Hemp hearts are the soft, inner part of the hemp seed, prized for their nutty flavor and high nutritional value, including essential fatty acids, protein, and fiber. Hemp hulls, on the other hand, refer to the outer shell of the seed, which is typically tougher and less digestible but useful in applications like animal bedding and fiber production. Choosing between hemp hearts and hulls depends on whether you prioritize dietary benefits or industrial uses.
Table of Comparison
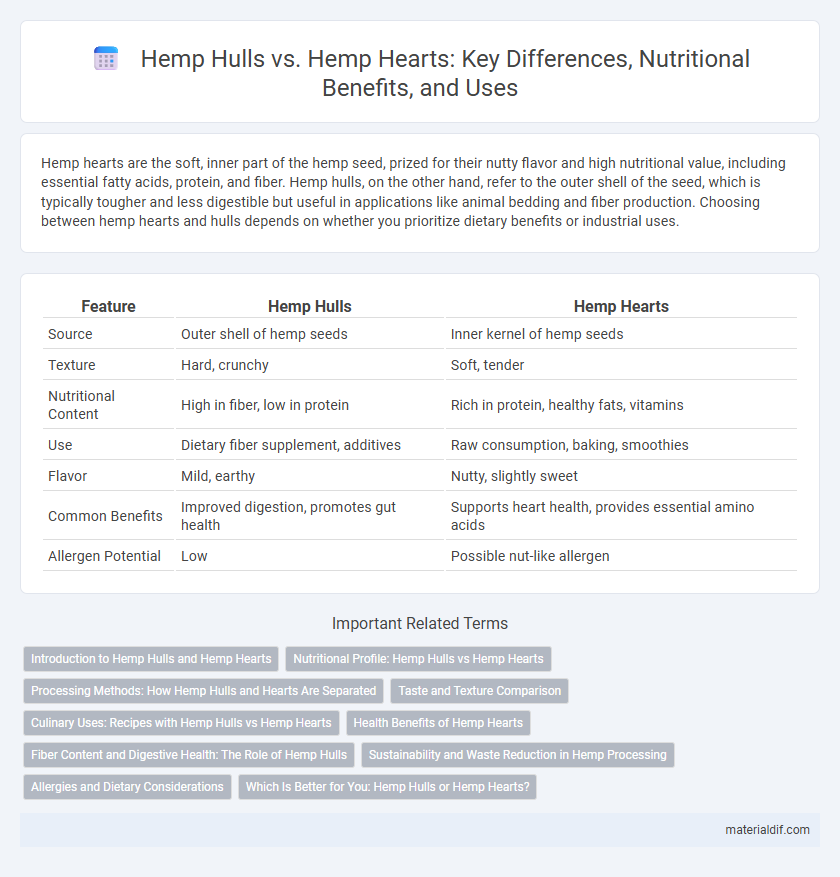
| Feature | Hemp Hulls | Hemp Hearts |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Outer shell of hemp seeds | Inner kernel of hemp seeds |
| Texture | Hard, crunchy | Soft, tender |
| Nutritional Content | High in fiber, low in protein | Rich in protein, healthy fats, vitamins |
| Use | Dietary fiber supplement, additives | Raw consumption, baking, smoothies |
| Flavor | Mild, earthy | Nutty, slightly sweet |
| Common Benefits | Improved digestion, promotes gut health | Supports heart health, provides essential amino acids |
| Allergen Potential | Low | Possible nut-like allergen |
Introduction to Hemp Hulls and Hemp Hearts
Hemp hulls are the outer shells of hemp seeds, rich in fiber and often used as a dietary supplement to promote digestive health. Hemp hearts, the inner kernels of hemp seeds, contain high levels of protein, essential fatty acids, and vitamins, making them a popular choice for nutrition-focused diets. Both hemp hulls and hemp hearts offer distinct nutritional benefits, with hulls providing fiber and hearts supplying concentrated nutrients.
Nutritional Profile: Hemp Hulls vs Hemp Hearts
Hemp hearts contain around 33% protein, rich in essential amino acids, and provide significant amounts of omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids, making them a highly nutritious source of plant-based protein and healthy fats. In contrast, hemp hulls primarily consist of fiber, particularly insoluble fiber, offering about 30-40% dietary fiber content that supports digestive health but have lower protein and fat levels compared to hemp hearts. The nutritional profile highlights hemp hearts as superior for protein and healthy fats, while hemp hulls excel in promoting gastrointestinal function through their fiber richness.
