Mechanical retting involves physically breaking down hemp stalks using equipment like decorticators, preserving fiber strength and enabling eco-friendly processing without chemicals. Chemical retting employs solutions such as alkalis or enzymes to dissolve pectins and separate fibers rapidly, but it may weaken fiber quality and produce harmful effluents. Choosing between mechanical and chemical retting depends on balancing environmental impact, fiber integrity, and processing speed for hemp fiber extraction.
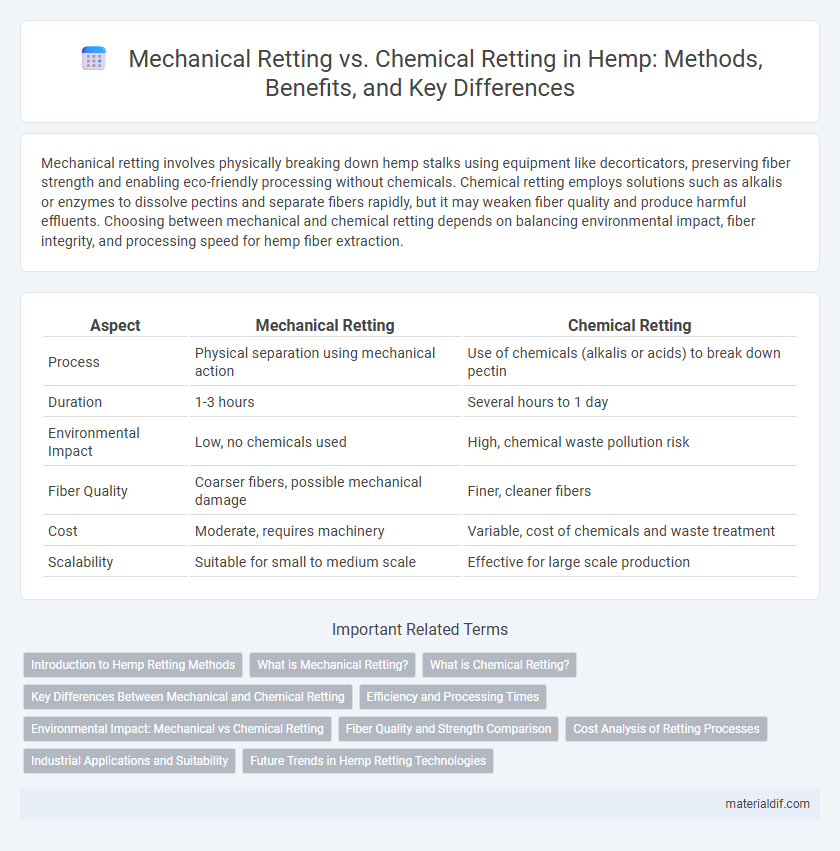
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Mechanical Retting | Chemical Retting |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Physical separation using mechanical action | Use of chemicals (alkalis or acids) to break down pectin |
| Duration | 1-3 hours | Several hours to 1 day |
| Environmental Impact | Low, no chemicals used | High, chemical waste pollution risk |
| Fiber Quality | Coarser fibers, possible mechanical damage | Finer, cleaner fibers |
| Cost | Moderate, requires machinery | Variable, cost of chemicals and waste treatment |
| Scalability | Suitable for small to medium scale | Effective for large scale production |
Introduction to Hemp Retting Methods
Mechanical retting involves physically breaking down hemp stalks through processes like breaking, scutching, and hackling to separate fibers, preserving fiber strength and quality. Chemical retting uses enzymes or alkalis to degrade pectin and other binding materials, accelerating fiber extraction but potentially weakening fibers. Choosing between hemp retting methods depends on factors such as fiber quality requirements, environmental impact, and production efficiency.
What is Mechanical Retting?
Mechanical retting is a physical process used to separate hemp fibers from the stalk by applying mechanical force such as crushing, breaking, or decortication. This method preserves fiber strength and quality without the use of chemicals, making it an environmentally friendly alternative to chemical retting. Mechanical retting is preferred for producing high-grade hemp fibers for textiles, composites, and industrial applications.
