Iron galvanizing offers superior corrosion protection by coating the metal with a layer of zinc, which prevents rust formation and extends the lifespan of iron products. Iron painting provides an aesthetic finish and a basic protective barrier but requires regular maintenance to prevent peeling and rust exposure. Choosing galvanizing over painting is ideal for outdoor applications where long-term durability is essential.
Table of Comparison
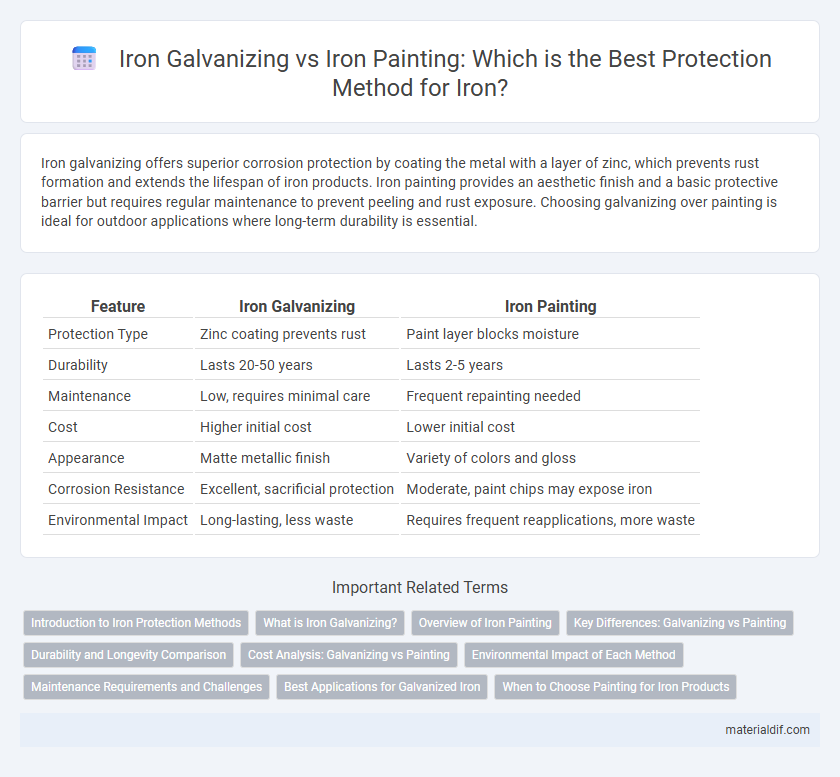
| Feature | Iron Galvanizing | Iron Painting |
|---|---|---|
| Protection Type | Zinc coating prevents rust | Paint layer blocks moisture |
| Durability | Lasts 20-50 years | Lasts 2-5 years |
| Maintenance | Low, requires minimal care | Frequent repainting needed |
| Cost | Higher initial cost | Lower initial cost |
| Appearance | Matte metallic finish | Variety of colors and gloss |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent, sacrificial protection | Moderate, paint chips may expose iron |
| Environmental Impact | Long-lasting, less waste | Requires frequent reapplications, more waste |
Introduction to Iron Protection Methods
Iron galvanizing involves coating iron with a protective layer of zinc, which prevents rust and corrosion by acting as a barrier and sacrificial anode, enhancing durability in harsh environments. Iron painting uses specialized rust-inhibitive primers and topcoats to create a waterproof shield that protects iron surfaces from moisture and oxidative damage. Both methods are essential for extending the lifespan of iron structures, with galvanizing offering more long-term corrosion resistance and painting providing customizable aesthetic options.
What is Iron Galvanizing?
Iron galvanizing is a corrosion protection process where a zinc coating is applied to the surface of iron or steel to prevent rust formation. This zinc layer acts as a sacrificial anode, providing long-lasting durability and resistance against environmental factors such as moisture and chemicals. Compared to iron painting, galvanizing offers superior protection by creating a metallurgical bond that extends the lifespan of iron structures significantly.
Overview of Iron Painting
Iron painting involves applying protective coatings to iron surfaces to prevent rust and corrosion, enhancing durability and aesthetic appeal. It typically uses primers and enamel or acrylic paints designed for metal, creating a barrier against moisture and oxygen. This method is cost-effective and allows for flexibility in color and finish, making it ideal for decorative and maintenance purposes.
Key Differences: Galvanizing vs Painting
Galvanizing involves coating iron with a layer of zinc to provide robust corrosion resistance, significantly extending the metal's lifespan by preventing rust. In contrast, iron painting offers a decorative and protective layer but tends to wear off faster, requiring frequent maintenance to avoid corrosion. The key difference lies in durability and protection, with galvanizing providing a permanent barrier against environmental damage, while painting offers less enduring, surface-level defense.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
Iron galvanizing creates a robust zinc coating that significantly enhances resistance to rust and corrosion, extending the metal's lifespan even in harsh environments. In contrast, iron painting provides a decorative layer that offers limited protection and requires frequent maintenance to prevent chipping and rust formation. Galvanizing is widely preferred for long-term durability in industrial and outdoor applications due to its superior corrosion resistance and minimal upkeep.
Cost Analysis: Galvanizing vs Painting
Iron galvanizing generally incurs higher upfront costs compared to iron painting due to the specialized zinc coating process, which provides long-term corrosion resistance. Iron painting typically involves lower initial expenses but may require frequent touch-ups and repainting, increasing maintenance costs over time. When evaluating total cost of ownership, galvanizing proves more economical for durability and reduced maintenance.
Environmental Impact of Each Method
Iron galvanizing involves coating iron with a layer of zinc, which prevents rust and extends the lifespan of the metal without frequent reapplications, reducing waste and resource consumption. In contrast, iron painting requires regular repainting with chemical-based paints that can release volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and heavy metals into the environment, contributing to air and water pollution. Galvanizing's longer durability and lower maintenance frequency make it a more environmentally sustainable choice compared to iron painting.
Maintenance Requirements and Challenges
Iron galvanizing requires minimal maintenance due to its robust zinc coating that prevents rust and corrosion for decades, making it ideal for outdoor structures exposed to harsh weather. Iron painting demands regular upkeep, including periodic repainting and inspection to prevent paint chipping and underlying rust formation, especially in high-moisture environments. Challenges with galvanizing include potential coating damage during installation, while painting faces issues such as paint degradation, UV exposure effects, and less effective corrosion protection over time.
Best Applications for Galvanized Iron
Galvanized iron offers superior corrosion resistance due to its protective zinc coating, making it ideal for outdoor structures, roofing, and industrial applications exposed to moisture and harsh weather conditions. Unlike painted iron, which requires regular maintenance and can chip or peel, galvanized iron provides long-lasting durability with minimal upkeep. This makes galvanized iron the best choice for environments where longevity and resistance to rust are critical.
When to Choose Painting for Iron Products
Painting is ideal for iron products exposed to indoor environments or low-humidity conditions where aesthetic customization and color variety are prioritized. It provides a smooth finish that can be easily touched up, making it suitable for decorative ironwork or furniture. For projects requiring enhanced corrosion resistance in high-moisture or outdoor settings, galvanizing remains the preferred option.
Iron Galvanizing vs Iron Painting Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com