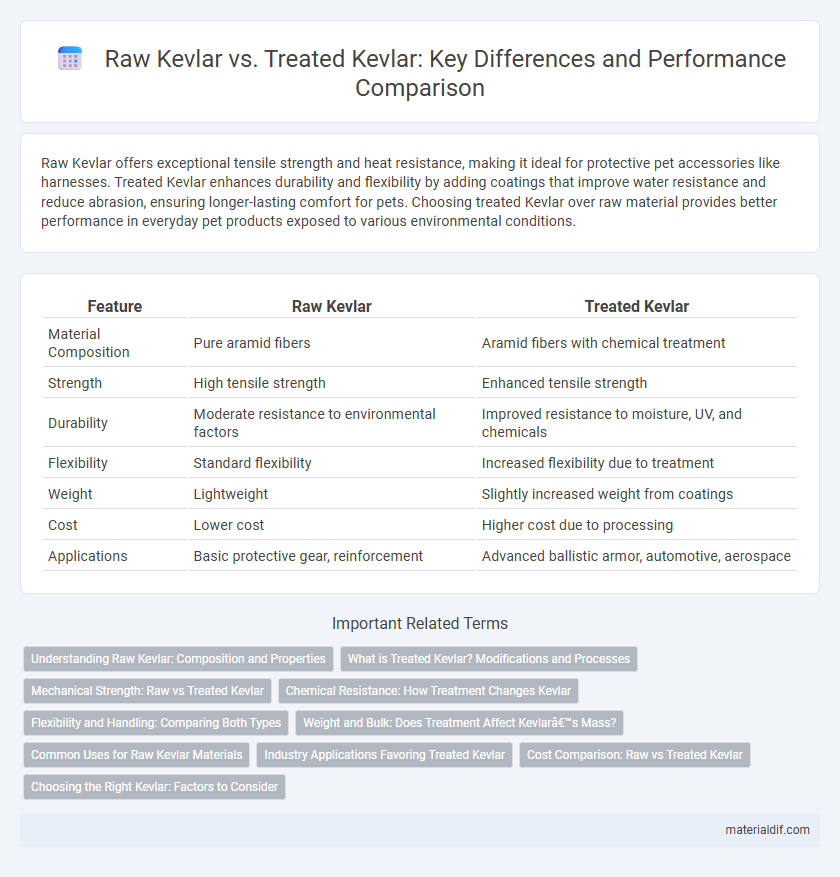
Raw Kevlar offers exceptional tensile strength and heat resistance, making it ideal for protective pet accessories like harnesses. Treated Kevlar enhances durability and flexibility by adding coatings that improve water resistance and reduce abrasion, ensuring longer-lasting comfort for pets. Choosing treated Kevlar over raw material provides better performance in everyday pet products exposed to various environmental conditions.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Raw Kevlar | Treated Kevlar |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Pure aramid fibers | Aramid fibers with chemical treatment |
| Strength | High tensile strength | Enhanced tensile strength |
| Durability | Moderate resistance to environmental factors | Improved resistance to moisture, UV, and chemicals |
| Flexibility | Standard flexibility | Increased flexibility due to treatment |
| Weight | Lightweight | Slightly increased weight from coatings |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost due to processing |
| Applications | Basic protective gear, reinforcement | Advanced ballistic armor, automotive, aerospace |
Understanding Raw Kevlar: Composition and Properties
Raw Kevlar consists of long chains of poly-paraphenylene terephthalamide molecules, forming a highly crystalline and tightly bonded fiber structure known for exceptional tensile strength and thermal stability. Its inherent resistance to impact, abrasion, and chemical degradation makes it ideal for industrial applications requiring durable, lightweight materials. Understanding raw Kevlar's molecular alignment and hydrogen bonding is crucial to optimizing its performance before chemical or physical treatments enhance flexibility or UV resistance.
