Kevlar reinforcing offers exceptional tensile strength and impact resistance, making it ideal for high-stress applications requiring lightweight durability in pet products. Basalt reinforcing provides excellent thermal stability and corrosion resistance, which enhances longevity in environments exposed to extreme temperatures or harsh conditions. Choosing between Kevlar and Basalt reinforcing depends on whether strength and flexibility or heat resistance and durability are the priority for pet safety and comfort.
Table of Comparison
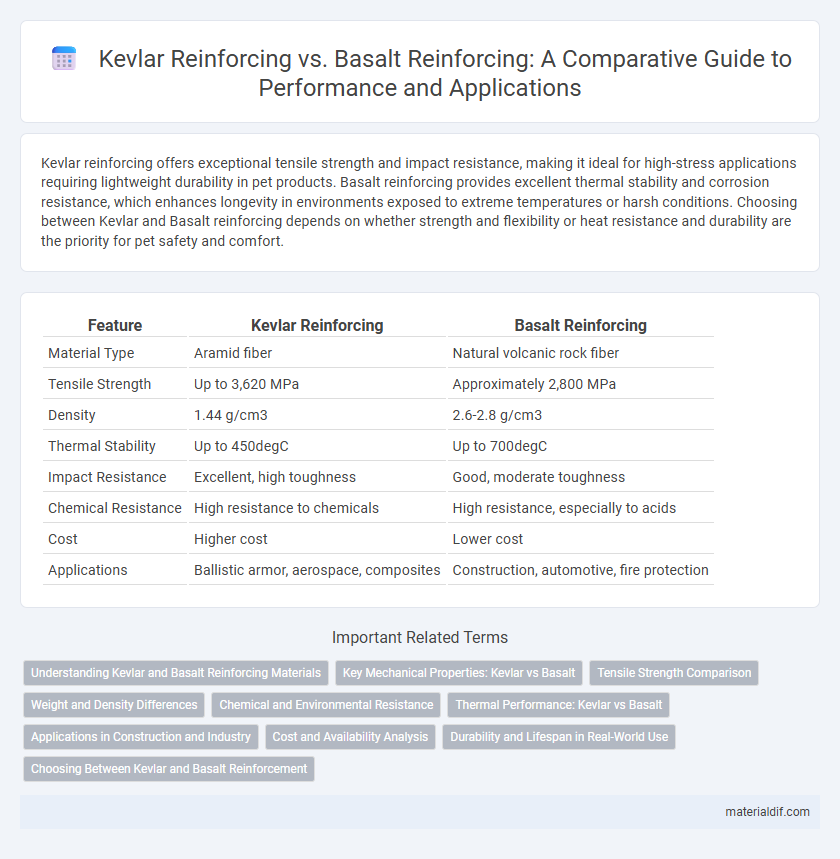
| Feature | Kevlar Reinforcing | Basalt Reinforcing |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Aramid fiber | Natural volcanic rock fiber |
| Tensile Strength | Up to 3,620 MPa | Approximately 2,800 MPa |
| Density | 1.44 g/cm3 | 2.6-2.8 g/cm3 |
| Thermal Stability | Up to 450degC | Up to 700degC |
| Impact Resistance | Excellent, high toughness | Good, moderate toughness |
| Chemical Resistance | High resistance to chemicals | High resistance, especially to acids |
| Cost | Higher cost | Lower cost |
| Applications | Ballistic armor, aerospace, composites | Construction, automotive, fire protection |
Understanding Kevlar and Basalt Reinforcing Materials
Kevlar reinforcing fibers exhibit exceptional tensile strength and impact resistance, making them ideal for applications requiring lightweight durability and high performance. Basalt reinforcing materials offer superior thermal stability and environmental resistance, which enhances composite longevity in extreme conditions. Understanding the distinct mechanical properties and environmental benefits of Kevlar versus Basalt reinforcements enables optimal material selection for advanced structural and protective applications.
