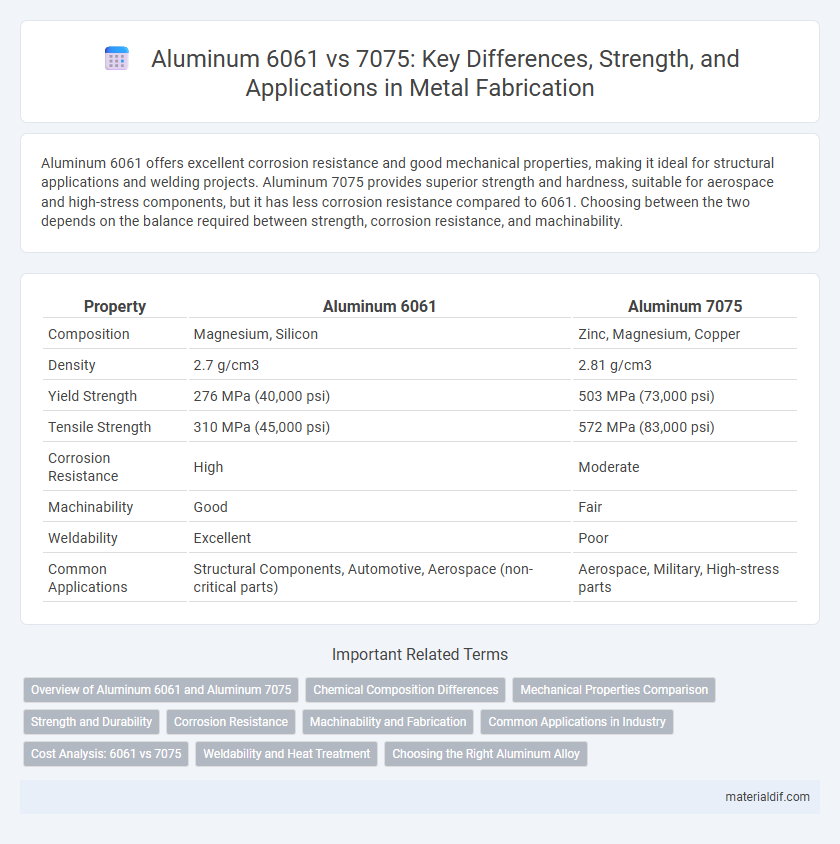
Aluminum 6061 offers excellent corrosion resistance and good mechanical properties, making it ideal for structural applications and welding projects. Aluminum 7075 provides superior strength and hardness, suitable for aerospace and high-stress components, but it has less corrosion resistance compared to 6061. Choosing between the two depends on the balance required between strength, corrosion resistance, and machinability.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Aluminum 6061 | Aluminum 7075 |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Magnesium, Silicon | Zinc, Magnesium, Copper |
| Density | 2.7 g/cm3 | 2.81 g/cm3 |
| Yield Strength | 276 MPa (40,000 psi) | 503 MPa (73,000 psi) |
| Tensile Strength | 310 MPa (45,000 psi) | 572 MPa (83,000 psi) |
| Corrosion Resistance | High | Moderate |
| Machinability | Good | Fair |
| Weldability | Excellent | Poor |
| Common Applications | Structural Components, Automotive, Aerospace (non-critical parts) | Aerospace, Military, High-stress parts |
Overview of Aluminum 6061 and Aluminum 7075
Aluminum 6061 features a balanced composition of magnesium and silicon, offering excellent corrosion resistance, weldability, and medium-to-high strength useful in structural applications. Aluminum 7075, alloyed predominantly with zinc, delivers superior strength comparable to some steels, making it ideal for aerospace and high-stress environments where durability is critical. While 6061 is preferred for its versatility and ease of machining, 7075 excels in performance-demanding scenarios requiring maximum strength and fatigue resistance.
