Hemp biocomposites offer a sustainable and eco-friendly alternative to fiberglass, providing excellent strength-to-weight ratios and enhanced biodegradability. Unlike fiberglass, hemp biocomposites reduce environmental impact through renewable fibers and lower carbon emissions during production. Their natural resistance to corrosion and improved energy absorption make hemp biocomposites ideal for applications in automotive and construction industries.
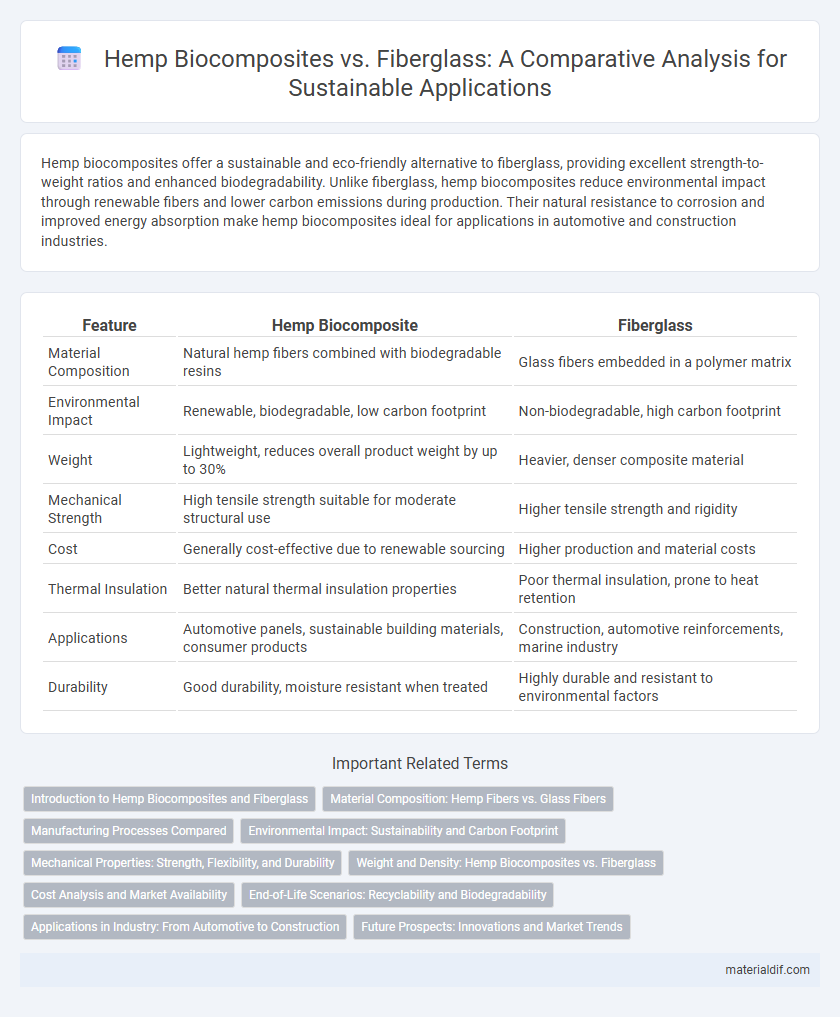
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Hemp Biocomposite | Fiberglass |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Natural hemp fibers combined with biodegradable resins | Glass fibers embedded in a polymer matrix |
| Environmental Impact | Renewable, biodegradable, low carbon footprint | Non-biodegradable, high carbon footprint |
| Weight | Lightweight, reduces overall product weight by up to 30% | Heavier, denser composite material |
| Mechanical Strength | High tensile strength suitable for moderate structural use | Higher tensile strength and rigidity |
| Cost | Generally cost-effective due to renewable sourcing | Higher production and material costs |
| Thermal Insulation | Better natural thermal insulation properties | Poor thermal insulation, prone to heat retention |
| Applications | Automotive panels, sustainable building materials, consumer products | Construction, automotive reinforcements, marine industry |
| Durability | Good durability, moisture resistant when treated | Highly durable and resistant to environmental factors |
Introduction to Hemp Biocomposites and Fiberglass
Hemp biocomposites combine natural hemp fibers with a polymer matrix, offering lightweight, sustainable alternatives to traditional materials. Fiberglass, composed of fine glass fibers embedded in resin, provides strong, durable reinforcement but lacks biodegradability. The growing demand for eco-friendly materials positions hemp biocomposites as a promising substitute for fiberglass in automotive, construction, and aerospace industries.
