Laser cutting offers high precision and excellent edge quality, making it ideal for thin metal sheets and intricate designs. Waterjet cutting can handle thicker materials and a wider variety of metals without heat distortion, preserving the metal's original properties. Both methods provide clean cuts, but the choice depends on material thickness, desired finish, and thermal sensitivity.
Table of Comparison
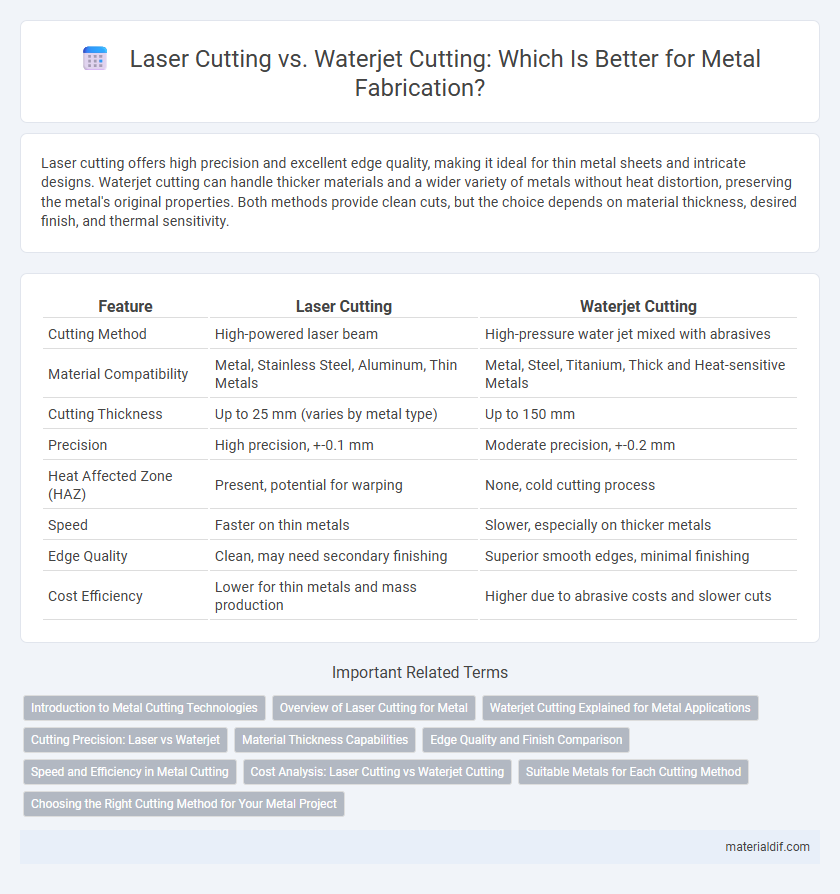
| Feature | Laser Cutting | Waterjet Cutting |
|---|---|---|
| Cutting Method | High-powered laser beam | High-pressure water jet mixed with abrasives |
| Material Compatibility | Metal, Stainless Steel, Aluminum, Thin Metals | Metal, Steel, Titanium, Thick and Heat-sensitive Metals |
| Cutting Thickness | Up to 25 mm (varies by metal type) | Up to 150 mm |
| Precision | High precision, +-0.1 mm | Moderate precision, +-0.2 mm |
| Heat Affected Zone (HAZ) | Present, potential for warping | None, cold cutting process |
| Speed | Faster on thin metals | Slower, especially on thicker metals |
| Edge Quality | Clean, may need secondary finishing | Superior smooth edges, minimal finishing |
| Cost Efficiency | Lower for thin metals and mass production | Higher due to abrasive costs and slower cuts |
Introduction to Metal Cutting Technologies
Laser cutting and waterjet cutting are advanced metal cutting technologies widely used in industrial applications for precision and efficiency. Laser cutting employs a focused beam of coherent light to melt or vaporize metal, enabling high-speed and intricate cuts with minimal heat-affected zones. Waterjet cutting utilizes a high-pressure stream of water mixed with abrasive particles to erode metal surfaces, offering cold cutting that prevents thermal distortion and suits thick or heat-sensitive materials.