Key Mechanical Properties: Kevlar vs Basalt
Kevlar exhibits superior tensile strength and impact resistance compared to basalt fibers, making it ideal for high-performance applications requiring lightweight and durable reinforcement. Basalt fibers offer excellent thermal stability and chemical resistance but generally have lower tensile strength and elongation at break than Kevlar. The higher specific strength and fatigue resistance of Kevlar contribute to its preference in ballistic protection and aerospace composites, whereas basalt is favored in environments demanding corrosion resistance and moderate mechanical performance.
Tensile Strength Comparison
Kevlar reinforcing fibers exhibit a tensile strength ranging from 3,620 to 4,100 MPa, significantly surpassing basalt fibers, which typically have tensile strengths between 2,800 and 3,500 MPa. The superior tensile strength of Kevlar makes it ideal for applications requiring high-performance reinforcement, such as ballistic protection and aerospace composites. Basalt fibers provide a cost-effective alternative with good tensile properties but do not match Kevlar's exceptional strength-to-weight ratio.
Weight and Density Differences
Kevlar reinforcing materials exhibit significantly lower density, approximately 1.44 g/cm3, compared to basalt fibers which typically have a density around 2.7 g/cm3, resulting in lighter composite structures when Kevlar is used. The reduced weight of Kevlar composites enhances performance in applications demanding high strength-to-weight ratios, such as aerospace and automotive industries. Despite basalt's higher density, its superior thermal resistance complements Kevlar's lightweight properties in hybrid reinforcing solutions.
Chemical and Environmental Resistance
Kevlar offers exceptional chemical resistance, maintaining strength when exposed to acids, bases, and solvents, making it ideal for harsh environments. Basalt fibers also exhibit good chemical resistance but are more susceptible to alkaline degradation compared to Kevlar. Environmental resistance in Kevlar includes superior UV stability and moisture resistance, whereas basalt reinforcement may degrade faster under prolonged UV exposure and moisture conditions.
Thermal Performance: Kevlar vs Basalt
Kevlar exhibits superior thermal stability with a decomposition temperature around 450degC, making it highly resistant to heat in reinforcing applications. Basalt fibers, while also thermally stable, have a slightly lower decomposition temperature near 600degC but offer better resistance to thermal shock and higher melting points. The choice between Kevlar and basalt for reinforcement depends on specific thermal performance requirements, with Kevlar excelling in sustained high-temperature exposure and basalt providing enhanced performance in fluctuating thermal environments.
Applications in Construction and Industry
Kevlar reinforcing in construction offers exceptional tensile strength and impact resistance, making it ideal for high-stress applications such as blast-resistant panels and earthquake-resistant structures. Basalt reinforcing provides superior thermal stability and chemical resistance, lending itself well to industrial environments like petrochemical plants and fireproofing applications. Both materials enhance structural durability, but Kevlar excels in military and safety-critical constructions while basalt is preferred for its eco-friendly production and corrosion resistance.
Cost and Availability Analysis
Kevlar reinforcing fibers typically exhibit higher costs than basalt fibers due to complex manufacturing processes and limited raw material sources, impacting budget-sensitive projects. Basalt reinforcement offers greater availability because basalt rock is abundantly found worldwide and processed with simpler, more cost-effective techniques. Cost efficiency and raw material accessibility make basalt an attractive alternative for large-scale structural reinforcement where financial constraints and steady supply are critical.
Durability and Lifespan in Real-World Use
Kevlar reinforcing offers superior durability and a longer lifespan in real-world applications due to its exceptional tensile strength and resistance to impact, abrasion, and fatigue. Basalt reinforcing, while also durable and resistant to chemical corrosion and high temperatures, generally exhibits lower fatigue resistance and a shorter service life compared to Kevlar under dynamic loading conditions. The enhanced durability of Kevlar composites makes them preferable for high-performance applications requiring extended operational life and consistent structural integrity.
Choosing Between Kevlar and Basalt Reinforcement
Kevlar reinforcement provides superior tensile strength and impact resistance, making it ideal for applications requiring high durability and lightweight properties, such as ballistic armor and aerospace components. Basalt reinforcement offers excellent thermal stability and chemical resistance, suitable for construction and automotive parts exposed to harsh environments. Choosing between Kevlar and Basalt depends on specific performance requirements, cost considerations, and environmental exposure conditions.
Kevlar reinforcing vs Basalt reinforcing Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com