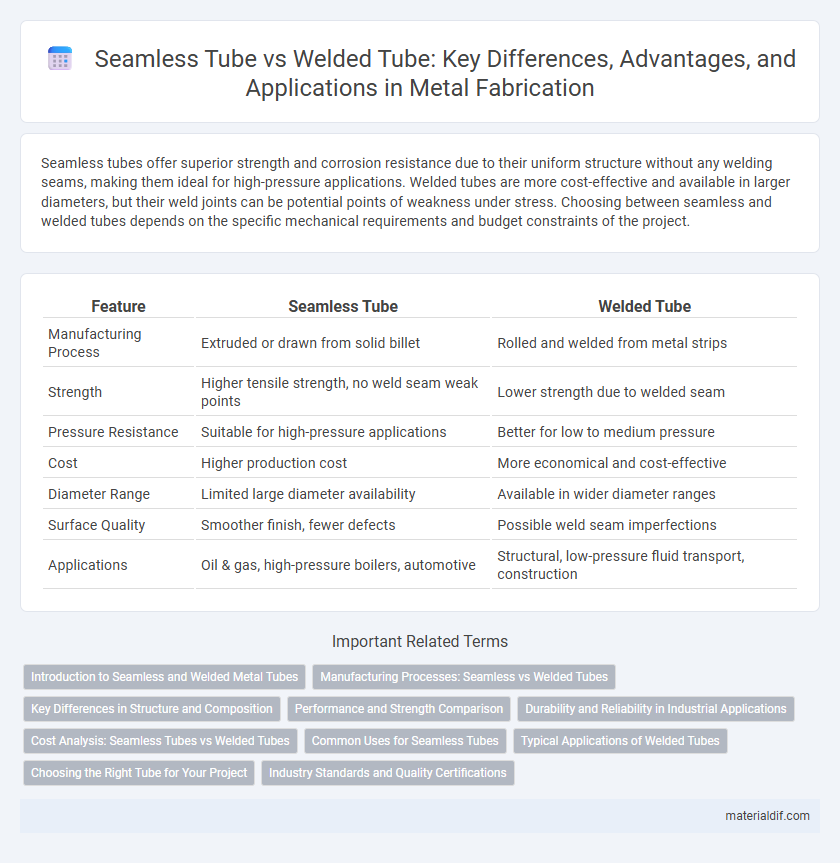
| Feature | Seamless Tube | Welded Tube |
|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing Process | Extruded or drawn from solid billet | Rolled and welded from metal strips |
| Strength | Higher tensile strength, no weld seam weak points | Lower strength due to welded seam |
| Pressure Resistance | Suitable for high-pressure applications | Better for low to medium pressure |
| Cost | Higher production cost | More economical and cost-effective |
| Diameter Range | Limited large diameter availability | Available in wider diameter ranges |
| Surface Quality | Smoother finish, fewer defects | Possible weld seam imperfections |
| Applications | Oil & gas, high-pressure boilers, automotive | Structural, low-pressure fluid transport, construction |
Introduction to Seamless and Welded Metal Tubes
Seamless tubes are manufactured through extrusion or drawing processes that create a uniform, joint-free cylindrical shape, offering superior strength and corrosion resistance for high-pressure applications. Welded tubes are formed by rolling metal sheets or strips and welding the edges, providing cost-effective solutions with customizable dimensions but potentially lower pressure capabilities. Both types serve critical roles in industries such as oil and gas, automotive, and construction, where material integrity and performance requirements dictate tube selection.
Manufacturing Processes: Seamless vs Welded Tubes
Seamless tubes are manufactured using hot extrusion or rotary piercing processes that create a tube without any joints, resulting in a uniform grain structure and higher pressure resistance. Welded tubes are produced by rolling metal strips and then welding the edges together, offering cost-effectiveness and faster production but with potential weld seam weaknesses. The choice between seamless and welded tubes depends on application requirements such as pressure rating, corrosion resistance, and mechanical strength.
Key Differences in Structure and Composition
Seamless tubes are manufactured by extruding a solid billet to create a hollow tube without any joints, resulting in uniform grain structure and higher strength, while welded tubes are made by rolling and welding metal strips, which introduces a welded seam that can affect integrity under high pressure. The composition of seamless tubes typically ensures better corrosion resistance and fatigue endurance due to the absence of weld seams, whereas welded tubes may have variable mechanical properties depending on the welding process and heat treatment. Structurally, seamless tubes offer superior roundness and dimensional tolerances, making them ideal for high-stress applications in oil, gas, and hydraulic systems compared to welded tubes.
Performance and Strength Comparison
Seamless tubes exhibit superior strength and pressure resistance due to their uniform structure without weld joints, making them ideal for high-stress applications such as oil and gas pipelines and hydraulic systems. Welded tubes, while generally more cost-effective and easier to manufacture in large diameters, may present weak points along the weld seam that can reduce overall structural integrity under extreme conditions. Performance-wise, seamless tubes offer better fatigue resistance and uniformity in wall thickness, enhancing durability in high-temperature or high-pressure environments compared to welded tubes.
Durability and Reliability in Industrial Applications
Seamless tubes exhibit superior durability and reliability in industrial applications due to their uniform structure, which eliminates weak points caused by welding seams. The absence of welds minimizes the risk of corrosion and pressure-related failures, making seamless tubes ideal for high-stress environments such as oil and gas, chemical processing, and power generation. Welded tubes, while cost-effective and suitable for lower pressure applications, typically lack the mechanical robustness required for critical industrial processes demanding exceptional structural integrity.
Cost Analysis: Seamless Tubes vs Welded Tubes
Seamless tubes typically incur higher production costs due to their complex manufacturing process involving extrusion or rotary piercing, leading to increased material and energy expenses. Welded tubes offer a cost advantage by using flat steel sheets or coils, which are more readily available and require less intensive processing, reducing both raw material and fabrication costs. Though welded tubes are generally more economical, seamless tubes provide superior strength and uniformity, justifying higher costs in critical applications.
Common Uses for Seamless Tubes
Seamless tubes are commonly used in high-pressure applications such as oil and gas pipelines, heat exchangers, and power plant systems due to their superior strength and resistance to corrosion. They are preferred in industries requiring high reliability and safety, including aerospace, automotive, and chemical processing. Seamless tubes provide uniformity and durability essential for critical structural components and fluid transport.
Typical Applications of Welded Tubes
Welded tubes are commonly used in automotive exhaust systems, structural components, and fluid conveyance due to their cost-effectiveness and versatility in various diameters and wall thicknesses. They are ideal for applications requiring precise dimensions and consistent mechanical properties, such as in HVAC systems, scaffolding, and furniture manufacturing. The welding process allows for efficient mass production, making welded tubes suitable for construction, pipelines, and general industrial uses where strength and durability are essential.
Choosing the Right Tube for Your Project
Selecting the right metal tube depends heavily on the specific requirements of your project, such as strength, durability, and application environment. Seamless tubes offer enhanced structural integrity and resistance to pressure, making them ideal for critical applications like aerospace or high-pressure fluid transport. Welded tubes provide cost-effective solutions and versatility for less demanding uses, including furniture or automotive components, where precision and load capacity are moderate.
Industry Standards and Quality Certifications
Seamless tubes comply with stringent industry standards such as ASTM A269 and ASME B36.10, ensuring superior mechanical properties and uniform integrity, critical for high-pressure applications. Welded tubes meet standards like ASTM A513 and EN 10217, offering cost-effective solutions with certifications including ISO 9001 for quality management and PED compliance for pressure equipment.
Seamless Tube vs Welded Tube Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com