Decorticated hemp refers to the fibers extracted from the outer layer of the hemp stalk, offering higher quality and purity for textile and industrial applications. Whole stem hemp includes the entire stalk, providing additional biomass for uses such as biofuel, animal bedding, and construction materials but with lower fiber quality. The choice between decorticated and whole stem hemp depends on the intended end product, balancing fiber quality and material versatility.
Table of Comparison
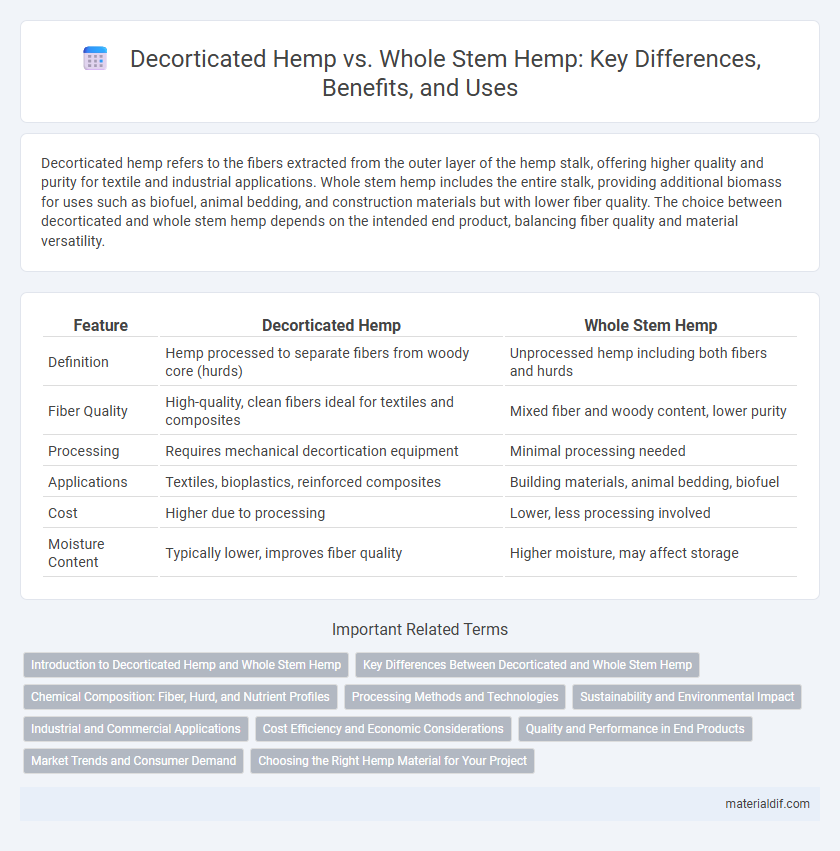
| Feature | Decorticated Hemp | Whole Stem Hemp |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Hemp processed to separate fibers from woody core (hurds) | Unprocessed hemp including both fibers and hurds |
| Fiber Quality | High-quality, clean fibers ideal for textiles and composites | Mixed fiber and woody content, lower purity |
| Processing | Requires mechanical decortication equipment | Minimal processing needed |
| Applications | Textiles, bioplastics, reinforced composites | Building materials, animal bedding, biofuel |
| Cost | Higher due to processing | Lower, less processing involved |
| Moisture Content | Typically lower, improves fiber quality | Higher moisture, may affect storage |
Introduction to Decorticated Hemp and Whole Stem Hemp
Decorticated hemp refers to hemp stalks that have been processed to remove the outer woody core, yielding fibers suitable for textiles, composites, and paper production. Whole stem hemp includes the entire plant stalk, preserving both the hurd and fiber components, commonly used in construction materials and bio-composites. The choice between decorticated and whole stem hemp impacts product quality, processing requirements, and end-use applications in industries such as automotive, construction, and textiles.
