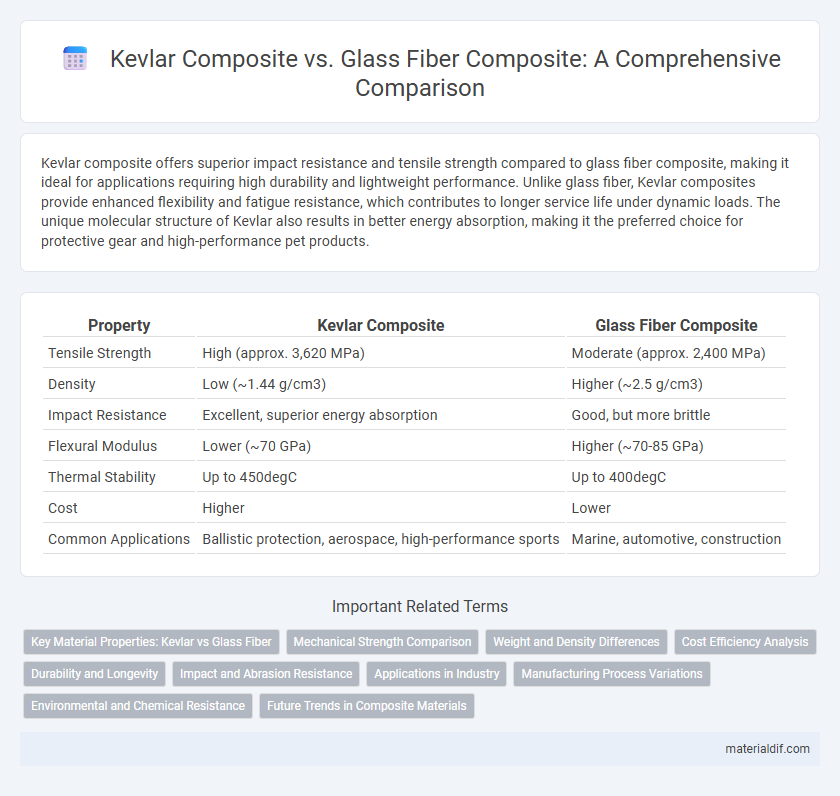
Kevlar composite offers superior impact resistance and tensile strength compared to glass fiber composite, making it ideal for applications requiring high durability and lightweight performance. Unlike glass fiber, Kevlar composites provide enhanced flexibility and fatigue resistance, which contributes to longer service life under dynamic loads. The unique molecular structure of Kevlar also results in better energy absorption, making it the preferred choice for protective gear and high-performance pet products.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Kevlar Composite | Glass Fiber Composite |
|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength | High (approx. 3,620 MPa) | Moderate (approx. 2,400 MPa) |
| Density | Low (~1.44 g/cm3) | Higher (~2.5 g/cm3) |
| Impact Resistance | Excellent, superior energy absorption | Good, but more brittle |
| Flexural Modulus | Lower (~70 GPa) | Higher (~70-85 GPa) |
| Thermal Stability | Up to 450degC | Up to 400degC |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Common Applications | Ballistic protection, aerospace, high-performance sports | Marine, automotive, construction |
Key Material Properties: Kevlar vs Glass Fiber
Kevlar composites exhibit superior tensile strength and impact resistance compared to glass fiber composites, making them ideal for high-performance applications requiring durability and lightweight characteristics. Kevlar offers exceptional energy absorption and flexibility, whereas glass fiber composites provide greater stiffness and cost efficiency. The density of Kevlar composites is significantly lower than glass fiber, contributing to better strength-to-weight ratios in aerospace and ballistic armor uses.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
Kevlar composite exhibits significantly higher tensile strength and impact resistance compared to glass fiber composite, making it ideal for applications requiring superior durability and lightweight performance. Kevlar's unique aramid fiber structure provides enhanced energy absorption and resistance to fracture under stress, outperforming the more brittle nature of glass fibers. This mechanical advantage leads to increased structural integrity in aerospace, military, and automotive components where strength-to-weight ratio is critical.
