Hemp biocomposites offer a sustainable alternative to ABS plastic by utilizing natural fibers that enhance biodegradability and reduce environmental impact. These composites provide comparable strength and durability while lowering carbon footprint through renewable materials. The use of hemp biocomposites promotes eco-friendly manufacturing and supports circular economy principles in plastic replacement.
Table of Comparison
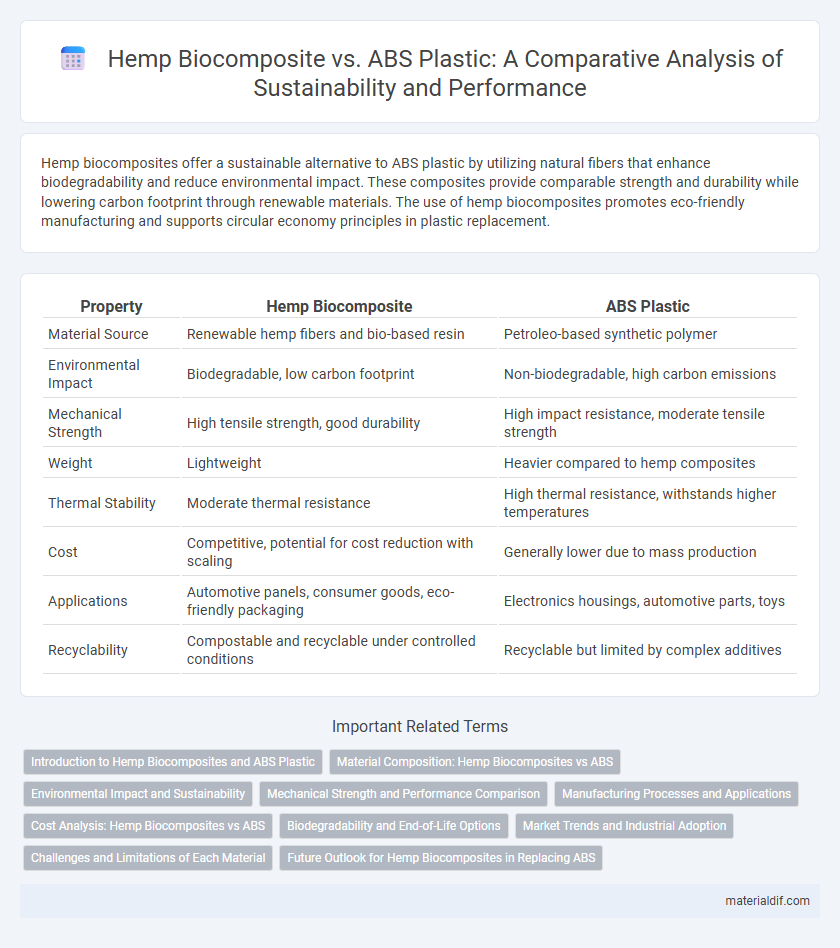
| Property | Hemp Biocomposite | ABS Plastic |
|---|---|---|
| Material Source | Renewable hemp fibers and bio-based resin | Petroleo-based synthetic polymer |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable, low carbon footprint | Non-biodegradable, high carbon emissions |
| Mechanical Strength | High tensile strength, good durability | High impact resistance, moderate tensile strength |
| Weight | Lightweight | Heavier compared to hemp composites |
| Thermal Stability | Moderate thermal resistance | High thermal resistance, withstands higher temperatures |
| Cost | Competitive, potential for cost reduction with scaling | Generally lower due to mass production |
| Applications | Automotive panels, consumer goods, eco-friendly packaging | Electronics housings, automotive parts, toys |
| Recyclability | Compostable and recyclable under controlled conditions | Recyclable but limited by complex additives |
Introduction to Hemp Biocomposites and ABS Plastic
Hemp biocomposites are innovative materials combining natural hemp fibers with polymer matrices, offering enhanced biodegradability and reduced environmental impact compared to traditional plastics. Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) plastic is a petroleum-based thermoplastic known for its toughness, impact resistance, and versatility in manufacturing but poses sustainability challenges due to its fossil fuel origin and non-biodegradable nature. The comparison between hemp biocomposites and ABS plastic highlights hemp's potential as a sustainable alternative in automotive, construction, and consumer goods industries aiming to reduce carbon footprint and waste.