Key Differences Between Decorticated and Whole Stem Hemp
Decorticated hemp refers to hemp stalks that have been processed to remove the outer woody core, resulting in separate bast fibers and hurd, whereas whole stem hemp consists of the entire unprocessed stalk. Decorticated hemp provides higher-quality fibers ideal for textiles and composites, while whole stem hemp retains all components useful for biomass, biofuel, and paper production. The key differences lie in processing level, fiber quality, and application versatility, making decorticated hemp preferable for fine fiber industries and whole stem hemp advantageous for bulk material uses.
Chemical Composition: Fiber, Hurd, and Nutrient Profiles
Decorticated hemp consists mainly of separated bast fibers, which contain higher cellulose content and lower lignin levels compared to whole stem hemp, making it ideal for textile and composite applications. Whole stem hemp retains both fibers and hurd, offering a balanced chemical composition with significant amounts of cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin, along with a nutrient-rich profile beneficial for bioenergy and animal bedding. Nutrient profiles differ as decorticated hemp fibers have lower mineral content, while hurd contains higher concentrations of nutrients such as calcium, potassium, and magnesium.
Processing Methods and Technologies
Decorticated hemp undergoes mechanical processing where the outer bast fibers are separated from the inner woody core through decortication machines, enhancing fiber quality and usability for textiles and composites. Whole stem hemp retains both bast fibers and hurd, requiring additional chemical or enzymatic treatments to break down lignin and improve material flexibility for applications like bioplastics or animal bedding. Advanced technologies, including steam explosion and microbial retting, optimize fiber extraction and material properties by targeting specific lignocellulosic components in both processing methods.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Decorticated hemp involves separating the bast fibers from the woody core, resulting in less waste and higher-quality fibers that are ideal for sustainable textiles and biocomposites. Whole stem hemp uses the entire stalk, maximizing biomass utilization but often requires more energy-intensive processing, impacting its overall environmental footprint. Choosing decorticated hemp supports resource efficiency and reduces carbon emissions compared to the whole stem approach, making it a greener option for eco-conscious industries.
Industrial and Commercial Applications
Decorticated hemp fibers offer superior quality for textile manufacturing, paper production, and biodegradable composites due to their refined texture and higher cellulose content. Whole stem hemp retains both bast fibers and woody core (hurds), making it ideal for construction materials such as hempcrete, animal bedding, and biofuel feedstock, where bulk and absorbency are crucial. Industrial processes leverage decorticated hemp for high-performance applications, while whole stem hemp provides cost-effective, sustainable raw material for broader commercial use.
Cost Efficiency and Economic Considerations
Decorticated hemp demonstrates superior cost efficiency compared to whole stem hemp due to reduced processing expenses and increased fiber quality that commands higher market prices. Investment in decortication technology can yield long-term economic benefits by minimizing waste and enhancing product consistency for industries such as textiles, construction, and bioplastics. Whole stem hemp requires less initial processing but often incurs higher downstream costs related to material separation and lower-value fiber output, impacting overall profitability.
Quality and Performance in End Products
Decorticated hemp offers superior quality in end products due to the removal of the outer bark, resulting in cleaner fibers with higher tensile strength and enhanced durability. Whole stem hemp retains the full stalk structure, providing a coarser material that can improve bulk but may reduce uniformity and performance in textiles and composites. Choosing decorticated hemp ensures better fiber consistency and optimized performance in applications requiring high-quality, lightweight, and strong materials.
Market Trends and Consumer Demand
Decorticated hemp, favored for its refined fiber quality, drives strong demand in textile and biocomposite markets, outperforming whole stem hemp in value. Market trends indicate a growing preference for decorticated hemp due to its versatility and higher processing efficiency, especially in sustainable product manufacturing. Consumer demand intensifies for eco-friendly materials, positioning decorticated hemp as a key player in green innovation and premium hemp-based goods.
Choosing the Right Hemp Material for Your Project
Decorticated hemp provides refined fibers free from bark and woody core, ideal for textile and composite applications requiring smooth, uniform materials. Whole stem hemp retains the outer bark and woody core, offering enhanced structural integrity and higher biomass useful in construction and biofuel production. Selecting between decorticated and whole stem hemp hinges on project specifications such as fiber quality, strength, and processing requirements.
Decorticated Hemp vs Whole Stem Hemp Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com