Material Composition: Hemp Fibers vs. Glass Fibers
Hemp biocomposites utilize natural hemp fibers composed of cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin, offering high tensile strength and biodegradability, whereas fiberglass consists of fine glass fibers made from silica-based materials, providing superior rigidity but non-biodegradable properties. The cellular structure of hemp fibers promotes better impact resistance and energy absorption compared to the brittle nature of glass fibers. Hemp biocomposites demonstrate enhanced environmental sustainability through renewable sourcing and carbon sequestration during fiber growth, contrasting with the energy-intensive production of fiberglass.
Manufacturing Processes Compared
Hemp biocomposite manufacturing involves eco-friendly processes such as resin infusion or compression molding, using natural hemp fibers combined with biodegradable or bio-based resins, reducing energy consumption and carbon footprint compared to fiberglass production. Fiberglass manufacturing requires energy-intensive procedures including glass fiber melting and weaving, followed by polymer resin application, which typically releases higher levels of volatile organic compounds (VOCs). The integration of hemp fibers in biocomposites offers enhanced sustainability and lower environmental impact while maintaining competitive mechanical properties in automotive and construction industries.
Environmental Impact: Sustainability and Carbon Footprint
Hemp biocomposites offer significantly lower carbon footprints compared to fiberglass due to hemp's rapid growth and high carbon sequestration capabilities. The production of hemp-based materials requires less energy and generates fewer greenhouse gas emissions, enhancing overall sustainability. Hemp biocomposites are also biodegradable and reduce reliance on non-renewable resources, contrasting with the energy-intensive manufacturing and non-biodegradable nature of fiberglass.
Mechanical Properties: Strength, Flexibility, and Durability
Hemp biocomposites exhibit high tensile strength and superior flexibility compared to traditional fiberglass, making them ideal for lightweight structural applications. The natural fiber matrix of hemp enhances impact resistance and durability under cyclic loading, outperforming fiberglass in fatigue behavior. Hemp biocomposites also offer better vibration damping, which contributes to extended lifecycle and improved mechanical performance in automotive and construction industries.
Weight and Density: Hemp Biocomposites vs. Fiberglass
Hemp biocomposites exhibit significantly lower density, typically around 1.2 g/cm3, compared to fiberglass, which ranges from 2.4 to 2.6 g/cm3, resulting in lighter material weight. This density advantage contributes to improved fuel efficiency and easier handling in automotive and construction applications. Consequently, hemp biocomposites provide an eco-friendly, lightweight alternative to fiberglass without compromising structural performance.
Cost Analysis and Market Availability
Hemp biocomposites offer a cost-effective alternative to fiberglass by reducing raw material expenses through renewable hemp fibers, which are generally cheaper and more sustainable than glass fibers. Market availability of hemp biocomposites is expanding rapidly due to growing demand in automotive and construction industries seeking eco-friendly materials, whereas fiberglass remains more established but faces price volatility linked to petroleum-based inputs. Cost analysis reveals hemp biocomposites not only lower production costs but also reduce environmental compliance expenses, positioning them as a competitive choice in regions promoting green manufacturing.
End-of-Life Scenarios: Recyclability and Biodegradability
Hemp biocomposites offer superior end-of-life benefits compared to fiberglass due to their natural biodegradability and easier recyclability, reducing environmental impact. Unlike fiberglass, which is challenging to recycle and often ends up in landfills or incineration, hemp biocomposites can be composted or repurposed with minimal processing. This makes hemp-based materials a sustainable alternative in industries prioritizing circular economy principles and reduced carbon footprint.
Applications in Industry: From Automotive to Construction
Hemp biocomposites are increasingly replacing fiberglass in automotive and construction industries due to their lightweight properties, biodegradability, and high strength-to-weight ratio. In automotive applications, hemp composites reduce vehicle weight, improving fuel efficiency while offering comparable durability and impact resistance to fiberglass. The construction sector benefits from hemp biocomposites' thermal insulation, moisture regulation, and sustainability, making them ideal for eco-friendly building materials and structural components.
Future Prospects: Innovations and Market Trends
Hemp biocomposites demonstrate significant potential in automotive and construction sectors due to their lightweight, eco-friendly properties, and biodegradability, offering a sustainable alternative to fiberglass. Innovations in hemp fiber treatment and resin formulations are enhancing mechanical strength, fire resistance, and durability, positioning hemp biocomposites as competitive materials for future market growth. Market trends indicate increasing consumer demand for green materials and regulatory support for renewable resources, driving investment and expansion opportunities in hemp-based biocomposites over traditional fiberglass products.
Hemp Biocomposite vs Fiberglass Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com