Kevlar layers offer exceptional tensile strength and abrasion resistance, making them ideal for pet protective gear that requires durability and impact protection. Spectra layers provide superior lightweight performance with high resistance to cuts and punctures, enhancing comfort and flexibility for active pets. Choosing between Kevlar and Spectra layers depends on balancing the need for robust protection versus lightweight mobility in pet safety products.
Table of Comparison
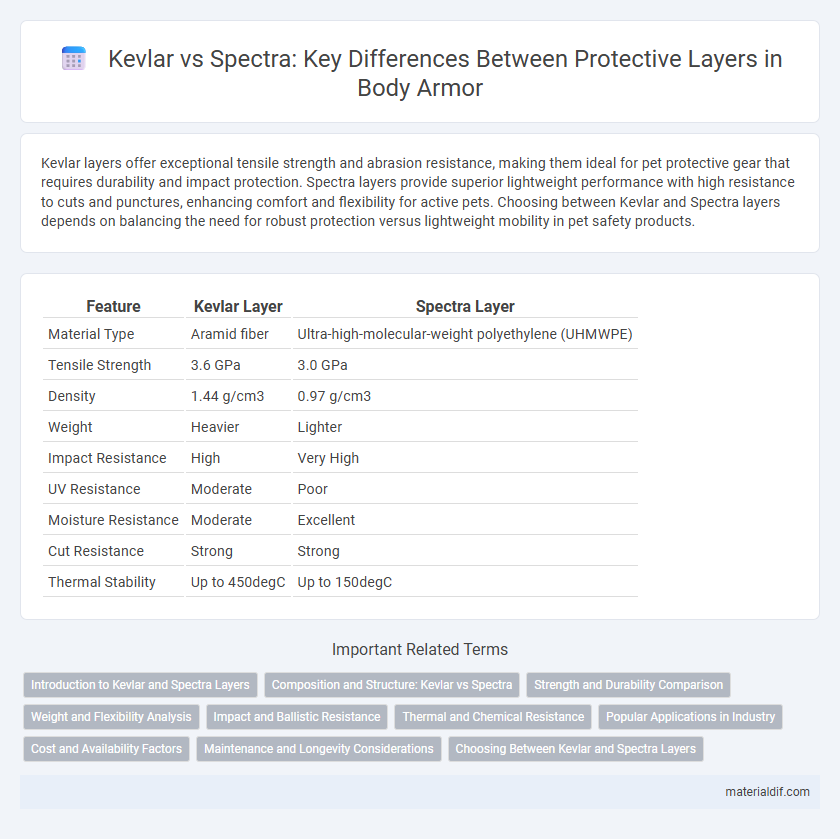
| Feature | Kevlar Layer | Spectra Layer |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Aramid fiber | Ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene (UHMWPE) |
| Tensile Strength | 3.6 GPa | 3.0 GPa |
| Density | 1.44 g/cm3 | 0.97 g/cm3 |
| Weight | Heavier | Lighter |
| Impact Resistance | High | Very High |
| UV Resistance | Moderate | Poor |
| Moisture Resistance | Moderate | Excellent |
| Cut Resistance | Strong | Strong |
| Thermal Stability | Up to 450degC | Up to 150degC |
Introduction to Kevlar and Spectra Layers
Kevlar layers consist of para-aramid fibers known for exceptional tensile strength and heat resistance, making them ideal for ballistic and protective applications. Spectra layers are made from ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene (UHMWPE) fibers, offering superior strength-to-weight ratio and excellent abrasion resistance. Both Kevlar and Spectra layers provide crucial protective properties but differ in fiber composition and performance characteristics.