Material Composition: Hemp Biocomposites vs ABS
Hemp biocomposites consist primarily of natural hemp fibers combined with biodegradable resins, offering enhanced sustainability and lower environmental impact compared to ABS plastic, which is petroleum-based and derived from acrylonitrile, butadiene, and styrene monomers. The cellulose-rich hemp fibers provide superior mechanical strength and lightweight properties, whereas ABS plastic is known for its rigidity and impact resistance but lacks biodegradability. Material composition differences influence thermal stability, recyclability, and carbon footprint, positioning hemp biocomposites as a greener alternative in various applications.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Hemp biocomposites significantly reduce carbon emissions compared to ABS plastic, as hemp plants absorb CO2 during growth and the biocomposite is biodegradable at end-of-life. The renewable nature of hemp, combined with lower energy consumption in production, enhances sustainability by minimizing reliance on fossil fuels and reducing landfill waste. Lifecycle assessments consistently show hemp biocomposites have a smaller ecological footprint, making them a greener alternative for eco-conscious manufacturing.
Mechanical Strength and Performance Comparison
Hemp biocomposites exhibit higher tensile strength and improved impact resistance compared to ABS plastic, making them suitable for applications requiring durability and stiffness. The natural fiber reinforcement in hemp composites enhances mechanical properties such as flexural strength and modulus, outperforming standard ABS formulations in terms of fatigue resistance. Hemp biocomposites also offer better environmental performance through biodegradability while maintaining competitive mechanical integrity.
Manufacturing Processes and Applications
Hemp biocomposites offer a sustainable alternative to ABS plastic, utilizing natural fibers combined with biodegradable resins through processes like compression molding and extrusion, which reduce carbon emissions and energy consumption. Manufacturing hemp biocomposites results in lighter, stronger, and more environmentally friendly materials ideal for automotive parts, consumer goods, and construction panels. Unlike ABS plastic, hemp composites provide enhanced biodegradability and improved mechanical properties, making them suitable for applications demanding eco-friendly and high-performance materials.
Cost Analysis: Hemp Biocomposites vs ABS
Hemp biocomposites offer a cost advantage over ABS plastic due to lower raw material expenses and reduced energy consumption during production. The renewable nature of hemp fiber contributes to sustainable manufacturing, often requiring less processing compared to petroleum-based ABS. Evaluating long-term economic benefits, hemp composites also reduce waste disposal costs, providing a financially viable alternative in automotive and consumer goods industries.
Biodegradability and End-of-Life Options
Hemp biocomposites offer superior biodegradability compared to ABS plastic, breaking down naturally within months under composting conditions, whereas ABS persists in landfills for decades. End-of-life options for hemp biocomposites include composting and anaerobic digestion, promoting environmental sustainability and reducing plastic pollution. In contrast, ABS plastic primarily relies on energy-intensive recycling or incineration, often releasing toxic emissions and contributing to long-term waste accumulation.
Market Trends and Industrial Adoption
Hemp biocomposites are rapidly gaining traction in the automotive and construction industries as sustainable alternatives to ABS plastic, driven by increasing environmental regulations and consumer demand for eco-friendly materials. Market analysis projects the global hemp biocomposites market to grow at a CAGR exceeding 15% through 2030, outpacing traditional ABS plastic applications due to superior biodegradability and comparable mechanical properties. Major manufacturers like Ford and BMW are integrating hemp biocomposites into vehicle interiors, signaling robust industrial adoption and a shift toward renewable resource-based composites.
Challenges and Limitations of Each Material
Hemp biocomposites face challenges such as inconsistent fiber quality, moisture absorption, and limited thermal stability, which can affect their mechanical performance and durability compared to ABS plastic. ABS plastic exhibits limitations including environmental concerns due to its petroleum-based origin and lower biodegradability despite offering superior impact resistance and heat tolerance. Both materials require advancements in processing techniques and material formulation to overcome their respective drawbacks for broader industrial adoption.
Future Outlook for Hemp Biocomposites in Replacing ABS
Hemp biocomposites exhibit superior sustainability due to their biodegradability and lower carbon footprint compared to ABS plastic, making them a promising alternative for eco-conscious industries. Advances in hemp fiber processing and resin compatibility enhance mechanical properties, positioning hemp biocomposites as viable replacements in automotive, construction, and consumer goods sectors. Continued innovation and government incentives are expected to accelerate adoption of hemp biocomposites, potentially reducing reliance on fossil fuel-based ABS plastics in the next decade.
Hemp biocomposite vs ABS plastic Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com