Weight and Density Differences
Kevlar composites exhibit significantly lower density, approximately 1.44 g/cm3, compared to glass fiber composites which have a density around 2.5 g/cm3, resulting in substantial weight savings for structural applications. The reduced weight of Kevlar composites enhances fuel efficiency and maneuverability in aerospace and automotive industries where lightweight materials are crucial. Despite its lower density, Kevlar maintains high tensile strength and impact resistance, making it an optimal choice for high-performance, lightweight composite structures.
Cost Efficiency Analysis
Kevlar composites exhibit higher initial material costs compared to glass fiber composites but offer superior strength-to-weight ratios that reduce overall structural weight and associated expenses in applications like aerospace and automotive industries. The long-term cost efficiency of Kevlar composites is enhanced by their greater impact resistance and durability, leading to lower maintenance and replacement costs over the product lifespan. Glass fiber composites remain cost-effective for large-scale production and less critical applications, where initial investment is a primary concern.
Durability and Longevity
Kevlar composite exhibits superior durability and longevity compared to glass fiber composite due to its exceptional tensile strength and resistance to impact and fatigue. Kevlar fibers maintain structural integrity under extreme conditions, making them ideal for applications requiring extended service life and reliable performance. Glass fiber composites tend to degrade faster under stress and environmental exposure, resulting in reduced lifespan and increased maintenance.
Impact and Abrasion Resistance
Kevlar composites exhibit superior impact resistance compared to glass fiber composites due to their high tensile strength and energy-absorbing molecular structure. The inherent toughness of aramid fibers in Kevlar enhances abrasion resistance, making these composites ideal for applications requiring durability under repetitive wear. Glass fiber composites, while stiff and cost-effective, typically fall short in impact and abrasion resistance when compared to Kevlar-based materials.
Applications in Industry
Kevlar composites exhibit superior impact resistance and higher tensile strength compared to glass fiber composites, making them ideal for aerospace, automotive, and ballistic protection applications. Industries favor Kevlar composites in manufacturing lightweight, durable armor, high-performance tires, and structural components requiring enhanced durability and fatigue resistance. Glass fiber composites are commonly used for cost-effective solutions in marine, wind energy, and construction sectors, where strength-to-weight ratio is important but extreme impact resistance is less critical.
Manufacturing Process Variations
Kevlar composite manufacturing requires precise control during resin impregnation due to Kevlar's low resin uptake and moisture sensitivity, leading to specialized processes like vacuum-assisted resin transfer molding (VARTM). In contrast, glass fiber composites benefit from higher resin permeability and simpler wet-out, allowing for more flexible manufacturing methods such as hand lay-up or spray-up techniques. The distinct fiber architectures and resin compatibility of Kevlar demand tailored curing cycles and temperature controls to optimize mechanical properties compared to the relatively straightforward processing of glass fiber composites.
Environmental and Chemical Resistance
Kevlar composite exhibits superior chemical resistance compared to glass fiber composite, effectively withstanding exposure to solvents, oils, and acids without significant degradation. Its low moisture absorption enhances durability in humid or wet environments, whereas glass fiber composites are more susceptible to moisture-induced weakening. This makes Kevlar composites preferable for applications requiring prolonged exposure to harsh chemical or environmental conditions.
Future Trends in Composite Materials
Future trends in composite materials highlight Kevlar composites for their superior impact resistance and lightweight properties compared to glass fiber composites, which primarily offer high tensile strength and cost-effectiveness. Innovations in hybrid composites integrating Kevlar with carbon or glass fibers aim to optimize mechanical performance, thermal stability, and durability for aerospace, automotive, and military applications. Emerging research on nanotechnology-enhanced Kevlar composites emphasizes enhanced fatigue resistance and multifunctional smart materials, positioning Kevlar as a critical component in next-generation composite manufacturing.
Kevlar composite vs Glass fiber composite Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com