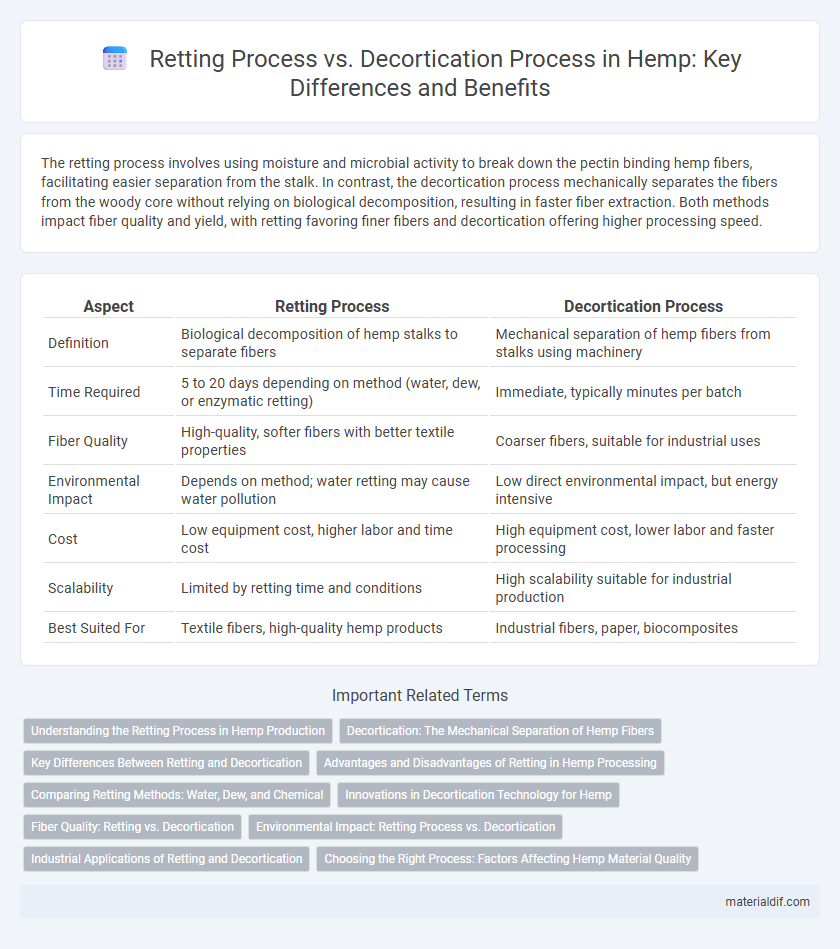
The retting process involves using moisture and microbial activity to break down the pectin binding hemp fibers, facilitating easier separation from the stalk. In contrast, the decortication process mechanically separates the fibers from the woody core without relying on biological decomposition, resulting in faster fiber extraction. Both methods impact fiber quality and yield, with retting favoring finer fibers and decortication offering higher processing speed.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Retting Process | Decortication Process |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Biological decomposition of hemp stalks to separate fibers | Mechanical separation of hemp fibers from stalks using machinery |
| Time Required | 5 to 20 days depending on method (water, dew, or enzymatic retting) | Immediate, typically minutes per batch |
| Fiber Quality | High-quality, softer fibers with better textile properties | Coarser fibers, suitable for industrial uses |
| Environmental Impact | Depends on method; water retting may cause water pollution | Low direct environmental impact, but energy intensive |
| Cost | Low equipment cost, higher labor and time cost | High equipment cost, lower labor and faster processing |
| Scalability | Limited by retting time and conditions | High scalability suitable for industrial production |
| Best Suited For | Textile fibers, high-quality hemp products | Industrial fibers, paper, biocomposites |
Understanding the Retting Process in Hemp Production
The retting process in hemp production involves microbial or chemical treatment to break down pectin and separate fiber from the stalk, enhancing fiber quality and ease of extraction. This traditional method contrasts with decortication, which mechanically separates the fiber without relying on microbial activity. Understanding retting is crucial for optimizing fiber strength and achieving desired textile or industrial applications.
