Hemp protein offers a complete amino acid profile with easy digestibility and is rich in fiber, supporting gut health better than many plant-based proteins. Soy protein, while also complete, contains compounds like phytoestrogens that may affect hormone balance in sensitive individuals. Choosing hemp protein provides a hypoallergenic alternative with omega-3 fatty acids, making it an ideal option for those seeking a natural, nutrient-dense plant protein.
Table of Comparison
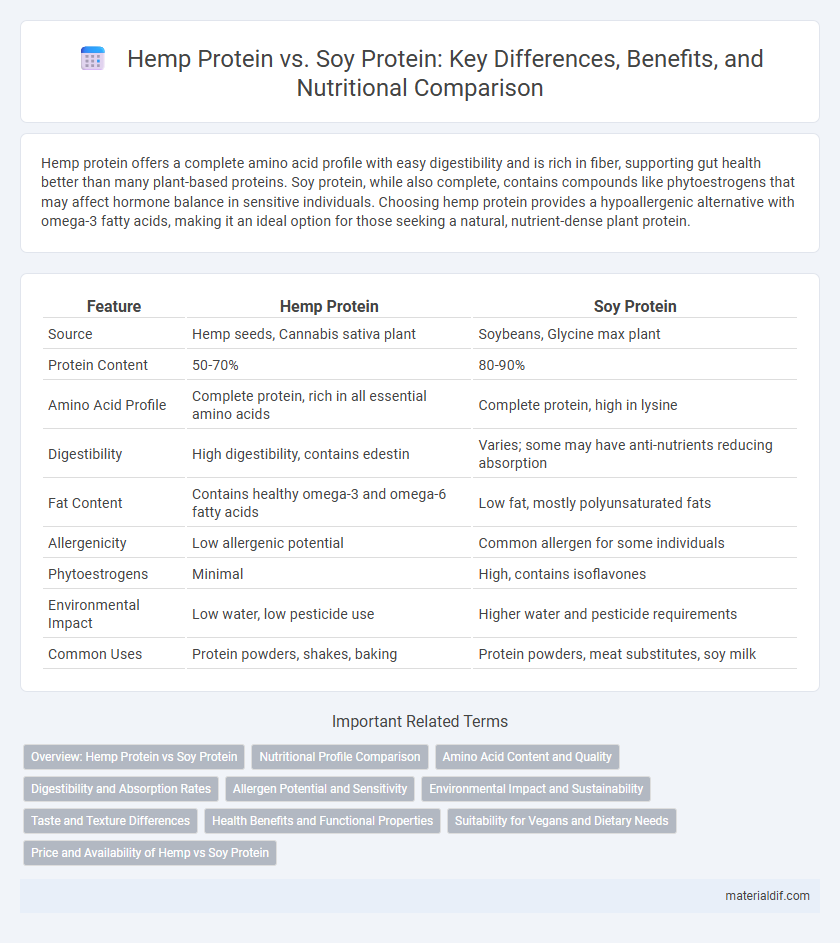
| Feature | Hemp Protein | Soy Protein |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Hemp seeds, Cannabis sativa plant | Soybeans, Glycine max plant |
| Protein Content | 50-70% | 80-90% |
| Amino Acid Profile | Complete protein, rich in all essential amino acids | Complete protein, high in lysine |
| Digestibility | High digestibility, contains edestin | Varies; some may have anti-nutrients reducing absorption |
| Fat Content | Contains healthy omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids | Low fat, mostly polyunsaturated fats |
| Allergenicity | Low allergenic potential | Common allergen for some individuals |
| Phytoestrogens | Minimal | High, contains isoflavones |
| Environmental Impact | Low water, low pesticide use | Higher water and pesticide requirements |
| Common Uses | Protein powders, shakes, baking | Protein powders, meat substitutes, soy milk |
Overview: Hemp Protein vs Soy Protein
Hemp protein contains all nine essential amino acids, making it a complete plant-based protein, with a digestibility score slightly lower than soy protein, which is also a complete protein and widely known for its high bioavailability. Hemp protein offers additional benefits such as a higher fiber content and rich omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids, while soy protein provides a robust source of isoflavones, known for their antioxidant properties. Both proteins support muscle recovery and heart health, but hemp protein is often preferred for its minimal processing and hypoallergenic profile compared to soy.
