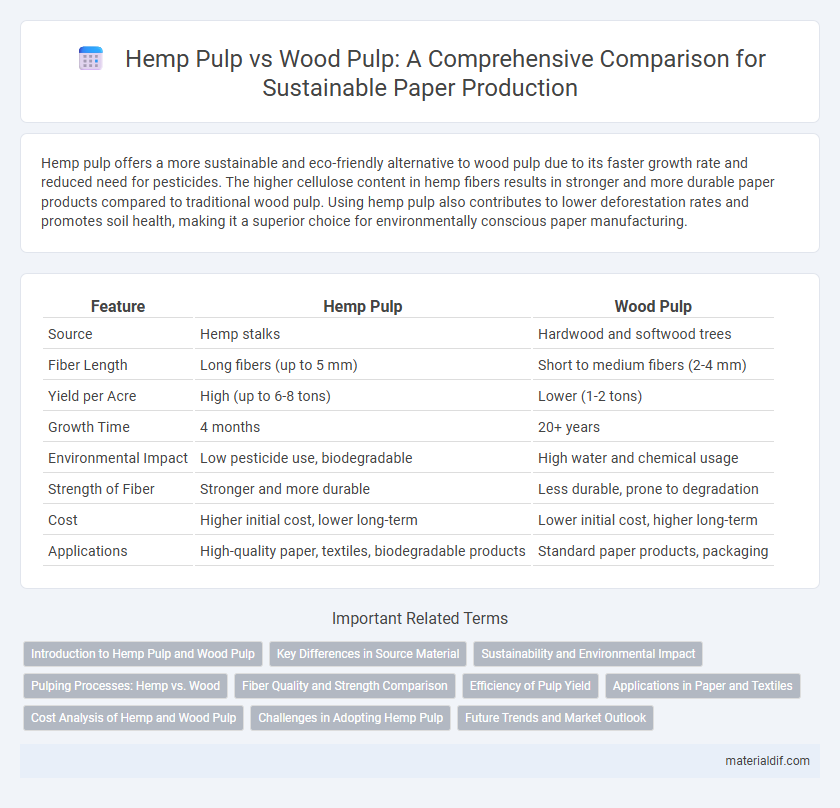
Hemp pulp offers a more sustainable and eco-friendly alternative to wood pulp due to its faster growth rate and reduced need for pesticides. The higher cellulose content in hemp fibers results in stronger and more durable paper products compared to traditional wood pulp. Using hemp pulp also contributes to lower deforestation rates and promotes soil health, making it a superior choice for environmentally conscious paper manufacturing.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Hemp Pulp | Wood Pulp |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Hemp stalks | Hardwood and softwood trees |
| Fiber Length | Long fibers (up to 5 mm) | Short to medium fibers (2-4 mm) |
| Yield per Acre | High (up to 6-8 tons) | Lower (1-2 tons) |
| Growth Time | 4 months | 20+ years |
| Environmental Impact | Low pesticide use, biodegradable | High water and chemical usage |
| Strength of Fiber | Stronger and more durable | Less durable, prone to degradation |
| Cost | Higher initial cost, lower long-term | Lower initial cost, higher long-term |
| Applications | High-quality paper, textiles, biodegradable products | Standard paper products, packaging |
Introduction to Hemp Pulp and Wood Pulp
Hemp pulp, derived from the stalks of hemp plants, contains long fibers that contribute to stronger and more durable paper compared to traditional wood pulp, which comes from trees. Unlike wood pulp that requires harsh chemicals and extensive processing, hemp pulp demands fewer chemicals and less energy, making it a more environmentally friendly option. The higher cellulose content in hemp pulp results in higher quality paper products with increased longevity and reduced yellowing over time.
Key Differences in Source Material
Hemp pulp and wood pulp differ primarily in their source material, where hemp is derived from the stalks of the Cannabis sativa plant, while wood pulp comes from trees such as pine, spruce, or eucalyptus. Hemp fibers are longer and contain lower lignin content compared to wood fibers, resulting in a more efficient extraction process and higher-quality pulp. The renewable nature and rapid growth cycle of hemp make it a more sustainable alternative to traditional wood pulp for paper and textile production.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Hemp pulp requires significantly less water and fewer pesticides compared to wood pulp, making it a more sustainable choice for paper production. It grows rapidly, producing up to four times more fiber per acre annually than trees, which reduces deforestation and habitat loss. Additionally, hemp's ability to capture carbon dioxide during growth contributes to lowering the carbon footprint in pulp manufacturing processes.
Pulping Processes: Hemp vs. Wood
Hemp pulp production uses a chemical-free or mild chemical retting process that breaks down hemp fibers into long, strong cellulose strands, enhancing paper strength and durability. In contrast, wood pulp requires energy-intensive chemical pulping methods like kraft or sulfite processes to remove lignin and separate cellulose fibers, often resulting in shorter fiber length. Hemp's naturally low lignin content simplifies pulping, reduces chemical usage, and lowers environmental impact compared to traditional wood pulp production.
Fiber Quality and Strength Comparison
Hemp pulp exhibits longer and stronger fibers compared to wood pulp, resulting in superior tensile strength and durability in paper production. The cellulose content in hemp fibers ranges from 70 to 74%, significantly higher than the 40 to 50% typically found in wood pulp, enhancing fiber quality and reducing paper porosity. These attributes make hemp pulp an eco-friendly alternative for producing high-quality, resilient paper products.
Efficiency of Pulp Yield
Hemp pulp produces significantly higher fiber yield per acre compared to wood pulp, offering up to three times more pulp from the same land area. The rapid growth cycle of hemp allows for multiple harvests annually, increasing overall pulp production efficiency. Hemp fibers are also longer and stronger, enhancing the quality and yield efficiency of the final pulp product.
Applications in Paper and Textiles
Hemp pulp offers higher cellulose content and longer fibers compared to wood pulp, resulting in stronger, more durable paper suitable for high-quality printing and specialty paper products. In textiles, hemp fibers provide natural resistance to pests and mold, superior breathability, and durability, making them ideal for eco-friendly clothing, upholstery, and industrial fabrics. The sustainable cultivation of hemp also reduces environmental impact by requiring less water and pesticides than traditional wood sources used in paper and textile industries.
Cost Analysis of Hemp and Wood Pulp
Hemp pulp generally incurs higher initial processing costs than wood pulp due to its labor-intensive extraction methods and limited scale of industrial equipment. However, hemp offers cost advantages through faster growth cycles, yielding up to four harvests per year compared to wood's 20-30 years, reducing long-term raw material expenses. Economically, hemp's higher fiber yield per acre and lower environmental remediation costs position it as a viable alternative despite current market price disparities with conventional wood pulp.
Challenges in Adopting Hemp Pulp
Hemp pulp presents challenges in adoption due to higher production costs and limited processing infrastructure compared to wood pulp, which benefits from well-established supply chains. The lower lignin content in hemp requires adjustments in pulping and bleaching processes, resulting in increased chemical usage and equipment modifications. Regulatory constraints and inconsistent hemp crop yields further complicate its integration into the conventional paper manufacturing industry.
Future Trends and Market Outlook
Hemp pulp offers a sustainable alternative to wood pulp, with faster growth cycles and higher cellulose content improving its market appeal in the paper and textile industries. Advancements in processing technology are reducing production costs, driving increased adoption of hemp pulp in eco-friendly packaging and bio-composites. Market analysis predicts a growing demand for hemp pulp driven by stringent environmental regulations and rising consumer preference for renewable, biodegradable materials.
hemp pulp vs wood pulp Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com