Hemp composites offer a sustainable alternative to glass fiber composites by providing comparable strength with significantly lower environmental impact due to their renewable nature and biodegradability. Hemp fibers enhance composite materials by reducing weight and improving vibration damping, resulting in improved performance in automotive and construction applications. The natural compatibility of hemp with bio-based resins also enables the development of eco-friendly composites that reduce reliance on non-renewable resources and lower carbon emissions.
Table of Comparison
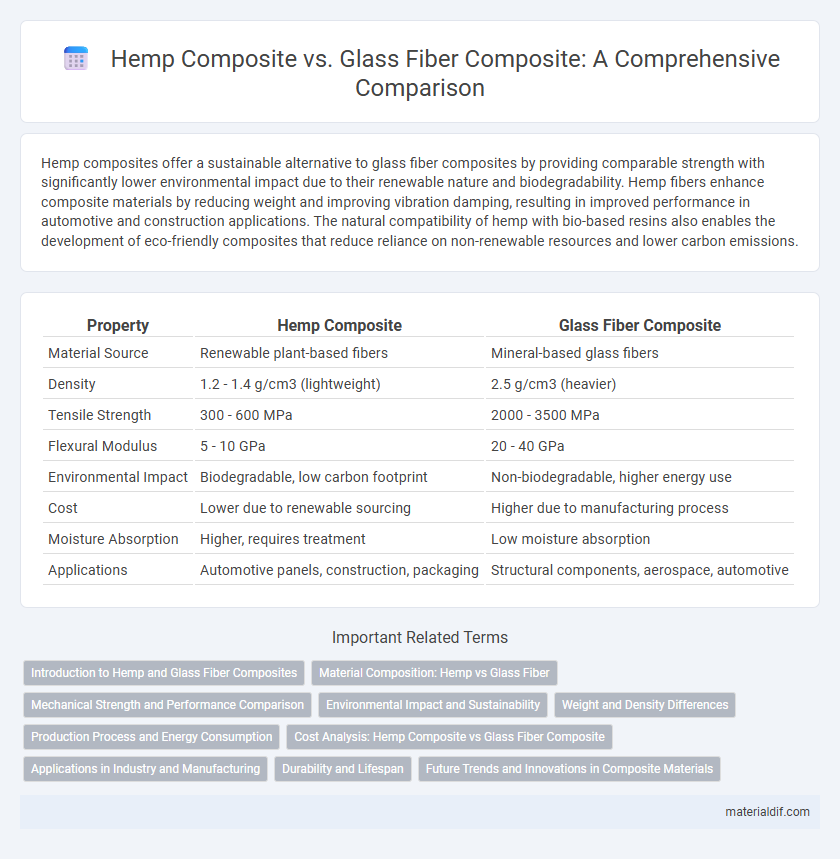
| Property | Hemp Composite | Glass Fiber Composite |
|---|---|---|
| Material Source | Renewable plant-based fibers | Mineral-based glass fibers |
| Density | 1.2 - 1.4 g/cm3 (lightweight) | 2.5 g/cm3 (heavier) |
| Tensile Strength | 300 - 600 MPa | 2000 - 3500 MPa |
| Flexural Modulus | 5 - 10 GPa | 20 - 40 GPa |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable, low carbon footprint | Non-biodegradable, higher energy use |
| Cost | Lower due to renewable sourcing | Higher due to manufacturing process |
| Moisture Absorption | Higher, requires treatment | Low moisture absorption |
| Applications | Automotive panels, construction, packaging | Structural components, aerospace, automotive |
Introduction to Hemp and Glass Fiber Composites
Hemp composites are made from natural hemp fibers combined with a polymer matrix, offering lightweight, biodegradable, and sustainable alternatives to traditional composites. Glass fiber composites consist of fine glass fibers embedded in a resin, providing high strength, durability, and resistance to corrosion, widely used in automotive and construction industries. The comparison emphasizes hemp's eco-friendly attributes versus glass fiber's superior mechanical properties and widespread industrial adoption.
