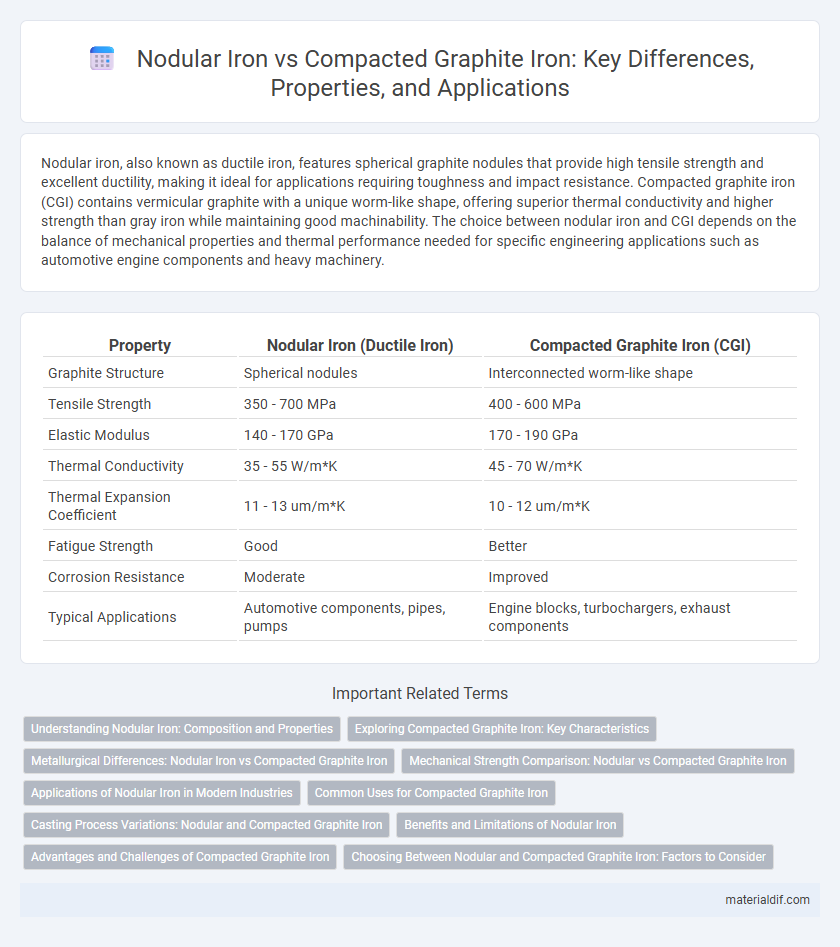
Nodular iron, also known as ductile iron, features spherical graphite nodules that provide high tensile strength and excellent ductility, making it ideal for applications requiring toughness and impact resistance. Compacted graphite iron (CGI) contains vermicular graphite with a unique worm-like shape, offering superior thermal conductivity and higher strength than gray iron while maintaining good machinability. The choice between nodular iron and CGI depends on the balance of mechanical properties and thermal performance needed for specific engineering applications such as automotive engine components and heavy machinery.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Nodular Iron (Ductile Iron) | Compacted Graphite Iron (CGI) |
|---|---|---|
| Graphite Structure | Spherical nodules | Interconnected worm-like shape |
| Tensile Strength | 350 - 700 MPa | 400 - 600 MPa |
| Elastic Modulus | 140 - 170 GPa | 170 - 190 GPa |
| Thermal Conductivity | 35 - 55 W/m*K | 45 - 70 W/m*K |
| Thermal Expansion Coefficient | 11 - 13 um/m*K | 10 - 12 um/m*K |
| Fatigue Strength | Good | Better |
| Corrosion Resistance | Moderate | Improved |
| Typical Applications | Automotive components, pipes, pumps | Engine blocks, turbochargers, exhaust components |
Understanding Nodular Iron: Composition and Properties
Nodular iron, also known as ductile iron, primarily consists of spherical graphite nodules dispersed within a pearlitic or ferritic matrix, which enhances its ductility and impact resistance. Its composition typically includes 3-4% carbon and 1.8-2.8% silicon, with smaller amounts of manganese, phosphorus, and sulfur to optimize mechanical properties. The spherical graphite structure minimizes stress concentration, resulting in superior tensile strength and elongation compared to other cast irons like compacted graphite iron.