Nutritional Profile Comparison
Hemp protein contains all nine essential amino acids, making it a complete plant-based protein source with a high digestibility rate of around 90%. Soy protein also offers a complete amino acid profile but has a slightly higher protein content per serving, typically around 25-30 grams compared to hemp's 15-20 grams. Hemp protein provides more fiber and essential fatty acids like omega-3 and omega-6, whereas soy protein is richer in isoflavones and generally lower in fat.
Amino Acid Content and Quality
Hemp protein contains all nine essential amino acids, making it a complete protein, while soy protein is also complete but higher in lysine, which is often limited in plant-based diets. Hemp protein provides a balanced ratio of essential amino acids with superior levels of arginine and glutamic acid, promoting cardiovascular health and muscle repair. Despite soy protein's high protein concentration and digestibility, hemp protein offers better omega fatty acid content and fiber, contributing to overall nutrient quality.
Digestibility and Absorption Rates
Hemp protein offers a digestibility rate of approximately 90%, making it easier for the body to break down compared to soy protein, which has a digestibility score around 85%. Its high fiber content slows digestion slightly, enhancing nutrient absorption over time versus the quicker absorption of soy protein. The presence of all nine essential amino acids in hemp protein ensures a balanced intake, supporting efficient utilization during digestion.
Allergen Potential and Sensitivity
Hemp protein exhibits a lower allergen potential compared to soy protein, making it a suitable alternative for individuals with soy allergies or sensitivities. Unlike soy, which contains phytoestrogens and may trigger allergic reactions or digestive discomfort in sensitive individuals, hemp protein is hypoallergenic and generally easier to digest due to its rich fiber and essential fatty acid content. Choosing hemp protein can reduce the risk of allergenic responses while providing a complete amino acid profile for optimal nutrition.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Hemp protein boasts a significantly lower environmental impact compared to soy protein due to its minimal water requirements and ability to grow in poor soil without pesticides. Hemp cultivation improves soil health through natural aeration and carbon sequestration, supporting long-term sustainability. Conversely, large-scale soy farming often involves deforestation and high water consumption, posing greater risks to ecosystems and biodiversity.
Taste and Texture Differences
Hemp protein has a nutty, earthy flavor with a slightly gritty texture, making it a preferred choice for those who enjoy a more natural, wholesome taste in smoothies and baked goods. In contrast, soy protein tends to have a milder, more neutral flavor and a smoother, creamier texture, which blends well in a variety of recipes without overpowering other ingredients. The distinct taste and texture profiles of hemp and soy proteins significantly influence their culinary applications and consumer preferences.
Health Benefits and Functional Properties
Hemp protein contains all nine essential amino acids and is rich in omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids, supporting heart health and reducing inflammation. Soy protein is a complete protein with high isoflavones content, which may help lower cholesterol and support bone health. Functionally, hemp protein offers superior digestibility and hypoallergenic properties, while soy protein provides better emulsifying and gelling capabilities in food products.
Suitability for Vegans and Dietary Needs
Hemp protein is highly suitable for vegans due to its complete amino acid profile and minimal processing, offering an easily digestible plant-based option rich in fiber and essential fatty acids. Soy protein also supports vegan diets, providing a complete protein with high protein content, but some individuals may avoid soy due to allergies or concerns about phytoestrogens. Both proteins accommodate diverse dietary needs, though hemp's hypoallergenic properties make it preferable for those with sensitivities or digestive issues.
Price and Availability of Hemp vs Soy Protein
Hemp protein is generally priced higher than soy protein due to limited cultivation and processing infrastructure, resulting in less market availability. Soy protein benefits from widespread global production, making it more affordable and readily accessible in most regions. Consumers often choose soy protein for budget-friendly options, while hemp protein appeals to niche markets prioritizing organic and sustainable sources despite its higher cost.
Hemp protein vs Soy protein Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com