Material Composition: Hemp vs Glass Fiber
Hemp composites consist of natural fibers derived from the stalks of Cannabis sativa plants, offering lightweight and biodegradable material properties, while glass fiber composites are made from fine strands of glass woven into mats or fabrics, providing superior tensile strength and durability. The cellulose content in hemp fibers contributes to better moisture regulation and lower density compared to the high silica content of glass fibers, which enhances thermal resistance but increases weight. Hemp composites present an eco-friendly alternative with renewable resources, whereas glass fiber composites rely on energy-intensive processes involving non-renewable materials.
Mechanical Strength and Performance Comparison
Hemp composites exhibit lower tensile strength and stiffness compared to glass fiber composites, with hemp fiber tensile strength ranging from 250 to 900 MPa versus glass fiber's 2000 to 3500 MPa. However, hemp composites offer superior impact resistance and better energy absorption, enhancing performance in applications requiring flexibility and vibration damping. The reduced density of hemp composites also contributes to lighter structures, providing advantages in weight-sensitive industries despite the lower mechanical strength.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Hemp composites exhibit significantly lower environmental impact than glass fiber composites due to their renewable origin and biodegradable properties, reducing landfill waste and carbon footprint. The cultivation of hemp requires less water and pesticides compared to glass fiber production, which involves energy-intensive processes and non-renewable resources. Sustainability advantages of hemp composites include carbon sequestration during growth and enhanced end-of-life disposal options, making them a preferred choice for eco-friendly manufacturing.
Weight and Density Differences
Hemp composites typically exhibit lower density values, around 1.2 g/cm3, compared to glass fiber composites, which range from 1.8 to 2.0 g/cm3, resulting in significantly reduced weight. The lightweight nature of hemp composite materials makes them ideal for automotive and aerospace applications seeking enhanced fuel efficiency and easier handling. Weight reduction of up to 30% is achievable with hemp composites without sacrificing mechanical strength, emphasizing their potential as sustainable, high-performance alternatives to traditional glass fiber composites.
Production Process and Energy Consumption
Hemp composites require significantly less energy during production compared to glass fiber composites, as hemp fibers undergo simpler mechanical processing without the need for energy-intensive melting or glass fiber spinning. The natural origin of hemp fibers allows for lower temperature treatments and reduced use of chemicals, resulting in lower carbon emissions throughout the manufacturing process. This energy efficiency makes hemp composites a more sustainable alternative in composite material production.
Cost Analysis: Hemp Composite vs Glass Fiber Composite
Hemp composites offer significant cost advantages over glass fiber composites due to lower raw material prices and reduced energy consumption during production. The cultivation of hemp requires fewer fertilizers and less water compared to the synthetic processes involved in glass fiber manufacturing, resulting in decreased overall expenses. Maintenance and disposal costs also favor hemp composites, attributed to their biodegradability and eco-friendly lifecycle.
Applications in Industry and Manufacturing
Hemp composites offer advantages in automotive, construction, and consumer goods by providing lightweight, biodegradable, and cost-effective alternatives to glass fiber composites. Glass fiber composites excel in high-strength and thermal resistance applications, making them ideal for aerospace, marine, and heavy-duty industrial components. Manufacturers increasingly adopt hemp composites to reduce environmental impact while maintaining adequate structural performance in sustainable product lines.
Durability and Lifespan
Hemp composites exhibit superior durability due to their natural resistance to moisture, UV radiation, and biodegradation, extending their lifespan compared to glass fiber composites. The lignin and cellulose structure in hemp fibers enhances impact resistance and fatigue strength, making hemp composites ideal for long-term applications in automotive and construction industries. Glass fiber composites may suffer from fiber degradation and delamination over time, resulting in reduced durability and shorter service life.
Future Trends and Innovations in Composite Materials
Hemp composites are gaining traction as sustainable alternatives to traditional glass fiber composites due to their lower environmental impact and renewable nature. Future trends emphasize enhancing the mechanical properties of hemp composites through advanced fiber treatments and hybridization with bio-based resins. Innovations include the development of nano-engineered hemp fibers and eco-friendly processing techniques that improve durability and reduce carbon footprints in automotive and construction industries.
Hemp composite vs Glass fiber composite Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com