Hemp-based biocomposites offer superior environmental benefits compared to traditional composites by utilizing renewable hemp fibers that reduce carbon footprint and promote biodegradability. These biocomposites exhibit comparable mechanical strength and durability, making them a sustainable alternative for automotive, construction, and packaging industries. The natural fibers in hemp composites also enhance moisture absorption and thermal insulation properties, improving overall material performance.
Table of Comparison
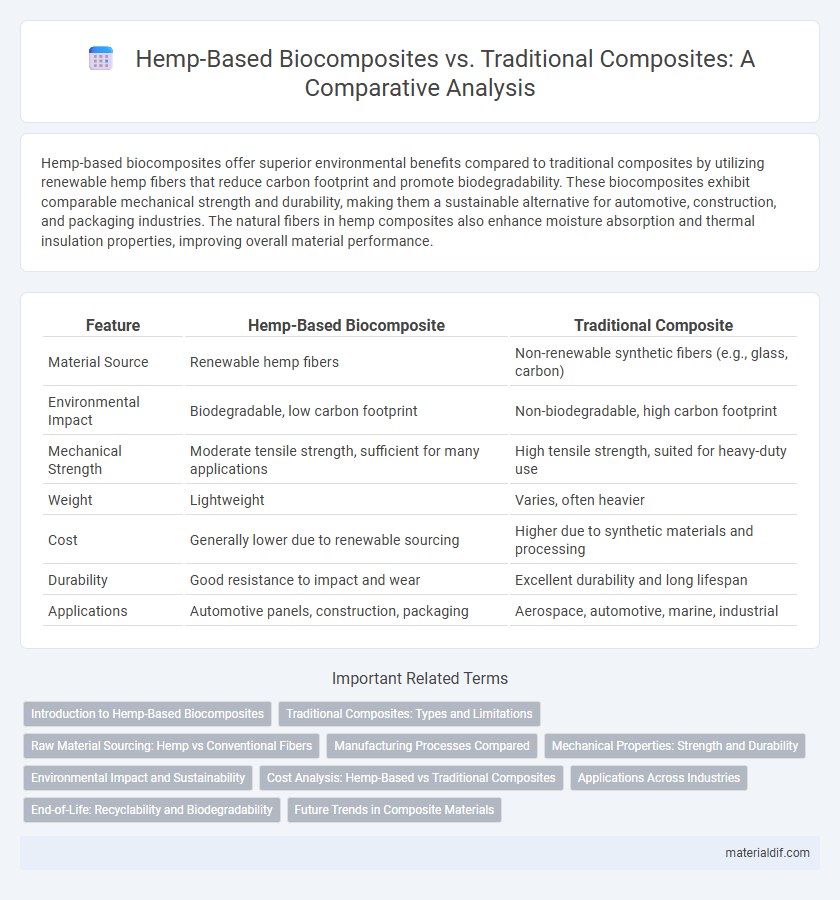
| Feature | Hemp-Based Biocomposite | Traditional Composite |
|---|---|---|
| Material Source | Renewable hemp fibers | Non-renewable synthetic fibers (e.g., glass, carbon) |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable, low carbon footprint | Non-biodegradable, high carbon footprint |
| Mechanical Strength | Moderate tensile strength, sufficient for many applications | High tensile strength, suited for heavy-duty use |
| Weight | Lightweight | Varies, often heavier |
| Cost | Generally lower due to renewable sourcing | Higher due to synthetic materials and processing |
| Durability | Good resistance to impact and wear | Excellent durability and long lifespan |
| Applications | Automotive panels, construction, packaging | Aerospace, automotive, marine, industrial |
Introduction to Hemp-Based Biocomposites
Hemp-based biocomposites are engineered materials combining natural hemp fibers with biodegradable polymers to create sustainable alternatives to traditional composites made from synthetic fibers and petroleum-based resins. These biocomposites offer improved environmental benefits, including reduced carbon footprint and enhanced biodegradability, while maintaining comparable mechanical properties such as tensile strength and stiffness. The incorporation of hemp fibers in composite manufacturing supports circular economy principles and addresses growing demand for eco-friendly construction, automotive, and packaging materials.