Chemical Composition Differences
Aluminum 6061 contains magnesium (0.8%-1.2%) and silicon (0.4%-0.8%) as its primary alloying elements, providing good corrosion resistance and weldability. Aluminum 7075 is alloyed mainly with zinc (5.1%-6.1%), magnesium (2.1%-2.9%), and a small amount of copper (1.2%-2.0%), resulting in superior strength but reduced corrosion resistance compared to 6061. The higher zinc content in 7075 significantly enhances its tensile strength, while the balanced magnesium and silicon in 6061 offer a versatile and more corrosion-resistant composition.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Aluminum 6061 offers a tensile strength of approximately 290 MPa and excellent corrosion resistance, making it suitable for structural applications requiring moderate strength and good weldability. In contrast, Aluminum 7075 exhibits a higher tensile strength around 570 MPa and superior fatigue resistance, ideal for aerospace and high-stress environments despite reduced corrosion resistance. The yield strength of 6061 averages 240 MPa, while 7075 can reach up to 500 MPa, highlighting 7075's advantage in load-bearing capacity and impact performance.
Strength and Durability
Aluminum 7075 offers higher tensile strength, typically reaching around 74,000 psi, making it ideal for applications requiring exceptional durability and resistance to stress. In contrast, Aluminum 6061 has a lower tensile strength of approximately 45,000 psi but provides better corrosion resistance and weldability. The choice between Aluminum 6061 and 7075 depends on balancing the need for strength versus durability in specific environments and structural demands.
Corrosion Resistance
Aluminum 6061 exhibits superior corrosion resistance compared to Aluminum 7075 due to its higher magnesium and silicon content, which promotes the formation of a stable oxide layer that protects against environmental degradation. This makes 6061 ideal for applications requiring exposure to moisture, saline environments, or varying weather conditions. In contrast, 7075, while offering higher strength, is more susceptible to corrosion, especially stress corrosion cracking, limiting its use in highly corrosive settings.
Machinability and Fabrication
Aluminum 6061 offers superior machinability due to its balanced alloy composition, enabling easier cutting, drilling, and shaping during fabrication processes. In contrast, Aluminum 7075, while stronger and more durable, presents challenges in machining because of its higher zinc content, requiring specialized tools and techniques to avoid tool wear and maintain precision. Fabrication of 6061 is generally more versatile and cost-effective for applications demanding intricate machining, whereas 7075 excels in high-stress environments but demands careful handling during manufacturing.
Common Applications in Industry
Aluminum 6061 is widely used in automotive parts, aerospace components, and structural frames due to its excellent corrosion resistance and good mechanical properties. Aluminum 7075 is preferred in high-stress applications like aerospace, military hardware, and sporting equipment because of its superior strength and fatigue resistance. Both alloys are integral to manufacturing but serve distinct roles based on performance requirements and environmental conditions.
Cost Analysis: 6061 vs 7075
Aluminum 6061 typically offers a lower cost compared to Aluminum 7075 due to its widespread availability and easier manufacturing processes. The higher strength and superior mechanical properties of 7075 result in increased material and processing expenses, making it a premium choice for high-performance applications. Cost analysis favors 6061 for budget-conscious projects requiring good corrosion resistance and weldability, whereas 7075 suits critical structural uses demanding maximum strength despite the higher price.
Weldability and Heat Treatment
Aluminum 6061 offers superior weldability due to its excellent response to various welding techniques like TIG and MIG, making it ideal for structural applications where strong joints are critical. In contrast, Aluminum 7075 has poor weldability because its high zinc content increases susceptibility to cracking during welding, requiring specialized methods and post-weld heat treatments to restore strength. Both alloys benefit from heat treatment, but 6061 responds well to T6 temper, enhancing its mechanical properties evenly, while 7075 requires precise aging processes in T6 temper to maximize its strength and resistance to stress corrosion.
Choosing the Right Aluminum Alloy
Aluminum 6061 offers excellent corrosion resistance, weldability, and moderate strength, making it ideal for structural applications requiring good machinability and durability. Aluminum 7075 provides superior strength and hardness, suitable for high-stress environments such as aerospace and military components where weight-to-strength ratio is critical. Selecting between these alloys depends on balancing mechanical properties, corrosion resistance, and fabrication processes based on specific project requirements.
Aluminum 6061 vs Aluminum 7075 Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com