Long fiber hemp offers superior strength and durability, making it ideal for textiles, ropes, and composites. Short fiber hemp is better suited for applications like paper production, insulation, and biodegradable plastics due to its finer texture and easier processing. Choosing between long fiber and short fiber hemp depends on the specific industrial or commercial use required.
Table of Comparison
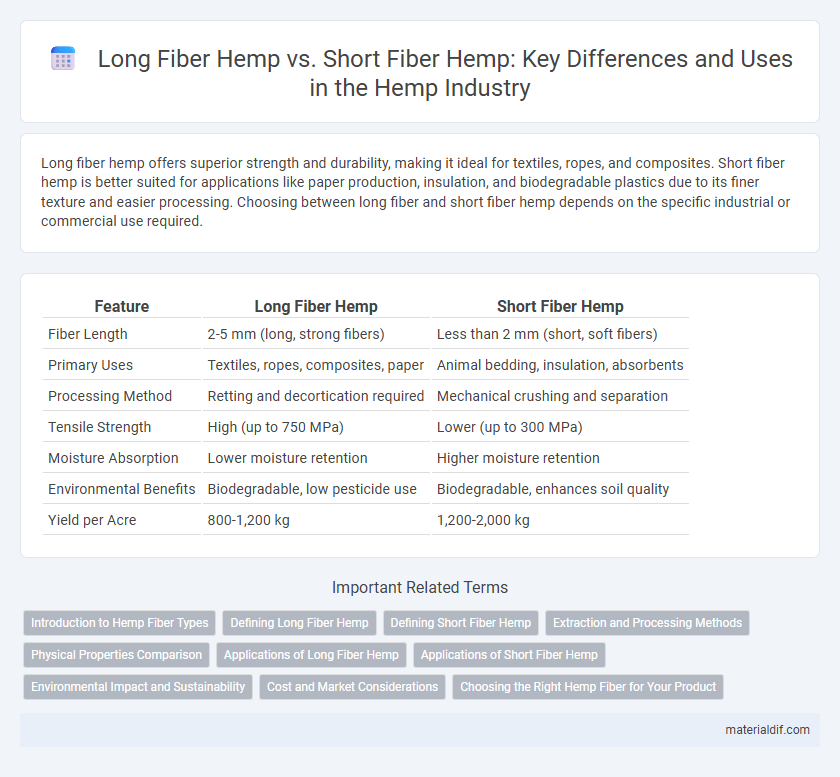
| Feature | Long Fiber Hemp | Short Fiber Hemp |
|---|---|---|
| Fiber Length | 2-5 mm (long, strong fibers) | Less than 2 mm (short, soft fibers) |
| Primary Uses | Textiles, ropes, composites, paper | Animal bedding, insulation, absorbents |
| Processing Method | Retting and decortication required | Mechanical crushing and separation |
| Tensile Strength | High (up to 750 MPa) | Lower (up to 300 MPa) |
| Moisture Absorption | Lower moisture retention | Higher moisture retention |
| Environmental Benefits | Biodegradable, low pesticide use | Biodegradable, enhances soil quality |
| Yield per Acre | 800-1,200 kg | 1,200-2,000 kg |
Introduction to Hemp Fiber Types
Long fiber hemp, also known as bast fiber, is derived from the outer stalk and is prized for its strength, flexibility, and durability, making it ideal for textiles, ropes, and biocomposites. Short fiber hemp, or hurd fiber, comes from the inner core of the stalk and is primarily used in construction materials, animal bedding, and paper production due to its coarser texture and absorbent properties. Understanding these two main hemp fiber types highlights their distinct industrial applications and supports sustainable material innovation.
Defining Long Fiber Hemp
Long fiber hemp is characterized by its lengthy, unbroken strands that can exceed several meters, making it ideal for industrial applications such as textiles, ropes, and composites due to its high tensile strength and durability. This type of hemp fiber retains its structural integrity through mechanical processing methods like decortication, which separates the bast fibers from the woody core without significant shortening. Compared to short fiber hemp, long fiber hemp offers superior flexibility, resilience, and consistency, making it the preferred choice in manufacturing environments requiring high-performance natural fibers.
Defining Short Fiber Hemp
Short fiber hemp is characterized by its finer, softer fibers mainly derived from the inner core of the hemp stalk, known as the hurds. These fibers are shorter in length compared to long fiber hemp, making them ideal for applications such as paper production, animal bedding, and bio-composites. Unlike long fiber hemp used for textiles and ropes, short fiber hemp offers versatility in industries requiring absorbent and lightweight materials.
Extraction and Processing Methods
Long fiber hemp is primarily extracted through decortication, where the outer bast fibers are separated using mechanical rollers or hammer mills, yielding strong, durable fibers ideal for textiles and composites. Short fiber hemp involves retting--either dew retting or water retting--that breaks down the pectin binding the fibers to the core, followed by scutching and hackling to refine the shorter, softer fibers used in paper or insulation materials. Both extraction methods require careful control of moisture and timing to maximize fiber quality and minimize damage during processing.
Physical Properties Comparison
Long fiber hemp exhibits superior tensile strength and flexibility compared to short fiber hemp, making it ideal for textiles and rope production. Short fiber hemp, with a coarser texture and lower elongation at break, is better suited for paper manufacturing and composite materials. Differences in fiber length directly impact the durability, moisture absorption, and surface smoothness of end products.
Applications of Long Fiber Hemp
Long fiber hemp is primarily used in manufacturing high-strength textiles, ropes, and biocomposites due to its superior tensile strength and durability compared to short fiber hemp. Its applications extend to the automotive industry for eco-friendly interior parts and in construction for reinforcing materials in hempcrete. The long fibers' ability to produce finer and more resilient products makes them ideal for sustainable industrial applications demanding lightweight yet robust materials.
Applications of Short Fiber Hemp
Short fiber hemp is primarily used in applications requiring enhanced flexibility and softness, such as textiles, paper production, and biodegradable composites. Its shorter fibers allow for easier processing into fine yarns and high-quality paper, making it ideal for clothing, upholstery, and specialty papers. The versatility of short fiber hemp supports sustainable product manufacturing in industries focused on eco-friendly materials.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Long fiber hemp requires less water and fewer pesticides compared to short fiber hemp, resulting in a lower environmental footprint. Its durability allows for longer-lasting products, reducing waste and supporting sustainable consumption patterns. Cultivating long fiber hemp enhances soil health through its extensive root system, promoting ecological balance and carbon sequestration.
Cost and Market Considerations
Long fiber hemp commands higher prices due to its superior strength and durability, making it ideal for textiles and composites, while short fiber hemp is more cost-effective, often utilized in paper, insulation, and animal bedding. Market demand for long fiber hemp is driven by specialized industries requiring premium materials, whereas short fiber hemp benefits from broader applications and volume-based pricing. Cost efficiency and targeted market needs dictate the selection between long and short fiber hemp in commercial production.
Choosing the Right Hemp Fiber for Your Product
Long fiber hemp, characterized by its durability and strength, is ideal for textiles, ropes, and biocomposites requiring high tensile strength. Short fiber hemp offers softer, more absorbent qualities suitable for paper production, insulation, and personal care products. Selecting the right hemp fiber depends on desired product performance, with long fibers enhancing structural integrity and short fibers providing comfort and flexibility.
Long fiber hemp vs Short fiber hemp Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com