Overview of Laser Cutting for Metal
Laser cutting for metal utilizes a high-powered laser beam to precisely melt, burn, or vaporize material along a designated path, achieving exceptional accuracy and smooth edges. This method excels in processing thin to moderately thick metals such as stainless steel, aluminum, and carbon steel, delivering fast cutting speeds and minimal material distortion. Advanced CNC-controlled systems enhance repeatability and enable intricate designs, making laser cutting a preferred choice for industries requiring precision and efficiency in metal fabrication.
Waterjet Cutting Explained for Metal Applications
Waterjet cutting uses a high-pressure jet of water mixed with abrasive particles to precisely cut through metal without generating heat, preserving material integrity and preventing thermal distortion. This method excels in cutting complex shapes and thick metal plates up to several inches, making it ideal for stainless steel, aluminum, and titanium applications. Its cold cutting process ensures minimal mechanical stress and clean edges, reducing the need for secondary finishing in metal fabrication.
Cutting Precision: Laser vs Waterjet
Laser cutting offers exceptionally high cutting precision with minimal kerf width, enabling intricate and detailed metal designs with tolerances as tight as +-0.1 mm. Waterjet cutting provides versatility by cutting thicker metals without heat distortion, maintaining precision typically around +-0.2 mm but excelling in materials prone to thermal damage. Choosing between laser and waterjet cutting depends on the required accuracy and material properties, with laser cutting preferred for fine detail and waterjet for thicker or heat-sensitive metals.
Material Thickness Capabilities
Laser cutting efficiently processes metal sheets up to approximately 25 mm thick, providing high precision and clean edges ideal for detailed designs. Waterjet cutting excels with thicker materials, handling metal plates up to 300 mm thick without altering the metal's structural properties. The choice between these methods depends largely on the required material thickness and finishing needs for specific metal fabrication projects.
Edge Quality and Finish Comparison
Laser cutting produces precise, clean edges with minimal thermal distortion, ideal for thin to medium-thickness metals requiring high detail. Waterjet cutting offers superior edge quality for thicker or heat-sensitive metals, delivering smooth, burr-free finishes without affecting the metal's structural integrity. Both methods excel in edge finish, but waterjet cutting excels in preserving metal properties while laser cutting achieves higher precision.
Speed and Efficiency in Metal Cutting
Laser cutting offers superior speed and precision for metal cutting, efficiently slicing through thin to medium-thickness metals with minimal heat distortion. Waterjet cutting excels in cutting thicker metals and materials sensitive to heat, but operates at a slower pace compared to laser technology. Efficiency in laser cutting is maximized through high automation and rapid processing, while waterjet cutting demands more time for heavier gauge metals due to abrasive material usage.
Cost Analysis: Laser Cutting vs Waterjet Cutting
Laser cutting generally offers lower operating costs due to faster processing speeds and reduced consumable usage, making it more cost-effective for thin to medium metal sheets. Waterjet cutting incurs higher expenses from abrasive materials and slower cutting speeds, but it excels in minimizing heat-affected zones, preserving material integrity for thicker or more complex metals. Evaluating cost efficiency depends on factors such as metal type, thickness, required precision, and production volume.
Suitable Metals for Each Cutting Method
Laser cutting is highly effective for thin to medium-thickness metals such as stainless steel, aluminum, and mild steel, offering precise cuts with minimal heat distortion. Waterjet cutting excels at processing thicker and harder metals like titanium, tool steel, and Inconel, as it uses high-pressure abrasive water to avoid thermal damage. Both methods suit specific metal types depending on thickness, heat sensitivity, and desired edge quality.
Choosing the Right Cutting Method for Your Metal Project
Laser cutting offers high precision and clean edges ideal for thin metals and intricate designs, with speeds suitable for large production runs. Waterjet cutting excels in versatility by cutting thicker metals without heat distortion, preserving material integrity for projects requiring complex shapes and varied thicknesses. Selecting the appropriate method depends on factors such as metal type, thickness, required edge quality, and production volume to optimize efficiency and final product performance.
Laser Cutting vs Waterjet Cutting Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com