What is Chemical Retting?
Chemical retting is a process that uses chemical solutions, such as alkalis or acids, to break down the pectins binding hemp fibers to the stalk, facilitating easier fiber extraction. This method accelerates retting time compared to traditional mechanical techniques and can enhance fiber quality by ensuring more consistent separation. However, chemical retting requires careful control of chemical concentrations and environmental considerations due to potential effluent pollution.
Key Differences Between Mechanical and Chemical Retting
Mechanical retting involves physically breaking down hemp stalks using equipment like decorticators, preserving fiber strength and producing coarse fibers ideal for textiles and composites. Chemical retting uses enzymes or alkalis to dissolve pectin, resulting in finer, cleaner fibers but potentially weakening fiber integrity due to harsh treatments. The key differences lie in fiber quality, processing time, environmental impact, and equipment requirements, with mechanical retting being more eco-friendly but slower, while chemical retting offers faster processing at the cost of increased chemical use.
Efficiency and Processing Times
Mechanical retting of hemp provides faster processing times by physically breaking down the stalk fibers through decortication or breaking, achieving fiber separation within hours to days. Chemical retting uses enzymes or alkalis to dissolve pectin bonds, resulting in higher fiber purity but requires longer processing times, often several days to weeks. Efficiency in mechanical retting depends on equipment investment and energy consumption, whereas chemical retting demands chemical management and wastewater treatment, influencing overall sustainability and cost-effectiveness.
Environmental Impact: Mechanical vs Chemical Retting
Mechanical retting of hemp uses physical processes like decortication and scraping, significantly reducing water pollution and chemical waste compared to chemical retting, which relies on strong alkalis or acids that generate hazardous effluents. The environmental impact of mechanical retting is notably lower, promoting sustainable fiber extraction by minimizing soil contamination and the need for toxic chemical disposal. Chemical retting, while faster, poses greater risks to aquatic ecosystems due to residual chemicals, whereas mechanical methods support eco-friendly hemp processing with reduced carbon footprint.
Fiber Quality and Strength Comparison
Mechanical retting preserves hemp fiber strength by minimizing cell wall damage through physical processes like decortication, resulting in coarser but more durable fibers. Chemical retting employs enzymes or alkalis to break down pectin bonds, producing finer fibers with higher cellulose purity but often compromising tensile strength due to fiber degradation. Optimal fiber quality balances mechanical methods for strength retention and chemical treatments for improved fiber fineness and flexibility.
Cost Analysis of Retting Processes
Mechanical retting of hemp typically incurs lower operational costs due to reduced chemical usage and simpler equipment requirements, yet it demands higher energy input for processing. Chemical retting involves expenses related to chemicals like alkalis and biological agents, which can increase material costs but often accelerates fiber separation, reducing labor duration. Cost efficiency hinges on scale, with mechanical retting favoring eco-friendly small to medium operations while chemical retting suits larger industrial setups aiming for rapid throughput.
Industrial Applications and Suitability
Mechanical retting preserves fiber strength and is ideal for industrial applications requiring high-quality hemp fibers, such as textiles and composites. Chemical retting, using alkali or enzyme treatments, accelerates fiber separation but can degrade fiber properties, limiting its use to applications where fiber strength is less critical. Industrial suitability favors mechanical retting for eco-friendly processes and high-value products, while chemical retting suits large-scale, cost-sensitive operations.
Future Trends in Hemp Retting Technologies
Future trends in hemp retting technologies emphasize eco-friendly and efficient methods, with mechanical retting advancing through automation and precision equipment to enhance fiber quality while reducing processing time. Chemical retting is evolving by incorporating biodegradable enzymes and green solvents that minimize environmental impact and improve fiber separation consistency. Innovations in combined mechanical and chemical retting processes are expected to optimize yield, sustainability, and cost-effectiveness for large-scale hemp fiber production.
Mechanical Retting vs Chemical Retting Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com