Exploring Compacted Graphite Iron: Key Characteristics
Compacted Graphite Iron (CGI) exhibits a unique microstructure with worm-like graphite particles, enhancing its tensile strength and thermal conductivity compared to Nodular Iron. CGI offers superior fatigue resistance and improved thermal fatigue properties, making it ideal for engine components and heavy-duty applications. Its balanced combination of castability and mechanical performance positions CGI as an advanced alternative to traditional Nodular Iron in demanding industrial uses.
Metallurgical Differences: Nodular Iron vs Compacted Graphite Iron
Nodular iron, also known as ductile iron, features spherical graphite nodules that enhance ductility and impact resistance, resulting from magnesium treatment during casting. Compacted graphite iron (CGI) contains vermicular, or worm-like, graphite shapes that offer a microstructure between gray iron and nodular iron, providing improved thermal conductivity and strength. The metallurgical differences stem from graphite morphology controlled by the composition and cooling rate, affecting mechanical properties and suitability for engine components and heavy-duty applications.
Mechanical Strength Comparison: Nodular vs Compacted Graphite Iron
Nodular iron exhibits superior mechanical strength due to its spherical graphite structure, enhancing tensile strength and ductility compared to compacted graphite iron. Compacted graphite iron balances strength and thermal conductivity with its vermicular graphite shape, offering improved fatigue resistance but lower tensile strength than nodular iron. This makes nodular iron ideal for applications requiring higher impact resistance, while compacted graphite iron suits environments demanding thermal stability and moderate mechanical durability.
Applications of Nodular Iron in Modern Industries
Nodular iron, known for its exceptional tensile strength and ductility, is widely used in automotive components such as crankshafts, gears, and suspension parts. Its superior impact resistance and fatigue performance make it ideal for heavy machinery, pipelines, and agricultural equipment. Modern industries rely on nodular iron for durable, cost-effective solutions in construction, manufacturing, and energy sectors.
Common Uses for Compacted Graphite Iron
Compacted Graphite Iron (CGI) is commonly used in automotive components such as engine blocks and exhaust manifolds due to its superior strength and thermal conductivity compared to Nodular Iron. CGI also finds applications in heavy-duty diesel engines, turbocharger housings, and railway brake discs where durability under high stress and thermal stability are critical. The material's enhanced fatigue resistance and lower weight than traditional cast irons make it ideal for performance-critical industrial machinery and structural parts.
Casting Process Variations: Nodular and Compacted Graphite Iron
Nodular iron casting involves the use of magnesium or cerium treatments to promote graphite spheroidization, enhancing ductility and impact resistance. In contrast, compacted graphite iron casting requires precise control of inoculants and cooling rates to achieve its unique worm-like graphite structure, balancing strength and thermal conductivity. Variations in melting temperature, agitation, and inoculation significantly influence the final microstructure and mechanical properties of both nodular and compacted graphite iron castings.
Benefits and Limitations of Nodular Iron
Nodular iron, also known as ductile iron, offers high tensile strength, excellent ductility, and superior impact resistance due to its spherical graphite structure, making it ideal for automotive and heavy machinery components. However, its limitations include lower thermal conductivity and reduced vibration damping compared to compacted graphite iron, which can impact performance in high-temperature and high-vibration applications. Despite these drawbacks, nodular iron remains favored for applications requiring a balanced combination of strength, toughness, and machinability.
Advantages and Challenges of Compacted Graphite Iron
Compacted Graphite Iron (CGI) offers superior strength, thermal conductivity, and fatigue resistance compared to Nodular Iron, making it ideal for high-performance engine components and heavy-duty applications. CGI's unique microstructure improves wear resistance and reduces weight, enhancing overall efficiency and durability. Challenges include higher production costs and more complex machining processes due to its hardness and brittleness relative to Nodular Iron.
Choosing Between Nodular and Compacted Graphite Iron: Factors to Consider
Choosing between nodular iron and compacted graphite iron depends on factors such as mechanical strength, thermal conductivity, and application requirements. Nodular iron offers excellent ductility and impact resistance suitable for automotive components, while compacted graphite iron provides superior thermal fatigue resistance and vibration damping ideal for engine blocks and exhaust manifolds. Cost considerations and machinability also influence the selection process for specific industrial uses.
Nodular Iron vs Compacted Graphite Iron Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com