Traditional Composites: Types and Limitations
Traditional composites, such as glass fiber-reinforced polymers (GFRP) and carbon fiber-reinforced polymers (CFRP), dominate industries due to their high strength-to-weight ratios and durability. These composites often rely on non-renewable, synthetic fibers and petrochemical-based resins, leading to environmental concerns including non-biodegradability and high energy consumption during production. Limitations also include susceptibility to moisture absorption, limited recyclability, and higher costs, which restrict their broader application compared to sustainable alternatives like hemp-based biocomposites.
Raw Material Sourcing: Hemp vs Conventional Fibers
Hemp-based biocomposites utilize hemp fibers, which are rapidly renewable and require less water and pesticides compared to conventional fibers like glass or carbon used in traditional composites. Hemp cultivation promotes sustainability through carbon sequestration and improved soil health while reducing reliance on petrochemical-based raw materials. These advantages make hemp fibers a more eco-friendly and cost-effective option for raw material sourcing in composite manufacturing.
Manufacturing Processes Compared
Hemp-based biocomposites utilize eco-friendly, low-energy manufacturing processes such as compression molding and extrusion, which reduce carbon footprints compared to traditional composites that often rely on energy-intensive techniques like autoclave curing. The natural fibers in hemp biocomposites enhance biodegradability and reduce dependence on synthetic resins, streamlining raw material sourcing and waste management. These manufacturing advantages contribute to more sustainable production cycles while maintaining competitive mechanical properties for automotive and construction applications.
Mechanical Properties: Strength and Durability
Hemp-based biocomposites exhibit competitive mechanical properties, offering notable tensile strength and durability compared to traditional composites like glass fiber-reinforced plastics. The natural fiber matrix in hemp composites provides enhanced impact resistance and fatigue durability while reducing material weight, contributing to improved sustainability without compromising performance. Research shows that optimizing fiber treatment and composite fabrication techniques further elevates the mechanical strength and long-term stability of hemp biocomposites in structural applications.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Hemp-based biocomposites significantly reduce environmental impact by utilizing renewable hemp fibers, which require less water and pesticides compared to traditional composites that rely on synthetic fibers like glass or carbon. These biocomposites offer enhanced biodegradability, lowering landfill waste and reducing carbon footprint throughout the product lifecycle. The sustainable cultivation of hemp promotes soil health and carbon sequestration, positioning hemp-based composites as superior eco-friendly alternatives in composite material industries.
Cost Analysis: Hemp-Based vs Traditional Composites
Hemp-based biocomposites typically offer a cost advantage over traditional composites due to the lower raw material expenses and reduced energy consumption during production. The renewable nature of hemp fibers contributes to a more sustainable supply chain, often lowering long-term operational costs. However, factors such as processing technology and scale of production influence the overall cost-effectiveness between hemp-based and traditional composite materials.
Applications Across Industries
Hemp-based biocomposites offer superior sustainability and lightweight properties compared to traditional composites, making them ideal for automotive, construction, and packaging industries. Their natural fibers enhance biodegradability and reduce carbon footprint without compromising mechanical strength, which is crucial for aerospace and consumer electronics applications. As demand for eco-friendly materials rises, hemp biocomposites present a versatile alternative, promoting circular economy practices across diverse industrial sectors.
End-of-Life: Recyclability and Biodegradability
Hemp-based biocomposites offer superior end-of-life options compared to traditional composites, as they are both recyclable and biodegradable, reducing environmental impact and waste accumulation. Traditional composites, often made from non-renewable petroleum-based resins and synthetic fibers, pose significant challenges in recycling and typically persist in landfills for decades. The natural fibers and bio-resins in hemp composites facilitate composting and energy recovery, aligning with circular economy principles and enhancing sustainability in materials management.
Future Trends in Composite Materials
Hemp-based biocomposites exhibit superior sustainability by reducing carbon footprint and enhancing biodegradability compared to traditional composites reliant on synthetic fibers and resins. Advances in nanocellulose extraction from hemp fibers are improving mechanical properties, paving the way for high-performance, eco-friendly materials in automotive and construction industries. Future trends emphasize integrating hemp biocomposites with smart technologies and bio-based resins to create lightweight, durable, and recyclable composites that meet stringent environmental regulations.
Hemp-based biocomposite vs Traditional composite Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com