Composition and Structure: Kevlar vs Spectra
Kevlar consists of tightly woven para-aramid fibers known for high tensile strength and thermal stability, while Spectra is composed of ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene (UHMWPE) fibers with a lower density and higher energy absorption capacity. The crystalline structure of Kevlar fibers provides rigidity and resistance to impact, whereas Spectra's molecular alignment offers superior flexibility and durability under dynamic loads. Both materials serve critical roles in ballistic armor and personal protective equipment, but their distinct compositions influence performance characteristics such as weight, abrasion resistance, and environmental resilience.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Kevlar layers exhibit exceptional tensile strength, boasting a tensile strength of approximately 3,620 MPa, which contributes to superior impact resistance and cut protection in ballistic applications. Spectra layers, derived from ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene (UHMWPE), provide higher tensile strength values up to 3,800 MPa and demonstrate remarkable durability with enhanced resistance to moisture, chemicals, and UV degradation. The durability advantage of Spectra fibers in harsh environments contrasts with Kevlar's slightly better thermal stability, making the choice between layers dependent on specific operational demands such as heat exposure versus prolonged environmental resilience.
Weight and Flexibility Analysis
Kevlar layers offer a balanced combination of high tensile strength and moderate flexibility, making them lightweight yet durable for ballistic and protective applications. Spectra layers are notably lighter than Kevlar, providing superior weight reduction but with increased rigidity, which may limit flexibility in certain uses. Weight analysis reveals that Spectra reduces overall garment or armor weight by up to 30%, while flexibility metrics show Kevlar maintains better performance for wearability and ergonomic movement.
Impact and Ballistic Resistance
Kevlar and Spectra layers both provide advanced ballistic resistance, but Spectra fibers offer superior impact absorption due to their higher tensile strength and lighter weight, enhancing overall performance in body armor. Kevlar layers maintain excellent ballistic resistance with high energy dispersion capabilities, making them effective against blunt force trauma. The combination of Kevlar's durability and Spectra's impact resistance results in optimized multilayered armor solutions for enhanced soldier protection.
Thermal and Chemical Resistance
Kevlar layers exhibit superior thermal resistance, maintaining structural integrity at temperatures up to 450degC, compared to Spectra layers which degrade above 150degC. Chemically, Kevlar resists a broad spectrum of solvents, oils, and fuels, whereas Spectra is more susceptible to damage from hydrocarbon-based chemicals. This makes Kevlar the preferred choice for applications requiring high thermal stability and chemical endurance.
Popular Applications in Industry
Kevlar layers are extensively used in ballistic vests, helmets, and automotive tires due to their high tensile strength and resistance to impact and abrasion. Spectra layers find popularity in maritime safety equipment, cowhides for protective gloves, and aerospace components because of their superior strength-to-weight ratio and chemical resistance. Both materials dominate industries requiring durable, lightweight protective layers, but Kevlar is preferred for impact absorption while Spectra excels in cut and chemical resistance.
Cost and Availability Factors
Kevlar layers typically offer a cost advantage over Spectra layers due to lower raw material expenses and more established production processes, making them more accessible for large-scale applications. Spectra layers, derived from ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene, involve higher manufacturing costs and limited global availability, which can increase overall project budgets. Availability of Kevlar fibers benefits from a broader supplier network, whereas Spectra's niche market results in more restricted supply chains and potential lead times.
Maintenance and Longevity Considerations
Kevlar layers require regular inspection for fiber wear and UV damage as exposure can degrade its aramid fibers, impacting durability and safety. Spectra layers offer higher resistance to moisture and UV rays, reducing maintenance frequency and extending the lifespan of protective gear. Proper cleaning, avoiding harsh chemicals, and storage in a cool, dry place are critical for maximizing the longevity of both materials.
Choosing Between Kevlar and Spectra Layers
Kevlar layers provide exceptional tensile strength and thermal resistance, making them ideal for applications requiring heat and abrasion protection. Spectra layers, composed of ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene fibers, offer superior cut resistance and are lighter in weight, enhancing mobility and comfort. Choosing between Kevlar and Spectra layers depends on prioritizing either heat resistance and durability (Kevlar) or lightweight, high-strength cut protection (Spectra).
Kevlar layer vs Spectra layer Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com