Decortication: The Mechanical Separation of Hemp Fibers
Decortication is a mechanical process that separates hemp fibers from the woody core, significantly improving fiber quality and reducing reliance on water-intensive retting. This method involves the use of specialized machinery such as roller decorticators or hammer mills to efficiently extract bast fibers, preserving fiber length and strength. Unlike retting, decortication offers faster processing times and environmentally friendly advantages by minimizing microbial degradation and wastewater production.
Key Differences Between Retting and Decortication
Retting process involves microbial or chemical treatment to break down the pectin binding hemp fibers, facilitating easier fiber separation, while decortication is a mechanical process that crushes and separates the fibers from the stalk without microbial activity. Retting typically results in higher fiber quality and softness but takes longer time and requires controlled moisture conditions, whereas decortication offers faster processing and higher throughput but may produce coarser fibers with more impurities. The choice between retting and decortication significantly affects fiber properties, industrial applications, and overall production efficiency in hemp processing.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Retting in Hemp Processing
Retting in hemp processing involves using moisture and microbes to separate fiber from the stalk, offering advantages such as enhanced fiber quality and increased softness. However, its disadvantages include higher labor intensity, longer processing time, and susceptibility to weather conditions that can affect consistency. Compared to decortication, retting delivers finer fibers but demands careful control to prevent over-retting and fiber degradation.
Comparing Retting Methods: Water, Dew, and Chemical
Water retting offers thorough fiber separation by submerging hemp stalks in water for 7-14 days, promoting microbial activity that breaks down pectin. Dew retting relies on natural environmental moisture and microbial action over 2-3 weeks, resulting in lower water usage but less uniform fiber quality. Chemical retting accelerates the process using enzymatic or alkaline treatments, providing faster fiber extraction with potential environmental concerns due to chemical waste.
Innovations in Decortication Technology for Hemp
Innovations in decortication technology for hemp have significantly enhanced fiber extraction efficiency by integrating advanced mechanical separators and automated fiber cleaning systems. Modern decorticators minimize fiber damage and increase throughput, enabling higher-quality bast fiber production suitable for textiles and composites. These technological advancements outperform traditional retting processes by reducing water usage and processing time, aligning with sustainable hemp cultivation practices.
Fiber Quality: Retting vs. Decortication
Retting yields higher-quality hemp fibers by breaking down pectins naturally, resulting in longer, softer, and more flexible fibers ideal for textiles. Decortication mechanically separates fibers quickly but often causes fiber damage, producing coarser and shorter fibers best suited for industrial applications. The choice between retting and decortication significantly impacts fiber strength, fineness, and suitability for specific end uses in hemp production.
Environmental Impact: Retting Process vs. Decortication
The retting process, which involves soaking hemp stalks to break down pectin, typically consumes significant water resources and can lead to water pollution if wastewater is not properly managed. In contrast, the decortication process mechanically separates the fiber from the stalk with minimal water use, reducing the risk of environmental contamination. Decortication is often considered more sustainable due to its lower ecological footprint and reduced water and chemical usage compared to traditional retting methods.
Industrial Applications of Retting and Decortication
The retting process, involving microbial or chemical breakdown of pectin binding hemp fibers, is crucial for producing high-quality bast fibers used in textiles and biocomposites, enhancing fiber flexibility and strength. Decortication mechanically separates the hemp stalk into fiber and hurd, facilitating large-scale industrial applications such as paper production, biofuel, and animal bedding due to its efficiency and scalability. Both processes are integral in industrial hemp production, with retting preferred for premium fiber quality and decortication favored for rapid, bulk material processing.
Choosing the Right Process: Factors Affecting Hemp Material Quality
Choosing the right processing method for hemp fibers--retting or decortication--depends heavily on factors such as fiber quality, intended end-use, and environmental conditions. Retting utilizes microbial or chemical processes to break down pectins, yielding finer and longer fibers ideal for textiles, while decortication mechanically separates fibers, resulting in coarser strands suited for composites or construction materials. Evaluating factors like processing efficiency, fiber strength, and moisture content is crucial to optimize hemp material quality for specific industrial applications.
Retting Process vs Decortication Process Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com