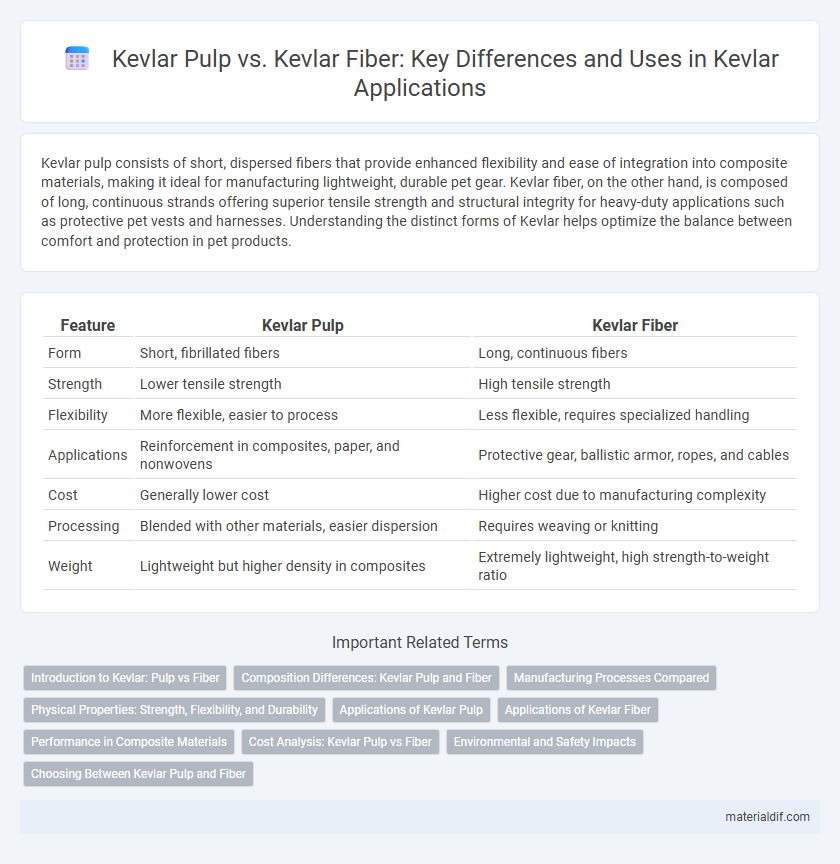
Kevlar pulp consists of short, dispersed fibers that provide enhanced flexibility and ease of integration into composite materials, making it ideal for manufacturing lightweight, durable pet gear. Kevlar fiber, on the other hand, is composed of long, continuous strands offering superior tensile strength and structural integrity for heavy-duty applications such as protective pet vests and harnesses. Understanding the distinct forms of Kevlar helps optimize the balance between comfort and protection in pet products.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Kevlar Pulp | Kevlar Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Form | Short, fibrillated fibers | Long, continuous fibers |
| Strength | Lower tensile strength | High tensile strength |
| Flexibility | More flexible, easier to process | Less flexible, requires specialized handling |
| Applications | Reinforcement in composites, paper, and nonwovens | Protective gear, ballistic armor, ropes, and cables |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Higher cost due to manufacturing complexity |
| Processing | Blended with other materials, easier dispersion | Requires weaving or knitting |
| Weight | Lightweight but higher density in composites | Extremely lightweight, high strength-to-weight ratio |
Introduction to Kevlar: Pulp vs Fiber
Kevlar pulp consists of chopped or short fibers used primarily in papermaking, offering enhanced strength and heat resistance in composite materials. Kevlar fiber, on the other hand, refers to continuous, long strands known for their exceptional tensile strength and durability in ballistic and protective applications. Understanding the difference between Kevlar pulp and fiber is essential for optimizing material performance in industrial and safety products.
Composition Differences: Kevlar Pulp and Fiber
Kevlar pulp consists of short, chopped aramid fibers processed into a cellulose-like form, enhancing its compatibility with paper and composite materials. Kevlar fiber is made of continuous, long filaments of para-aramid synthetic polymer, providing superior tensile strength and durability. The primary composition difference lies in fiber length and processing, where Kevlar pulp's shorter strands enable improved bonding in pulp-based applications, while Kevlar fiber retains maximum structural integrity for high-performance uses.
