Galvanized iron features a protective zinc coating that prevents rust and enhances durability in outdoor and industrial applications. Painted iron offers aesthetic customization and weather resistance but requires regular maintenance to avoid peeling and corrosion. Choosing between galvanized and painted iron depends on the balance between long-term protection and visual appeal for specific projects.
Table of Comparison
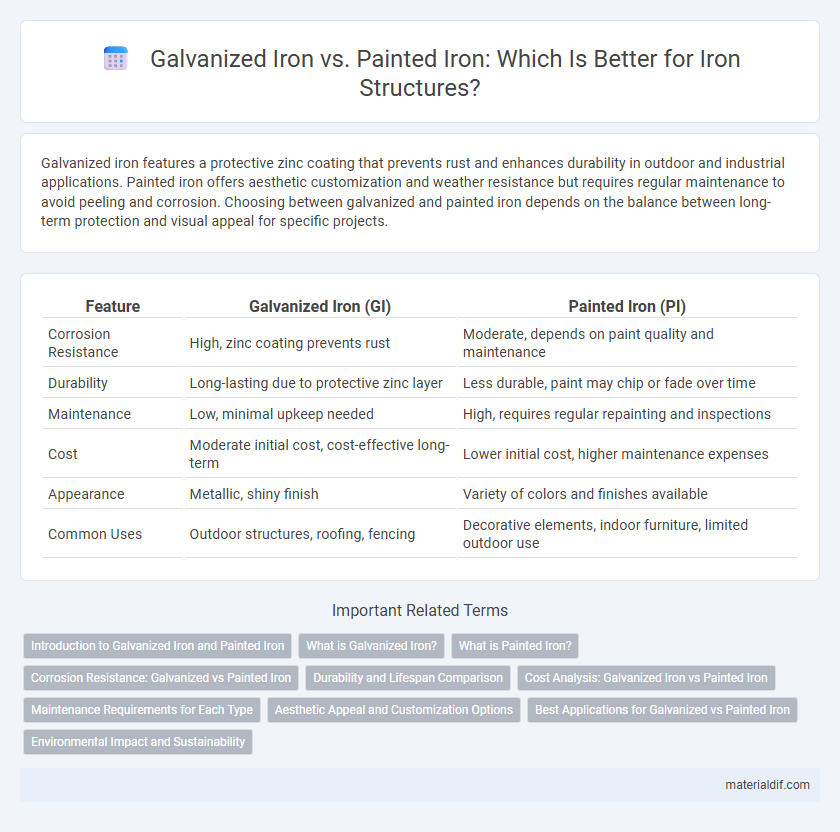
| Feature | Galvanized Iron (GI) | Painted Iron (PI) |
|---|---|---|
| Corrosion Resistance | High, zinc coating prevents rust | Moderate, depends on paint quality and maintenance |
| Durability | Long-lasting due to protective zinc layer | Less durable, paint may chip or fade over time |
| Maintenance | Low, minimal upkeep needed | High, requires regular repainting and inspections |
| Cost | Moderate initial cost, cost-effective long-term | Lower initial cost, higher maintenance expenses |
| Appearance | Metallic, shiny finish | Variety of colors and finishes available |
| Common Uses | Outdoor structures, roofing, fencing | Decorative elements, indoor furniture, limited outdoor use |
Introduction to Galvanized Iron and Painted Iron
Galvanized iron features a protective zinc coating that prevents rust and corrosion, making it ideal for outdoor and industrial applications. Painted iron involves applying a layer of paint for aesthetic appeal and additional surface protection, but it requires more maintenance to prevent chipping and exposure to moisture. Both materials offer durability, with galvanized iron excelling in long-term corrosion resistance and painted iron providing customizable finishes.
What is Galvanized Iron?
Galvanized iron refers to steel or iron coated with a protective layer of zinc to prevent rust and corrosion, enhancing its durability in outdoor and industrial environments. This zinc coating provides superior resistance against moisture and chemical exposure compared to regular painted iron, which relies solely on surface paint for protection. The galvanization process extends the lifespan of the iron by minimizing oxidation and maintenance requirements, making it ideal for construction, roofing, and automotive applications.
What is Painted Iron?
Painted iron is steel or iron coated with a layer of paint to prevent rust and corrosion while enhancing its aesthetic appeal. The paint acts as a protective barrier against moisture, chemicals, and environmental factors that typically cause iron to oxidize and deteriorate. Compared to galvanized iron, which uses a zinc coating for corrosion resistance, painted iron relies on surface coatings that can be reapplied and customized in different colors and finishes.
Corrosion Resistance: Galvanized vs Painted Iron
Galvanized iron exhibits superior corrosion resistance due to its zinc coating, which acts as a sacrificial barrier preventing rust formation even if the surface is scratched. Painted iron relies on a protective paint layer that can chip or wear over time, exposing the metal underneath to moisture and air, leading to rust. Zinc's cathodic protection in galvanized iron extends the lifespan significantly compared to standard painted iron surfaces.
Durability and Lifespan Comparison
Galvanized iron offers superior durability through its zinc coating that protects against rust and corrosion, significantly extending its lifespan compared to painted iron. Painted iron relies on surface coatings that can chip or peel over time, exposing the metal to environmental damage and reducing its longevity. In environments with high moisture or industrial pollution, galvanized iron typically lasts 30-50 years, whereas painted iron may require maintenance or replacement within 10-15 years.
Cost Analysis: Galvanized Iron vs Painted Iron
Galvanized iron typically incurs higher initial costs due to the zinc coating process, which enhances corrosion resistance and extends lifespan, reducing long-term maintenance expenses. Painted iron offers lower upfront prices but demands frequent repainting and upkeep, leading to increased cumulative costs over time. Evaluating total cost of ownership, galvanized iron proves more cost-effective for projects prioritizing durability and minimal maintenance.
Maintenance Requirements for Each Type
Galvanized iron requires minimal maintenance due to its zinc coating which prevents rust and corrosion, making it ideal for outdoor applications exposed to moisture. Painted iron necessitates regular upkeep, such as periodic repainting and rust treatment, to maintain its protective layer and aesthetic appeal. Over time, painted iron is more prone to chipping and corrosion if not properly maintained.
Aesthetic Appeal and Customization Options
Galvanized iron offers a sleek, metallic finish that resists rust and requires minimal maintenance, making it ideal for industrial and contemporary designs. Painted iron provides diverse color options and finishes, enabling tailored aesthetic appeal that matches specific design themes and personal preferences. Both materials allow customization, but painted iron excels in versatility with a wide range of hues and textures to enhance architectural and decorative applications.
Best Applications for Galvanized vs Painted Iron
Galvanized iron, coated with a layer of zinc, offers superior corrosion resistance, making it ideal for outdoor structures, roofing, and environments exposed to moisture. Painted iron provides enhanced aesthetic appeal and additional protection against rust, suitable for indoor furniture, decorative elements, and areas with minimal exposure to harsh weather. Choosing galvanized iron ensures durable performance in industrial and marine applications, while painted iron is preferred for customizable finishes in residential and commercial interiors.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Galvanized iron offers superior corrosion resistance due to its zinc coating, reducing the frequency of replacement and lowering long-term environmental impact compared to painted iron, which often requires reapplication of chemical coatings that can release volatile organic compounds (VOCs). The production of galvanized iron involves energy-intensive processes but results in longer-lasting durability and recyclability, contributing to sustainability by minimizing waste. Painted iron may have a lower initial manufacturing carbon footprint but demands frequent maintenance and disposal of paint waste, posing greater risks to soil and water contamination.
Galvanized Iron vs Painted Iron Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com