What is Treated Kevlar? Modifications and Processes
Treated Kevlar refers to Kevlar fibers that have undergone chemical or physical modifications to enhance properties such as durability, UV resistance, and adhesion. Common processes include coating with resins, surface plasma treatments, and incorporation of anti-static agents to improve performance in composite materials. These modifications enable Treated Kevlar to offer superior mechanical strength, environmental stability, and compatibility in various industrial applications compared to Raw Kevlar.
Mechanical Strength: Raw vs Treated Kevlar
Raw Kevlar fibers exhibit high tensile strength and excellent elasticity but lack resistance to environmental factors, which can compromise mechanical performance over time. Treated Kevlar undergoes chemical and thermal processes that enhance fiber bonding, resulting in improved mechanical strength, durability, and resistance to wear, moisture, and UV exposure. This treatment significantly increases Kevlar's tensile strength and impact resistance, making it more suitable for demanding applications in aerospace, body armor, and industrial use.
Chemical Resistance: How Treatment Changes Kevlar
Raw Kevlar exhibits strong mechanical properties but has limited chemical resistance due to its unmodified polymer structure. Chemical treatment processes, such as surface coating with fluoropolymers or resin impregnation, enhance Kevlar's resistance to acids, solvents, and UV degradation. Treated Kevlar maintains structural integrity in harsh chemical environments, significantly extending its application lifespan in protective gear and industrial uses.
Flexibility and Handling: Comparing Both Types
Raw Kevlar exhibits higher stiffness and lower flexibility, making it less adaptable for applications requiring frequent bending or shaping. Treated Kevlar undergoes processes such as resin coating or heat treatment, enhancing its pliability and improving handling characteristics without significantly compromising strength. The improved flexibility of treated Kevlar benefits industries like aerospace and sports equipment, where ease of manipulation and comfort are critical.
Weight and Bulk: Does Treatment Affect Kevlar’s Mass?
Treated Kevlar often exhibits a slight increase in weight due to coatings or resin applications that enhance durability and environmental resistance. Raw Kevlar fibers maintain a lower bulk and mass, making them ideal for applications prioritizing lightweight materials. The treatment process generally adds minimal weight, but the overall impact depends on the type and amount of resin or coating used.
Common Uses for Raw Kevlar Materials
Raw Kevlar retains its high tensile strength and lightweight properties, making it ideal for integration into composite materials used in aerospace and automotive industries. It serves as a fundamental reinforcement in ballistic panels, helmets, and protective clothing, where its natural durability provides robust resistance to impact and abrasion. Manufacturers also utilize raw Kevlar fibers in ropes and cables, capitalizing on its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio for applications requiring reliable load-bearing performance.
Industry Applications Favoring Treated Kevlar
Treated Kevlar offers enhanced durability, chemical resistance, and improved tensile strength compared to raw Kevlar, making it the preferred choice in demanding industrial applications such as aerospace, automotive, and military armor. The treatment process improves Kevlar's resistance to UV degradation and abrasion, extending the service life of protective gear and structural components. Industries favor treated Kevlar for its superior performance in extreme environments, ensuring safety and reliability in critical applications.
Cost Comparison: Raw vs Treated Kevlar
Raw Kevlar typically has a lower upfront cost compared to treated Kevlar due to the absence of additional chemical processing and coating applications. Treated Kevlar, enhanced for increased durability, UV resistance, and improved mechanical properties, commands higher prices reflecting its advanced performance benefits. The cost differential often justifies the investment in treated Kevlar for applications requiring extended lifespan and enhanced safety features.
Choosing the Right Kevlar: Factors to Consider
Raw Kevlar offers high tensile strength and thermal resistance but lacks flexibility and chemical resistance, making it ideal for structural reinforcement applications. Treated Kevlar undergoes processes such as coating or resin impregnation to enhance durability, UV resistance, and abrasion protection, suitable for protective gear and composite materials. When choosing the right Kevlar, consider the specific performance requirements like mechanical strength, environmental exposure, and end-use conditions to ensure optimal functionality.
Raw Kevlar vs Treated Kevlar Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com