Processing Methods: How Hemp Hulls and Hearts Are Separated
Hemp hulls are separated from hemp hearts through a meticulous mechanical dehulling process using impact or abrasive dehulling machines that crack the outer shell without damaging the nutrient-rich kernel inside. After harvesting, hemp seeds undergo cleaning and conditioning to optimize hull separation efficiency, ensuring minimal loss of hemp hearts, which contain essential fatty acids and proteins. Post-dehulling, hemp hearts are collected for consumption or further processing, while the separated fibrous hulls are repurposed for uses in animal bedding, composites, and biofuel production.
Taste and Texture Comparison
Hemp hearts have a mild, nutty flavor with a soft, buttery texture, making them ideal for sprinkling on salads or blending into smoothies. Hemp hulls possess a more fibrous, slightly earthy taste and a coarse texture that works well as a dietary fiber supplement but may be less palatable on their own. The distinction in flavor and mouthfeel between hemp hearts and hemp hulls determines their specific culinary applications and nutritional uses.
Culinary Uses: Recipes with Hemp Hulls vs Hemp Hearts
Hemp hearts, rich in protein and healthy fats, are commonly used in smoothies, salads, and baking for a nutty flavor and creamy texture, enhancing dishes like granola bars and energy bites. Hemp hulls, also known as hemp shells, are less popular in direct culinary applications but can be ground into fiber-rich flour for adding texture to bread or crackers. Recipes with hemp hearts emphasize nutritional benefits and versatility, while hemp hulls cater to fiber enhancement and unique textural elements in cooking.
Health Benefits of Hemp Hearts
Hemp hearts, the nutrient-dense inner kernels of hemp seeds, provide a rich source of plant-based protein, essential fatty acids, and vital minerals such as magnesium, zinc, and iron, supporting cardiovascular health and immune function. Unlike hemp hulls, which are primarily fiber-rich outer shells without significant nutritional value, hemp hearts offer omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids in an ideal ratio for anti-inflammatory effects and brain health. Consuming hemp hearts regularly can improve digestion, enhance skin health, and promote heart health through their abundance of antioxidants and essential nutrients.
Fiber Content and Digestive Health: The Role of Hemp Hulls
Hemp hulls contain a significantly higher fiber content compared to hemp hearts, making them essential for supporting digestive health by promoting regular bowel movements and improving gut function. The fibrous outer shell of hemp seeds acts as a natural bulking agent that aids in relieving constipation and enhancing overall digestion. In contrast, hemp hearts primarily provide protein and healthy fats with minimal fiber, emphasizing the unique digestive benefits offered by hemp hulls.
Sustainability and Waste Reduction in Hemp Processing
Hemp hulls, often discarded as a byproduct, serve as sustainable materials in animal bedding and mulch, significantly reducing agricultural waste. Hemp hearts, the nutrient-rich seeds, maximize resource efficiency by utilizing the core edible portion, promoting zero-waste practices in hemp processing. Integrating hemp hulls and hearts in production cycles enhances overall sustainability, minimizing landfill contributions and supporting circular economy principles in the hemp industry.
Allergies and Dietary Considerations
Hemp hulls are the outer shells of hemp seeds and may contain higher fiber content, which can be beneficial for digestive health but might trigger sensitivities in individuals prone to fiber-related allergies or gastrointestinal issues. Hemp hearts, the shelled seeds, offer a nutrient-dense profile rich in protein, healthy fats, and essential amino acids, making them suitable for most dietary plans, including gluten-free and vegan diets, with a lower risk of allergic reactions compared to whole seeds or hulls. People with seed allergies should consult healthcare providers before consuming either form, as allergic responses can vary based on seed processing and individual sensitivity.
Which Is Better for You: Hemp Hulls or Hemp Hearts?
Hemp hearts, the soft inner seeds, offer a superior nutritional profile with high levels of protein, omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids, and essential vitamins and minerals, making them an excellent choice for promoting heart health and supporting muscle growth. Hemp hulls, the outer shells, are rich in fiber, aiding digestion and improving gut health, but lack the concentrated nutrients found in hemp hearts. Choosing between hemp hearts and hemp hulls depends on whether your priority is maximizing nutrient intake or enhancing dietary fiber for digestive benefits.
Hemp hulls vs Hemp hearts Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com