Manufacturing Processes Compared
Kevlar fiber is produced through a spinning process where liquid polymer is extruded and coagulated into strong continuous filaments, ensuring high tensile strength and flexibility. Kevlar pulp, on the other hand, is made by cutting these fibers into short lengths followed by mechanical fibrillation to create a pulp form suitable for applications like composites and paper reinforcement. The manufacturing process differences directly affect the material's physical properties and usability, with fibers offering superior strength in textiles and pulps providing enhanced bonding in composite materials.
Physical Properties: Strength, Flexibility, and Durability
Kevlar fiber exhibits superior tensile strength and exceptional durability, making it ideal for high-performance applications such as ballistic protection and aerospace components. Kevlar pulp, derived from the fiber, offers enhanced flexibility and ease of processing, which suits composite materials and paper reinforcement without compromising fundamental strength. Both forms maintain Kevlar's inherent heat resistance and lightweight properties, but fibers provide maximum structural integrity while pulp enables versatile manufacturing options.
Applications of Kevlar Pulp
Kevlar pulp is widely used in reinforcing composites, enhancing ballistic protection in body armor and helmets due to its excellent tensile strength and energy absorption properties. It is preferred over Kevlar fiber in applications requiring uniform dispersion within resins, such as in automotive brake pads and friction materials, providing improved wear resistance and thermal stability. Kevlar pulp's fine fibrillar structure contributes to lightweight, high-performance materials in aerospace and industrial equipment, offering enhanced durability and impact resistance.
Applications of Kevlar Fiber
Kevlar fiber is widely utilized in high-performance applications such as ballistic body armor, aerospace components, and automotive parts due to its exceptional tensile strength and lightweight properties. Unlike Kevlar pulp, which serves as a raw material for composite manufacturing and paper production, Kevlar fiber is directly woven or molded to create durable, impact-resistant textiles and structural materials. This fiber's ability to withstand extreme stresses while maintaining flexibility makes it ideal for protective gear, ropes, and reinforcement in sporting goods.
Performance in Composite Materials
Kevlar fiber exhibits superior tensile strength and impact resistance compared to Kevlar pulp, making it the preferred reinforcement in high-performance composite materials. Kevlar fiber's continuous filament structure provides enhanced load-bearing capacity and durability, critical for aerospace and ballistic applications. In contrast, Kevlar pulp's shorter fiber length results in composites with improved toughness but lower mechanical strength, suitable for use in non-structural or hybrid composite systems.
Cost Analysis: Kevlar Pulp vs Fiber
Kevlar pulp offers a cost-effective alternative to Kevlar fiber due to lower raw material and processing expenses, making it suitable for large-scale applications requiring moderate strength. Kevlar fiber, while more expensive, delivers superior tensile strength and durability critical for high-performance uses such as ballistic protection and aerospace components. Evaluating total lifecycle costs, Kevlar pulp reduces upfront material investment, whereas Kevlar fiber's higher price is offset by enhanced performance and longevity in specialized applications.
Environmental and Safety Impacts
Kevlar pulp, derived from breaking down Kevlar fibers into finer strands, offers enhanced biodegradability compared to traditional Kevlar fibers, which are highly resistant to decomposition. This improved biodegradability reduces long-term environmental pollution, making Kevlar pulp a more eco-friendly alternative for certain industrial applications. From a safety standpoint, Kevlar pulp presents fewer inhalation hazards during manufacturing processes due to its less rigid structure, whereas Kevlar fibers can pose respiratory risks if airborne fibers are inhaled.
Choosing Between Kevlar Pulp and Fiber
Selecting between Kevlar pulp and Kevlar fiber depends on the specific application requirements such as strength, flexibility, and ease of processing. Kevlar pulp offers excellent dispersibility and is ideal for enhancing composite materials and paper products with lightweight reinforcement. Kevlar fiber provides superior tensile strength and durability, making it suitable for ballistic protection, ropes, and high-performance fabrics requiring maximum impact resistance.
Kevlar pulp vs Kevlar fiber Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com